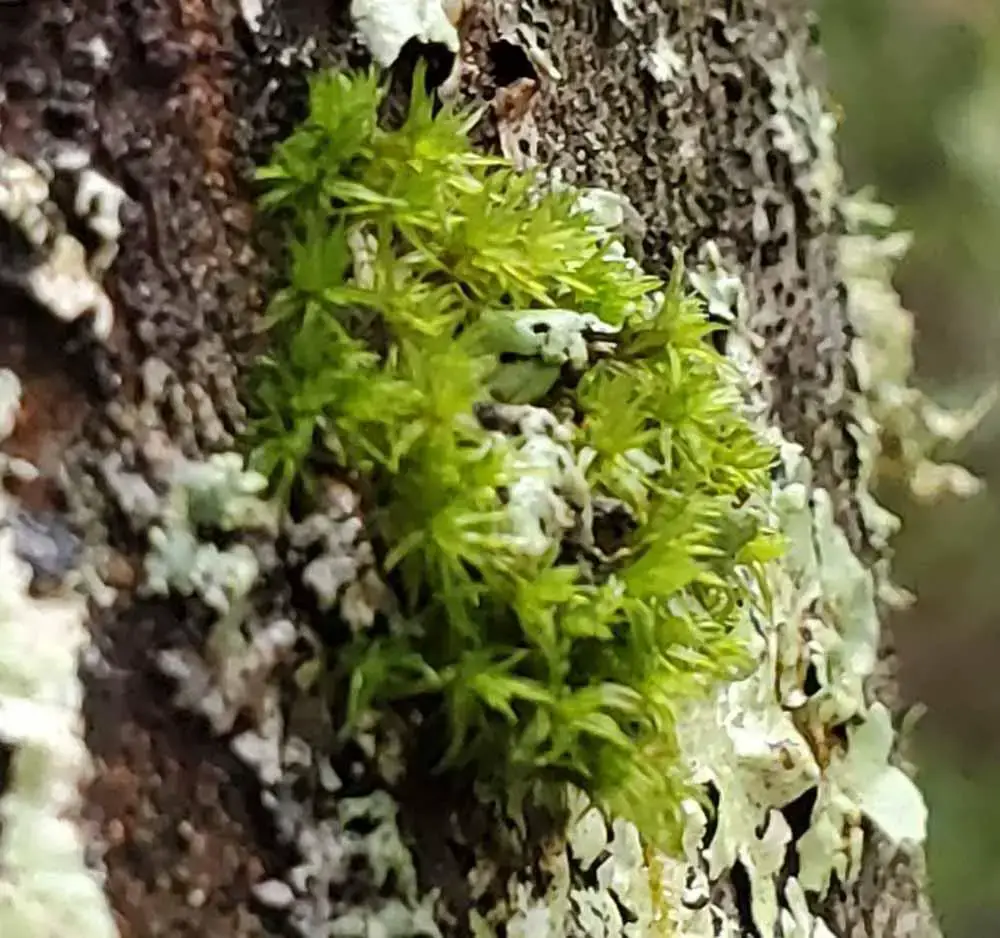

a-crisped-moss-ulota-sp.-pl.jpg from: https://wcbotanicalclub.org/a-crisped-moss-ulota-sp-pl/
Discovering the Wonders of Ulota perichaetialis Moss

Ulota_crispa-4234545F82.jpg from: https://www.florafinder.org/Species/Ulota_crispa.php
Ulota perichaetialis (Sainsbury) Goffinet, commonly known as Ulota moss, is a fascinating species of moss belonging to the Orthotrichaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles and boasts unique adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Ulota perichaetialis and uncover its secrets.
Background on Bryophytes
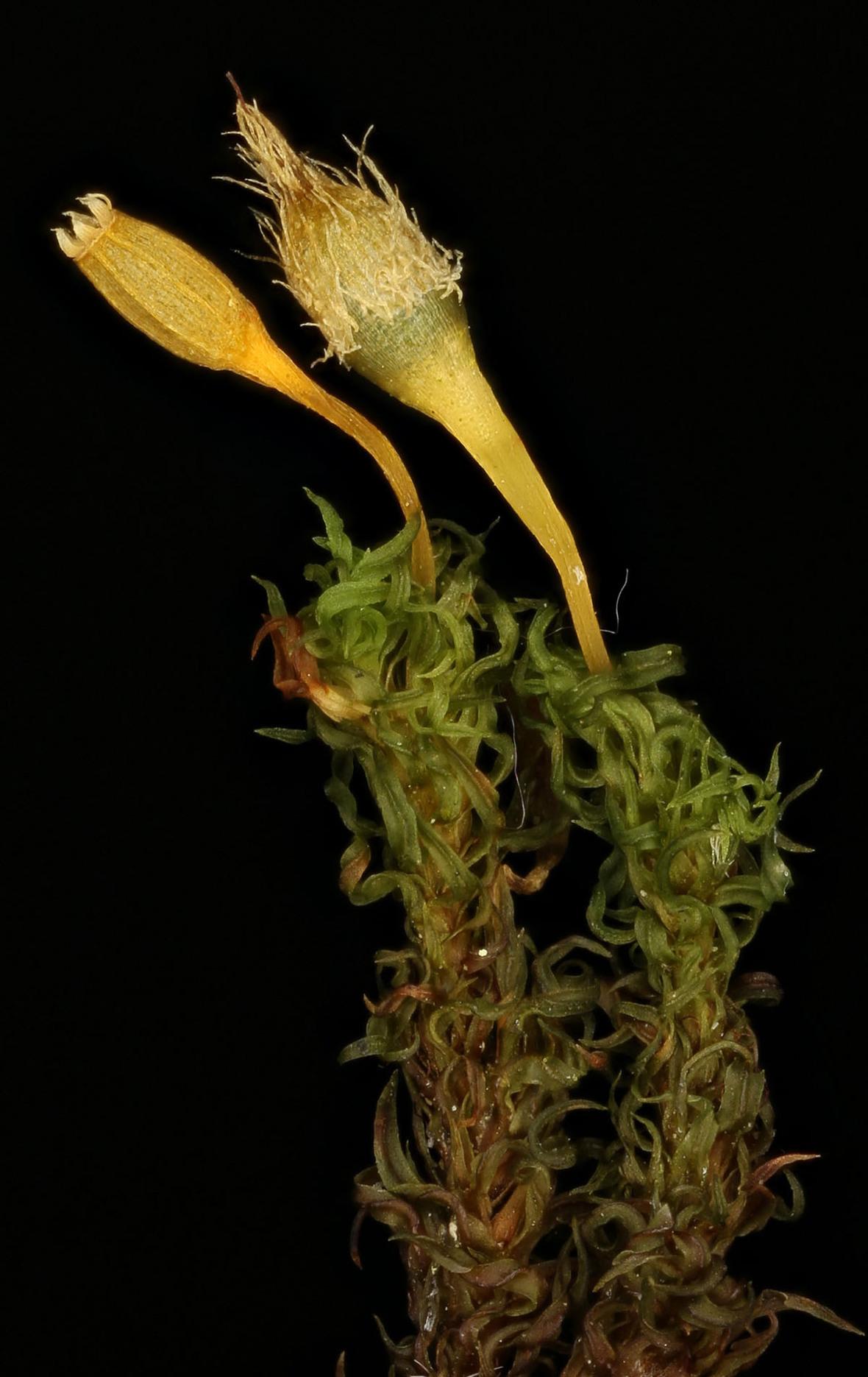

