387469857067262d0ba59529ddb7b843.jpg from: https://eunis.eea.europa.eu/species/317287
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm of Phascum Hedw., a remarkable moss species belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Phascum, this diminutive plant holds a special place in the hearts of bryophyte enthusiasts worldwide. Despite its unassuming appearance, Phascum plays a vital role in the intricate tapestry of ecosystems, serving as a living testament to the resilience and adaptability of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Phascum, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses, collectively known as Bryophyta
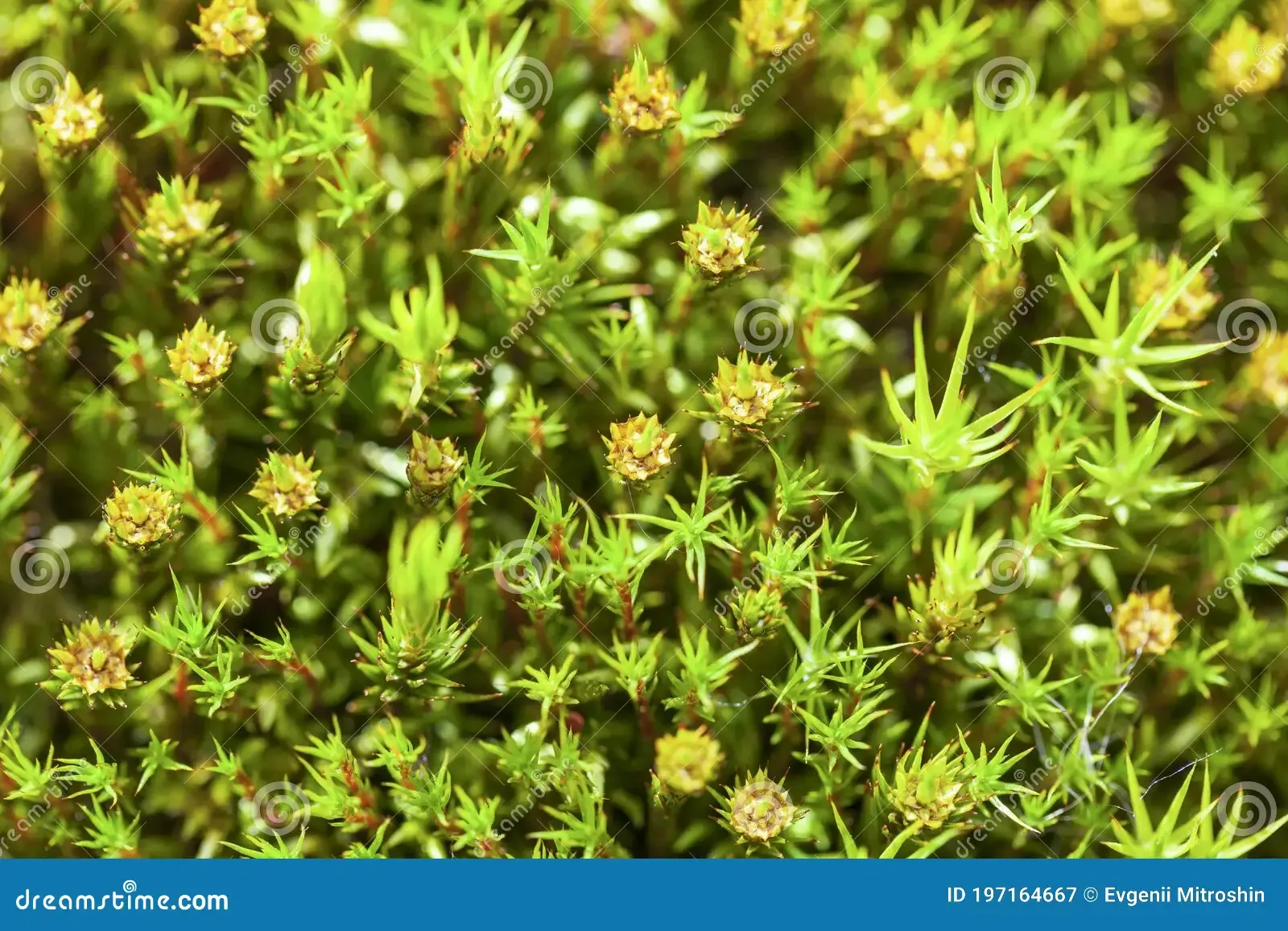

haircap-moss-flowering-macro-polytrichum-commune-hedw-197164667.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/haircap-moss-flowering-macro-polytrichum-commune-hedw-image197164667
, are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they possess specialized structures called gametophytes and sporophytes, which play crucial roles in their unique life cycle. These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants, and have adapted to thrive in a wide range of habitats.

