Image2E3Clarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Macromitrium-prorepens.html
Macromitrium prorepens: The Fascinating Moss of the Orthotrichaceae Family
macromitrium_pro908_caps94-800.jpg from: https://www.nzplants.auckland.ac.nz/en/about/mosses/native-species/orthotrichaceae/Macromitrium-prorepens.html
Macromitrium prorepens (Hook.) Schwägr., commonly known as

20191018_a-hook-moss-leucodon-sp.-02-kb.jpg from: https://wcbotanicalclub.org/20191018_a-hook-moss-leucodon-sp-02-kb/
Macromitrium

large.jpeg from: https://inaturalist.nz/observations/88236610
, is a captivating species of moss belonging to the Orthotrichaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems and boasts unique adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Macromitrium prorepens and explore its morphology, global distribution, habitat, ecological roles, and remarkable adaptations.
Background on Bryophyta and Bryopsida
Before we delve into the specifics of Macromitrium prorepens, let’s briefly touch on the broader groups it belongs to. Bryophyta is the division that encompasses all mosses, while Bryopsida is the class that contains the vast majority of moss species, including Macromitrium prorepens. Mosses are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves, but they have evolved to thrive in a wide range of environments.
Morphology and Identification
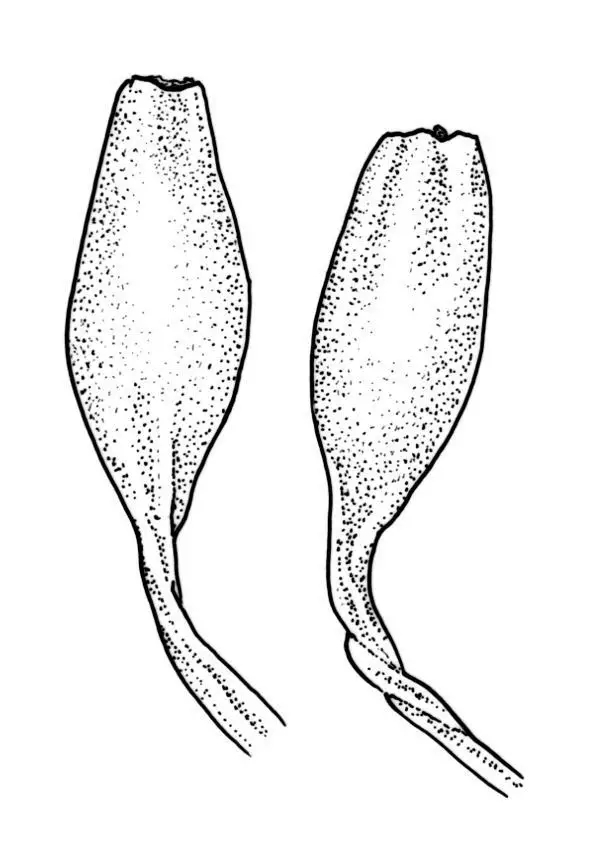
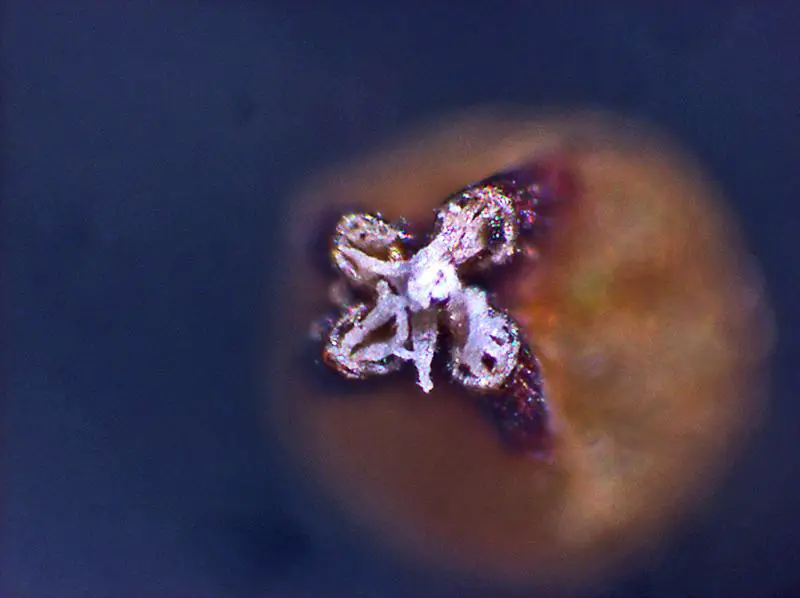
Macromitrium prorepens is a small, cushion-forming moss with a creeping growth habit. Its stems are prostrate and can reach lengths of up to 2 cm. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate, typically measuring 1-2 mm long, and have a pointed apex. The leaf margins are entire, and the midrib extends to the leaf tip. Macromitrium prorepens is autoicous, meaning that both male and female reproductive structures are present on the same plant. The capsules are erect and cylindrical, with a peristome of 16 teeth.
Global Distribution and Habitat
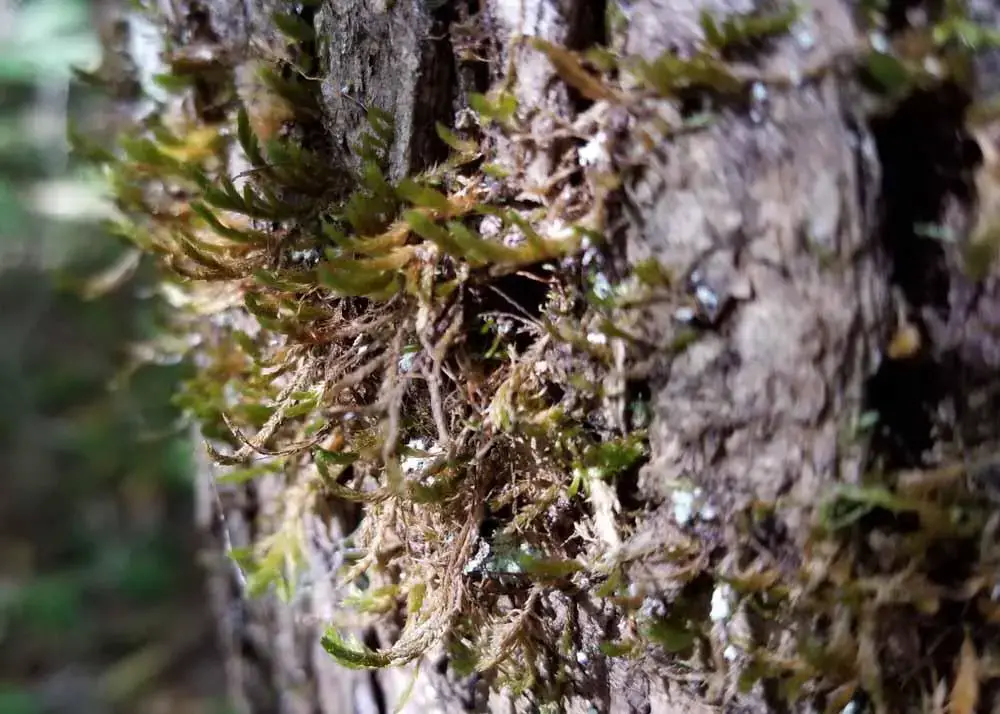
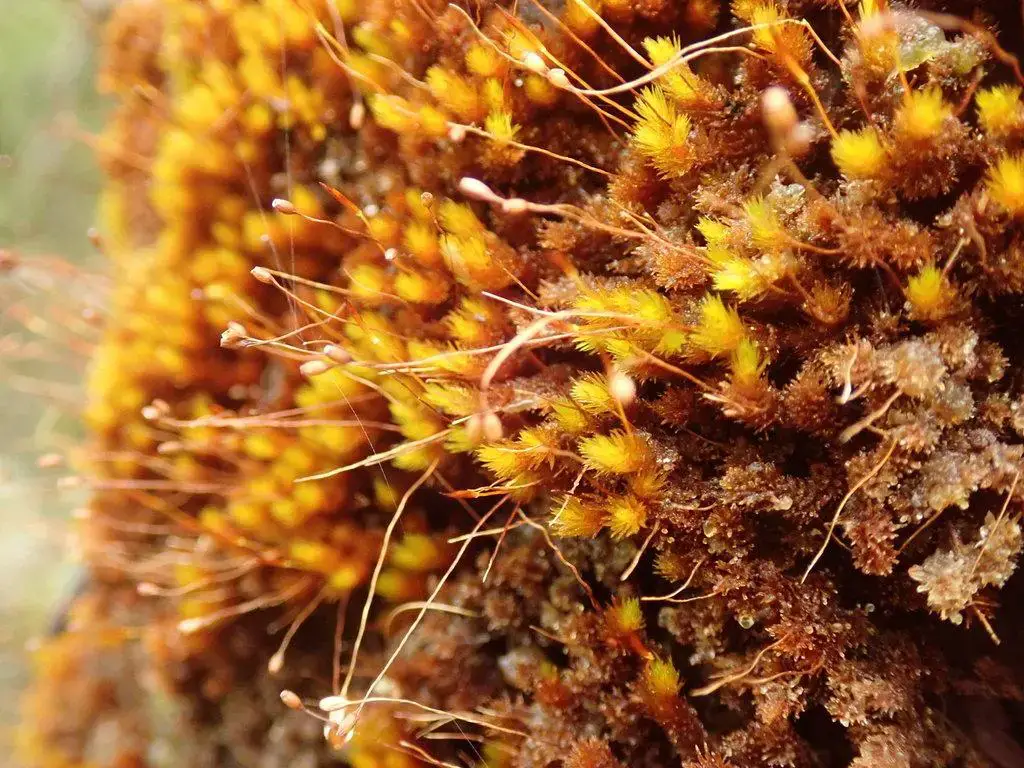
Macromitrium prorepens has a wide global distribution, found in tropical and subtropical regions across the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. It typically grows on the bark of trees

Macromitrium-prolong01l.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Macromitrium prolongatum/Macromitrium_prolongatum.html
, particularly in humid forests and woodland habitats. This epiphytic lifestyle allows Macromitrium prorepens to access moisture and nutrients without relying on soil.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Macromitrium prorepens plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to nutrient cycling, water retention, and provides shelter for small invertebrates. The creeping growth habit of Macromitrium prorepens allows it to form dense mats, which help to stabilize the substrate and prevent erosion.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Macromitrium prorepens is its ability to tolerate periods of desiccation. When moisture is scarce, the moss can enter a dormant state, suspending its metabolic activities until water becomes available again. This adaptation enables Macromitrium prorepens to survive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Genus | Macromitrium |
| Species | M. prorepens |
| Growth Habit | Creeping, prostrate |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Midrib | Extending to leaf tip |
| Reproduction | Autoicous |
| Capsule Shape | Erect, cylindrical |
| Peristome Teeth | 16 |
Conclusion
Macromitrium prorepens may be small in size, but it is a fascinating and ecologically important moss species. Its unique morphology, wide global distribution, and remarkable adaptations make it a subject of interest for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. The next time you find yourself in a humid forest, take a closer look at the tree bark—you might just spot a patch of Macromitrium prorepens thriving in its natural habitat. What other secrets might these tiny plants hold?