Goffinet_-_Ulota.jpg from: https://madmimi.com/s/6ba5301
Before we explore Ulota perichaetialis specifically, let’s review some background on mosses. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves like other land plants. Instead, they have rhizoids, stems, and leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in diverse habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Ulota perichaetialis is a small, cushion-forming moss. Its shoots grow upright and are densely packed together. The
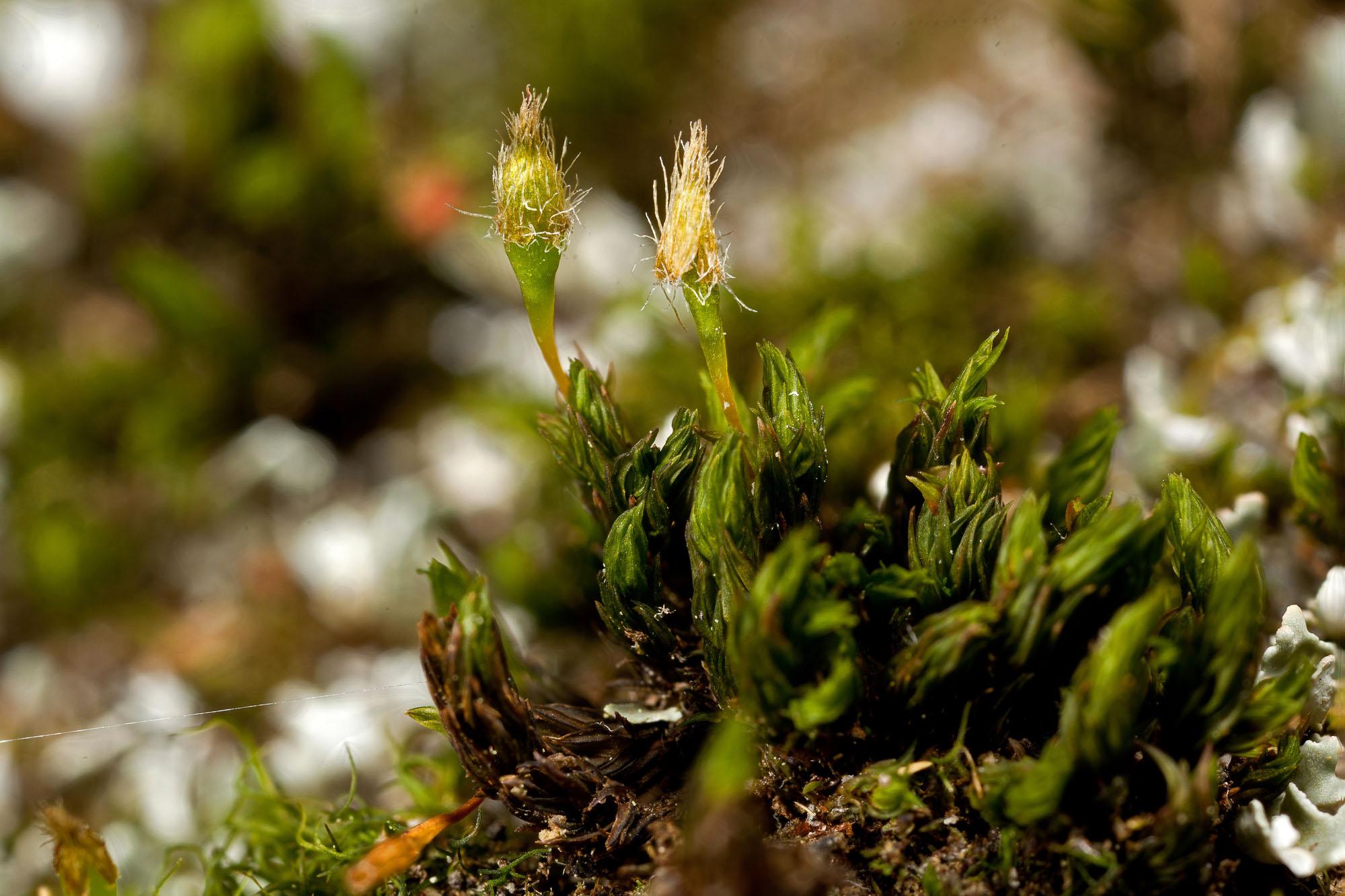

Ulota-hutchinsiae.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-ulota-hutchinsiae/
phyllids are lance-shaped

aP1260437.jpg from: https://faaxaal.blogspot.com/2017/09/Photo-de-Mousse-Ulota-coarctata-Houppe-a-massue-Club-pincushion-moss-Orthotric-de-Ludwig.html
with a strong midrib and are arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem. Ulota perichaetialis is autoicous, meaning both male and female reproductive structures are found on the same plant.
The most distinguishing feature of Ulota perichaetialis is its distinctive perichaetial leaves that surround the female reproductive structures. These specialized leaves are much larger than the regular phyllids and have a sheathing base that wraps around the stem. The capsules are cylindrical and ribbed when dry, another key identification feature.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Ulota perichaetialis has a wide global distribution, found on multiple continents including North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania. It grows in a variety of habitats including on tree bark, rocks, and human-made structures like walls and roofs. This moss prefers humid environments and is often found in forests and near bodies of water.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Ulota perichaetialis plays several important ecological roles:
- Erosion control: Its dense mats help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.