45594192.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/231236729?_popup=1
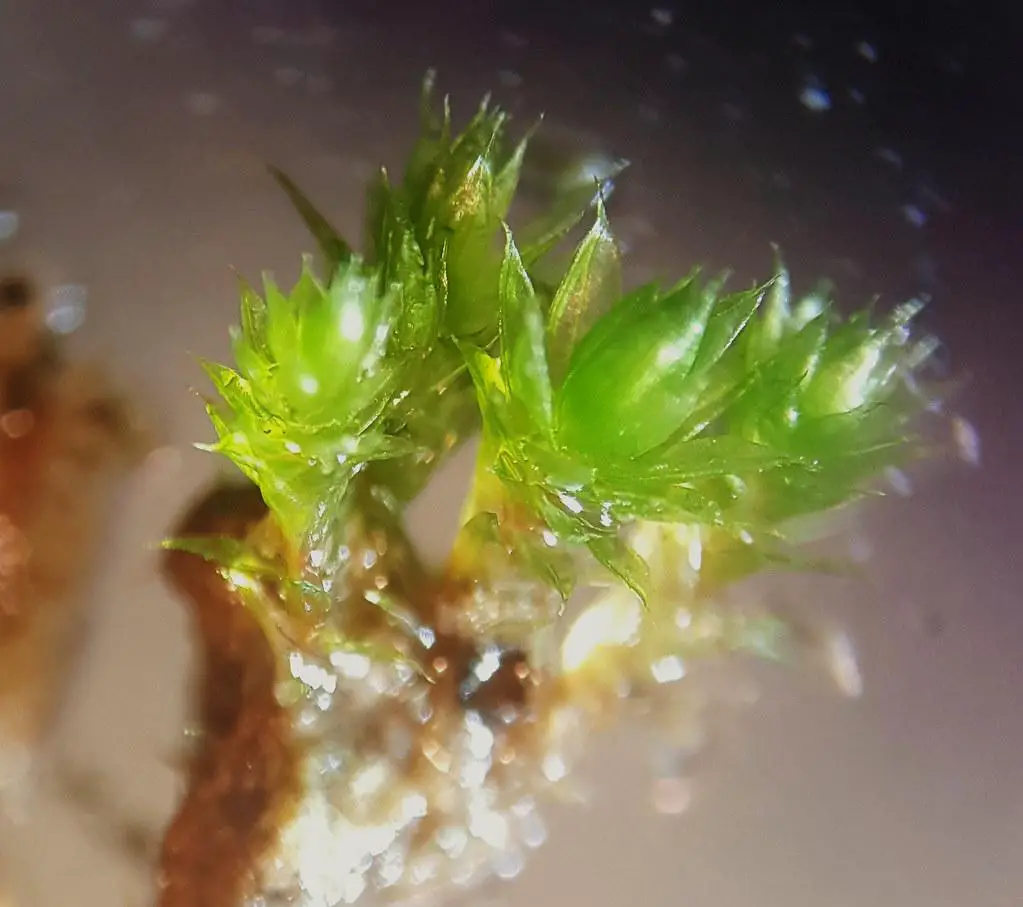

51699179325_24231d1c0d_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/51699179325/
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Phascum is a genus of acrocarpous mosses, meaning their sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the gametophyte stems. These tiny plants form dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, often adorning the surfaces of soil, rocks, or tree bark with their vibrant shades of green. One of the distinguishing features of Phascum is its immersed capsule, which remains partially buried within the gametophyte, giving it a unique appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Phascum species can be found across various regions of the world, from temperate to tropical climates. They thrive in a diverse range of habitats, including grasslands, forests, deserts, and even urban areas. Their ability to colonize disturbed or degraded environments makes them valuable indicators of environmental health and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
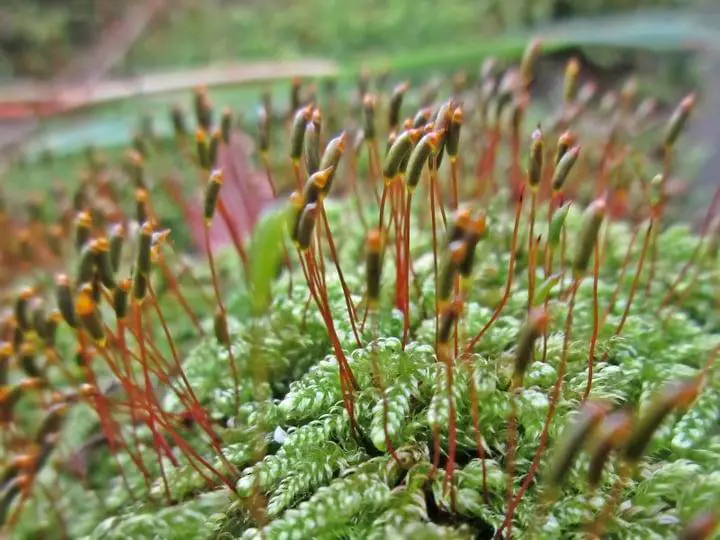

