2021-05-08-09-22-53-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/seligeria-patula/
Introduction
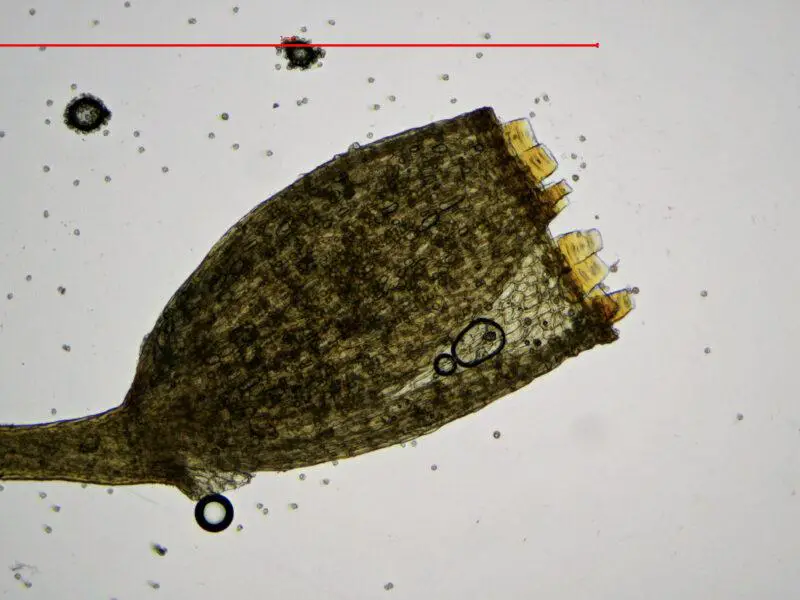

2020-09-14-20-52-08-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/seligeria-pusilla/
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Seligeria patula (Lindb.) Broth., a captivating moss species from the Seligeriaceae family, commonly known as Seligeria. Prepare to be enchanted by the intricate details and remarkable adaptations of this tiny, yet mighty, member of the Bryophyta (mosses) division.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Seligeria patula, let’s set the stage with a brief background on mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Bryopsida class and are among the oldest land plants on Earth. Despite their small stature, mosses play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
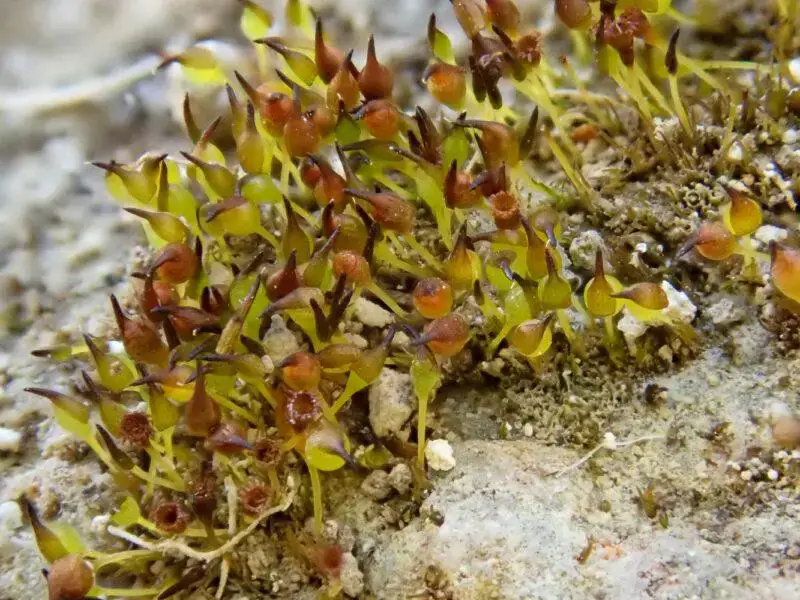