Physcomitrium.jpg from: https://bryology.uconn.edu/author/beg02003/
- Water retention: It absorbs and retains water, regulating moisture in its environment.
- Habitat provision: It provides shelter and habitat for micro-organisms and small invertebrates.
- Nutrient cycling: It aids in breaking down organic matter and cycling nutrients.
Ulota perichaetialis has special adaptations to survive in its environment:
- Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of drying out and rehydrate when moisture is available again.
- Freeze tolerance: It can withstand freezing temperatures.
- Spore dispersal: Its spores are wind-dispersed, allowing it to colonize new areas.
Image2FG8large.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Ulota-perichaetialis.html
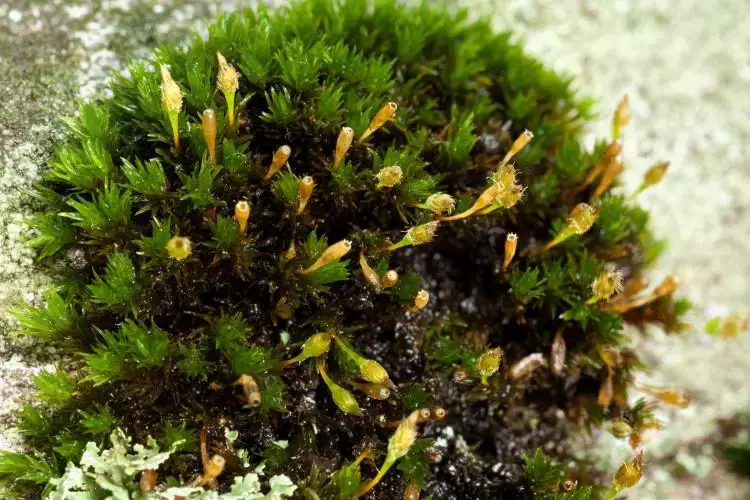

Ulota-hutchinsiae-750×500.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/ulota-hutchinsiae-6/

29304340552_d7c2de2919.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/124484193@N02/29304340552/
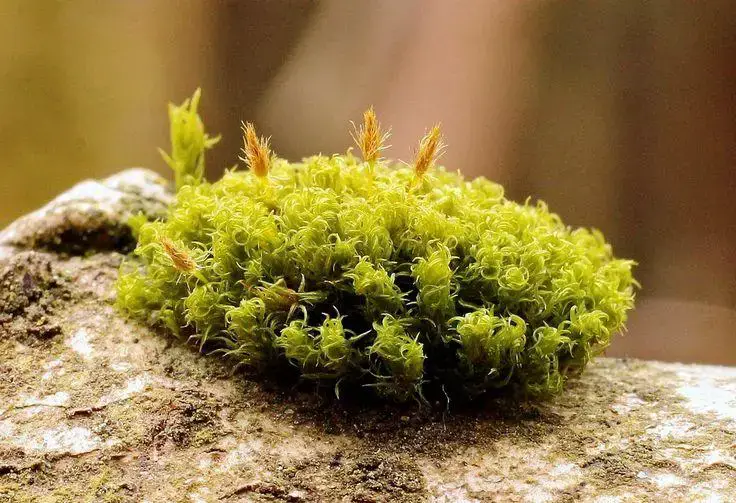

4d5ce6b12ca8666adf0acf96ab9dafc7.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/777152479423470303/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Genus | Ulota |
| Species | U. perichaetialis |
| Growth Form | Cushion |
| Sexuality | Autoicous |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical, ribbed when dry |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, walls, roofs |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Oceania |
Conclusion
Ulota perichaetialis is a small but fascinating moss with a global reach. Its unique morphology, ecological importance, and resilient adaptations make it a true wonder of the plant kingdom. Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot this marvelous moss! What other mighty mosses have you encountered?