hypnum-cupressiforme-moss.jpg from: https://www.plantedwell.com/moss-gardening-ideas/
Despite their diminutive size, Phascum mosses play crucial roles in their ecosystems. They act as pioneers, being among the first plants to colonize bare or disturbed areas, stabilizing the soil and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, they contribute to nutrient cycling, water retention, and provide microhabitats for a myriad of microscopic organisms, further enhancing biodiversity.
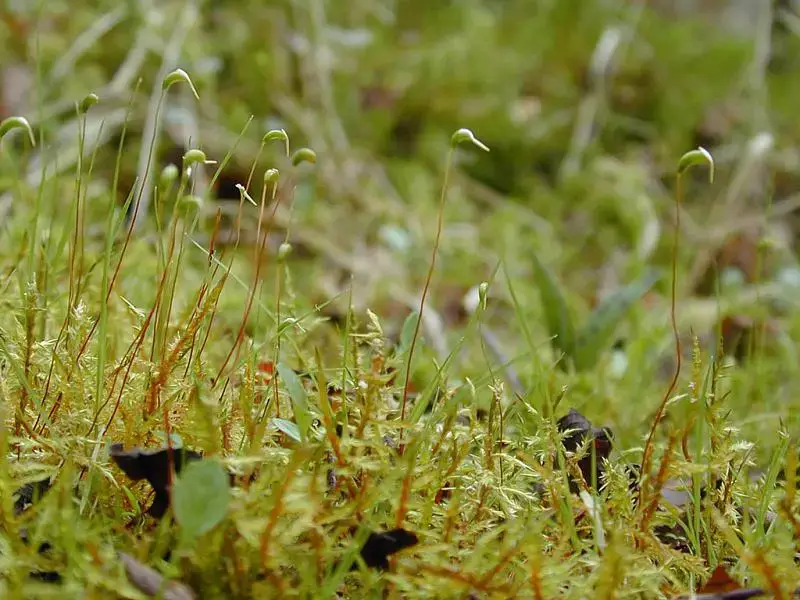
One of the remarkable adaptations of Phascum is its ability to survive extreme conditions, such as drought and desiccation. These mosses can enter a state of dormancy, known as

