TAXILEJEUNEA%2B-%2BCopy.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/03/hepaticas-lobadas-lejeunaceae_52.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Taxilejeunea nymannii Steph. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Taxilejeunea nymannii Steph., a small but mighty moss in the

image_fd34aa09-a1e7-46f7-bfaf-a1b6daefd7a1.jpg from: https://stephthefairymaker.com/products/fairy-garden-moss-mounds-1
Lejeuneaceae

73032_orig.jpg from: https://idfg.idaho.gov/species/taxa/6521
family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant.
Background
Taxilejeunea nymannii Steph., also known simply as Taxilejeunea, is a species of leafy liverwort moss. It belongs to the division Marchantiophyta

frulania.jpg from: https://elfragmento.com/datos-curiosos/todas-las-especies-endemicas-de-la-flora-ecuatoriana/
and class Jungermanniopsida. The species was first described by German botanist Franz Stephani in 1890 and named after Swedish bryologist Hjalmar Nyman.
Morphology and Identification
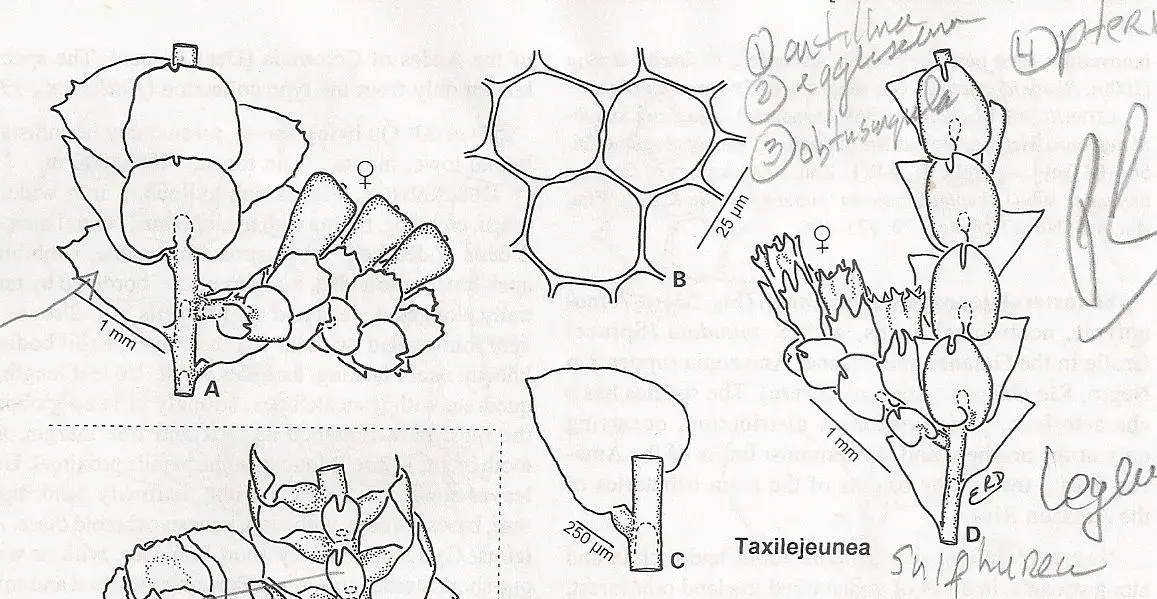
T. nymannii is a small moss, typically growing in dense mats. The leaves are arranged in two rows and are deeply bilobed. The underleaves are much smaller than the leaves. Key identification features include:
- Leaves 0.4-0.8 mm long
- Leaf cells with trigones (thickenings at cell corners)
- Underleaves distant, 2-3 times wider than the stem
- Perianths (female reproductive structures) 5-keeled
Global Distribution and Habitat

taiwan-moss.jpg from: https://plantsnshrimps.com/plantas/taiwan-moss-taxiphyllum-alternans/
T. nymannii has a wide global distribution, found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, Africa, and Asia. It typically grows on tree trunks, branches, and leaves in humid forests. The moss is epiphytic, meaning it grows on other plants but is not parasitic.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, T. nymannii plays important ecological roles:
- Moisture retention: The dense mats help retain moisture in the ecosystem.
- Microhabitats: The mats provide shelter for small invertebrates.
- Nutrient cycling: Mosses aid in nutrient cycling by trapping and breaking down organic matter.
T. nymannii

il_1588xN.3234510694_qe1f.jpg from: https://www.etsy.com/listing/1045586246/taiwan-moss-taxiphyllum-alternans-taiwan
has several adaptations for its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Small size allows it to grow on small branches and leaves
- Rhizoids (root-like structures) help it attach to surfaces

20191129_094417.jpg from: https://www.planterandforester.com/2021/09/tillandsia-usneoides-sang-jenggot-musa.html
- Leaves with lobules can hold water
Conclusion
Taxilejeunea nymannii Steph. may be small, but it is a prime example of the incredible diversity and adaptations found in the world of mosses. Next time you’re in a humid forest, take a closer look – you might just spot this tiny but fascinating plant! What other overlooked species are out there waiting to be appreciated?