Seligeria-calcarea2-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/seligeria-calycina/
Main Content
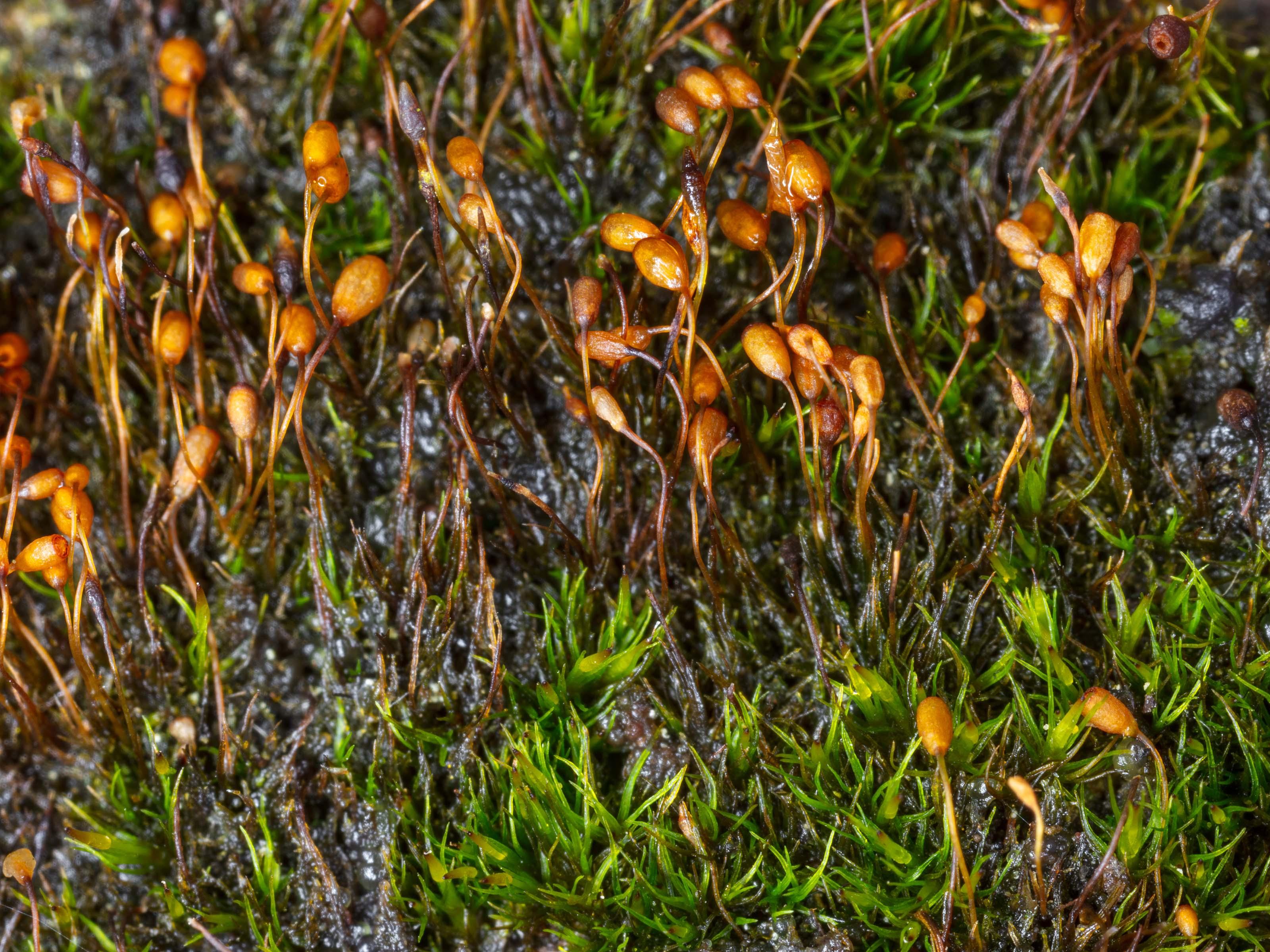

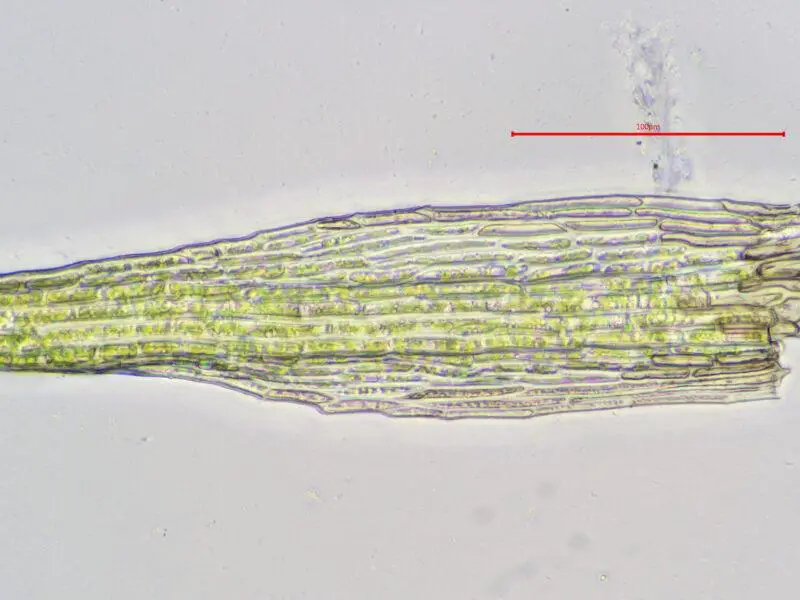
seligeria_recurvata.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/seligeriaceae/index.html
Morphology and Identification
Seligeria patula is a tiny acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow vertically from the tips of the stems. Its leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and spirally arranged around the stem, creating a distinctive appearance. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the leaf tips are acute (sharply pointed). One of the key identifying features of this moss is its peristome (tooth-like structures surrounding the capsule mouth), which is double and twisted.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Seligeria patula has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It thrives in calcareous (calcium-rich) habitats, such as limestone rocks, cliffs, and soil-covered boulders. This moss prefers shaded and moist environments, often found in woodlands, gorges, and rocky outcrops.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Seligeria patula plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss exhibits remarkable adaptations to its environment, such as the ability to tolerate desiccation (drying out) and

242709.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5349
rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Seligeria patula growing on limestone outcrops. This finding highlighted the moss’s ability to colonize and thrive in challenging environments, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Seligeriaceae |
| Genus | Seligeria |
| Species | patula |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged |
| Leaf Margins | Recurved |
| Leaf Tips | Acute |
| Peristome | Double, twisted |
Conclusion
Seligeria patula is a remarkable moss species that deserves our admiration and appreciation. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore the world of mosses, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often overlooked, yet vital, components of our ecosystems?