Calliergonella_cuspidata_Kapseln.jpg from: https://www.naturvielfalt.ch/en/organism/33110
cryptobiosis, during which their metabolic processes slow down significantly, allowing them to withstand prolonged periods of unfavorable conditions. When conditions improve, they can rapidly rehydrate and resume their growth and reproduction.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered a diverse array of
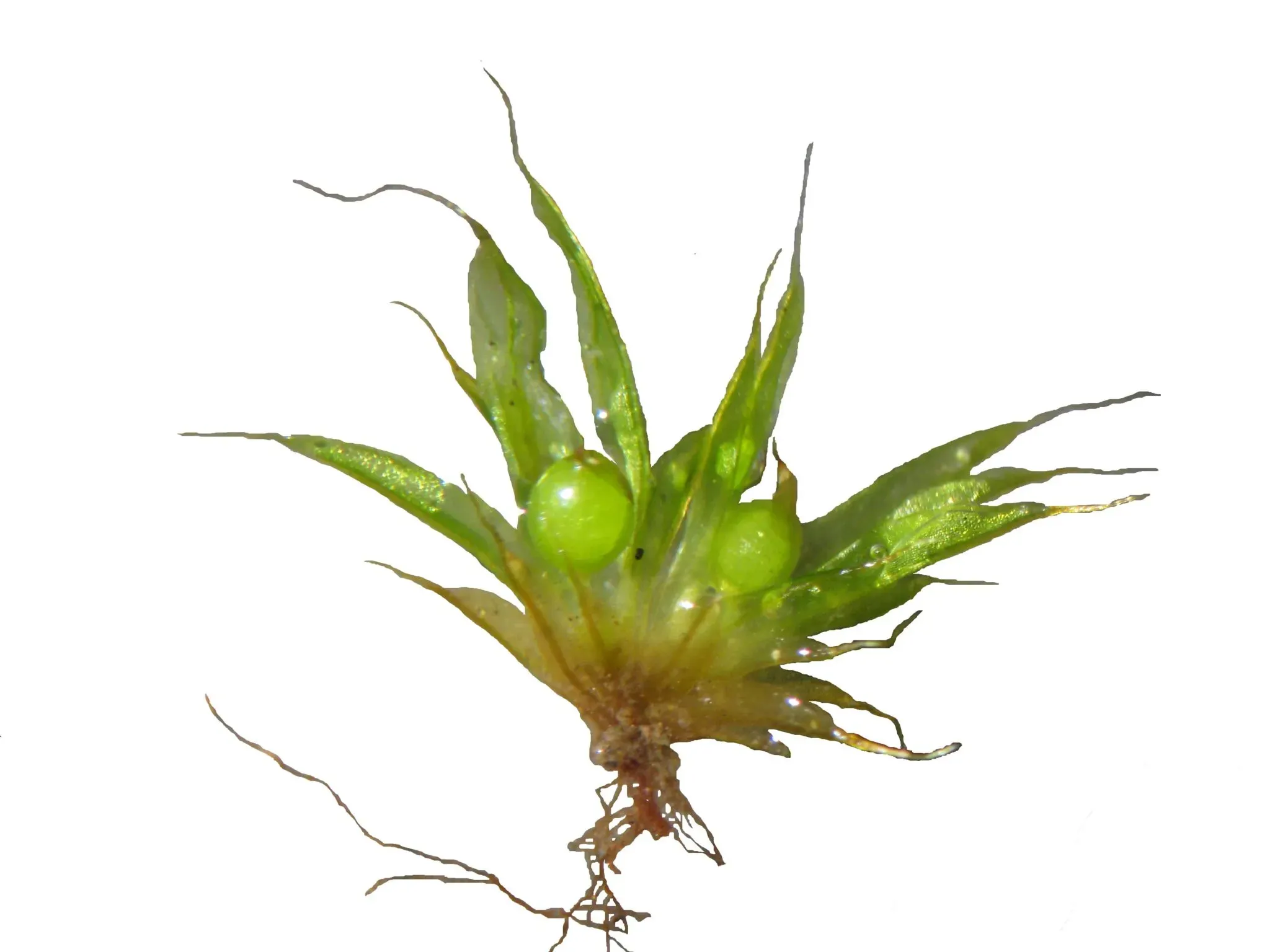

Phascum-cuspidatum-scaled.jpg from: https://www.wildflowerjournal.net/toothed-phascum-moss/
Phascum species thriving in various habitats, from old-growth forests to disturbed areas. The study highlighted the importance of these mosses in maintaining soil stability and providing microhabitats for other organisms, contributing to the overall ecosystem health.
Technical Table

Botanical_Moss_Curtis_William_PhascumSubulatumandPhascumCuspidatum_FloraLondonensis_c1817_470x285mm_p140x175mm_530x@2x.jpg from: https://antiquarianprintshop.com/products/botanical-curtis-william-moss-phascum-subulatum-and-phascum-cuspidatum-flora-londinensis-c1817
| Species | Habitat | Distribution | Distinguishing Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phascum cuspidatum | Soil, rocks, disturbed areas | Widespread across temperate regions | Cuspidate (pointed) leaf tips, immersed capsules |
| Phascum crispum | Calcareous soils, rocks | Europe, North Africa, Western Asia | Crisped (wavy) leaves when dry, immersed capsules |
| Phascum floerkeanum | Acidic soils, rocks | North America, Europe | Reddish-brown coloration, immersed capsules |
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of nature, Phascum mosses stand as unsung heroes, quietly contributing to the health and resilience of ecosystems worldwide. Their ability to thrive in diverse habitats, withstand extreme conditions, and facilitate the growth of other organisms is truly remarkable. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us not overlook the significance of these tiny, yet mighty plants. Perhaps the next time you encounter a vibrant green mat adorning the soil or a rock surface, you’ll pause and marvel at the incredible journey of Phascum.
Ponder this: In a world where size often dictates importance, what lessons can we learn from the resilience and adaptability of these microscopic marvels?