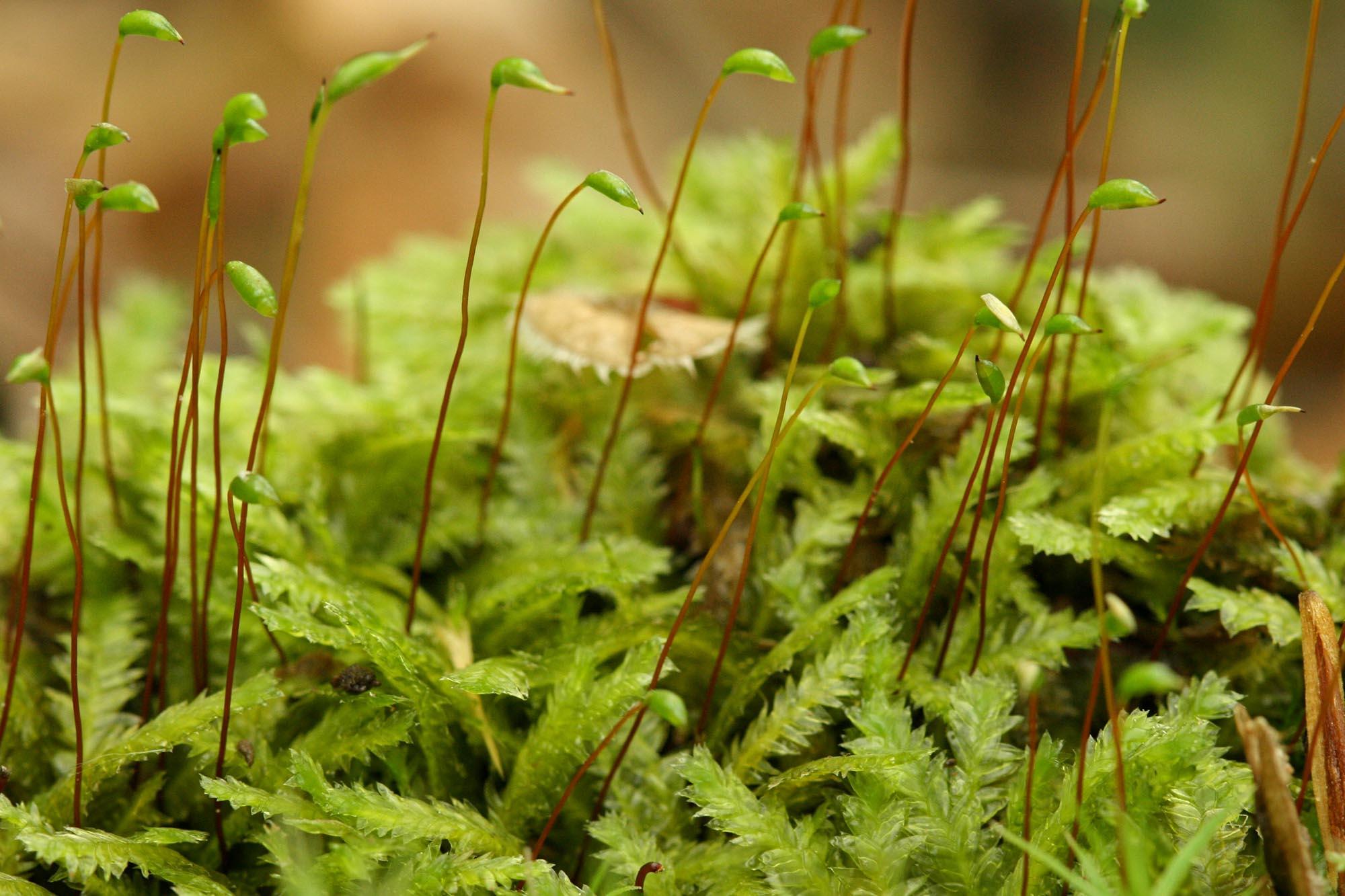

Plagiothecium-denticulatum-9.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-plagiothecium-denticulatum/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog moss
Plagiothecium-cavifolium-10.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-plagiothecium-cavifolium/
stands out as a remarkable species within the Plagiotheciaceae family. Often referred to simply as Plagiothecium, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Bryopsida member and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricate details of Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive yet resilient plants belong to the Bryophyta division, which encompasses a diverse array of non-vascular species. Mosses play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, creating a feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of conostegium, a term referring to the cone-shaped capsules that house the spores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock crevices to the bark of trees and decaying logs. Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid environments, where it can form dense mats or cushions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in challenging environments and contributes to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog in an old-growth forest. The moss played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem, providing a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates and contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog |
| Family | Plagiotheciaceae |
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Capsule Shape | Cone-shaped (conostegium) |
Conclusion
The Plagiothecium conostegium Herzog moss, a member of the Plagiotheciaceae family, is a remarkable species that deserves our appreciation and understanding. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these vital components of our ecosystems, ensuring their continued existence for generations to come?