
original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2674292
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Racomitrium lamprocarpum (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the

General-morphology-of-Pogonatum-A-male-gametophytes-with-perigonia-on-the-top-B_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B_fig9_331675612
Grimmiaceae family, this unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this extraordinary plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Racomitrium lamprocarpum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as Bryophyta, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing barren landscapes and contributing to soil formation.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
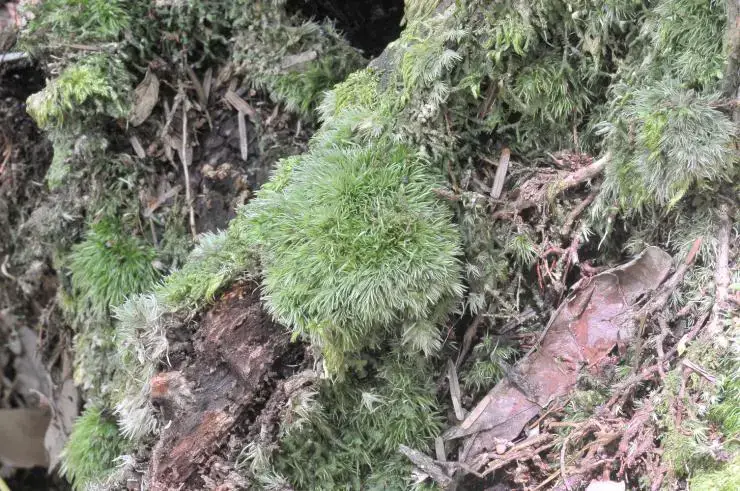
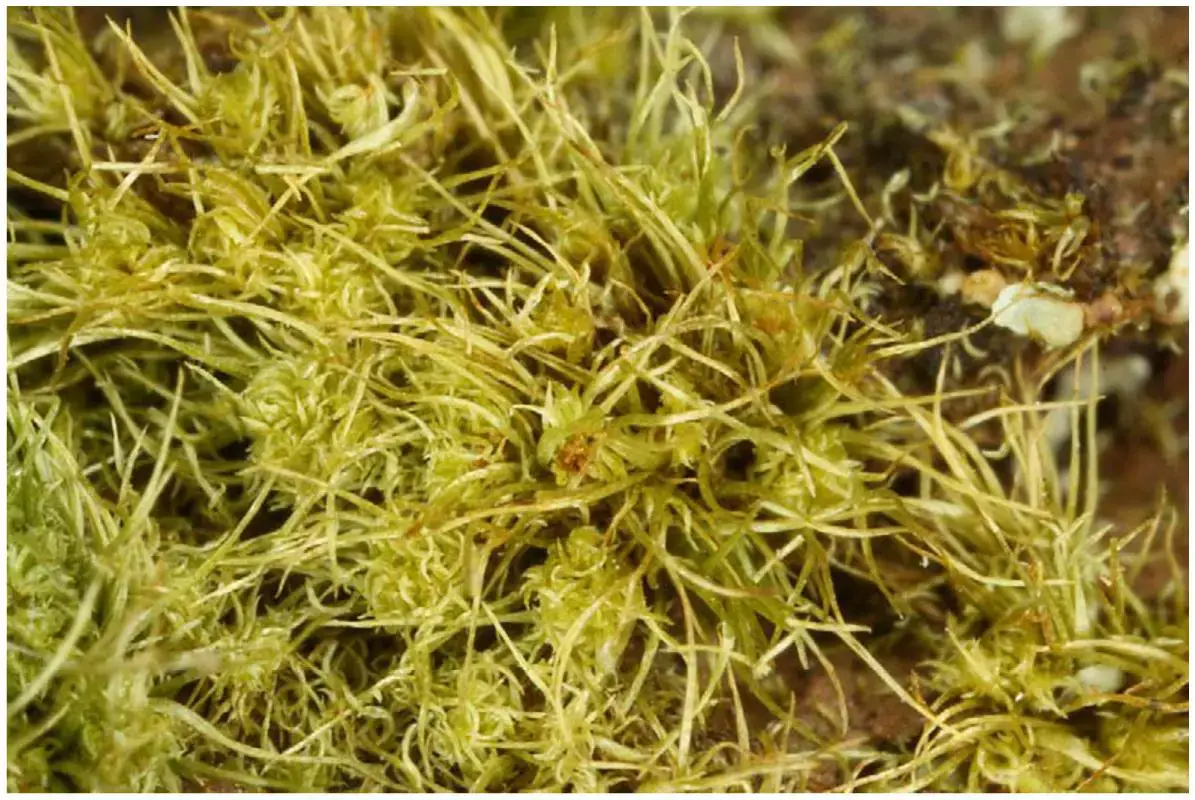
Racomitrium lamprocarpum is a acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the stems. Its slender, branched stems form dense tufts or cushions, often adorned with a striking golden-green hue. The leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and tightly appressed to the stem, giving the plant a distinctive appearance.
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its lamprocharpous capsules, which are curved and asymmetrical. These capsules, borne on short setae (stalks), are a defining characteristic of the Racomitrium genus.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Racomitrium lamprocarpum is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from rocky outcrops and cliffs to tree bark and soil. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry, exposed environments, making it a true survivor in harsh conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Racomitrium lamprocarpum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, acting as a pioneer species in colonizing barren areas. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for birds.

Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
One of the remarkable adaptations of Racomitrium lamprocarpum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can curl up its leaves and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture. When water becomes available, it quickly revives, showcasing its remarkable resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Racomitrium lamprocarpum is a common sight on rocky outcrops and cliffs. Its golden-green tufts add a vibrant touch to the landscape, contrasting beautifully with the surrounding vegetation.
Technical Table

a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914

50948153257_4fd1b6001b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/47945928@N02/50948153257
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta
 Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_fig1_318217800 |
| Class | Bryopsida
 24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_fig2_270427958 |
| Order | Grimmiales |
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Genus | Racomitrium |
| Species | lamprocarpum |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lance-shaped |
| Capsule Shape | Curved, asymmetrical (lamprocharpous
 7037e79d418c961c5141889e083833ce.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/2355523fe7d6b11d4b7a8ac495911fd7 ) |
Conclusion
The

f02_69.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Evansia/volume-28/issue-3/079.028.0302/Brothera-leana-Sull-Müll-Hal-Dicranaceae-in-New-Mexico/10.1639/079.028.0302.full
Racomitrium lamprocarpum (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its striking golden-green hue to its remarkable ability to withstand harsh conditions, this moss continues to captivate enthusiasts worldwide. As we appreciate the beauty and ecological significance of this species, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us, waiting to be explored and cherished.
Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do_fig6_262547004
Ponder this: In a world where change is constant, how can we ensure the preservation of these remarkable bryophytes for future generations to marvel at?