
image from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/es/especies-de-las-azores/breutelia-azorica-12085/
Introduction
Prepare to embark on an extraordinary journey into the captivating world of Pseudospiridentopsis horrida (Mitt. ex Cardot) M.Fleisch., a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Meteoriaceae family. Often referred to simply as Pseudospiridentopsis, this unassuming plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered by enthusiasts like you.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of this moss, let’s set the stage with a brief background. Bryophytes, the group to which mosses belong, are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back over 400 million years. These resilient organisms have played a crucial role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems, paving the way for more complex plant life to thrive.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Pseudospiridentopsis horrida is a true marvel of nature, with its delicate fronds and intricate structures. This moss boasts a

image from: http://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/breutelia-azorica-12085/
creeping or pendulous growth habit, often forming dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like awn. The capsules, which contain the spores, are erect and cylindrical, adding to the plant’s unique appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including

image from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/6598e0029b8a327090e4091299244815
Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from tropical and subtropical forests to temperate regions. Pseudospiridentopsis horrida is often found growing on tree trunks, rocks, and even soil, showcasing its adaptability to different substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Pseudospiridentopsis horrida plays a vital role in its ecosystems. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare surfaces and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. They also contribute to soil formation and water retention, creating microhabitats for countless other organisms.
Moreover, Pseudospiridentopsis horrida possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to thrive in challenging environments. Its ability to

image from: https://softsolder.com/2022/01/22/euphorbia-horrida-flower/

image from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/tetrastichium-fontanum-11813/
desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available is a testament to its resilience. Additionally, the presence of specialized structures called

image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/01b6e5fa4c93a37a1e5d0c57dea81875
phyllids helps protect the moss from excessive water loss and UV radiation.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest, researchers discovered that Pseudospiridentopsis horrida played a crucial role in the regeneration of this threatened ecosystem. The moss acted as a nursery for various tree seedlings, providing them with a suitable microhabitat and facilitating their growth and survival.
Technical Table
image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/01b6e5fa4c93a37a1e5d0c57dea81875

image from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/61c0cc1dddb489ae4b135051dc513fdb
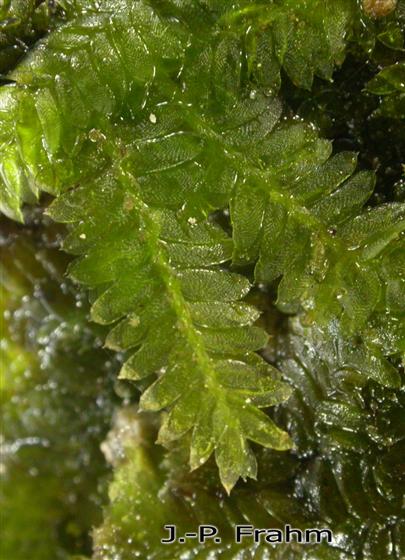

image from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/tetrastichium-fontanum-11813/
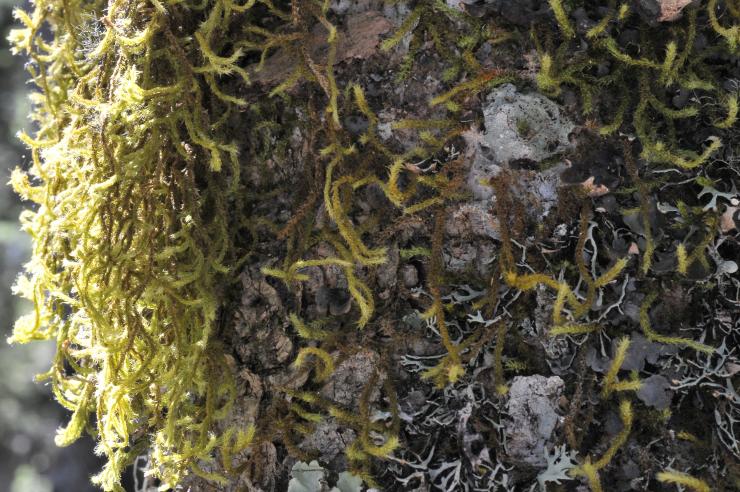

image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Meteoriaceae |
| Genus | Pseudospiridentopsis |
| Species | horrida |
| Growth Habit | Creeping or pendulous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Hair-like awn |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical |