
2021-02-27-13-26-59-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lepidozia-pearsonii/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce

Lepidozia-pearsonii-Lochaber-2015.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/habitats/temperate-rainforest/
, a moss in the Lepidoziaceae family. Also known simply as Lepidozia, this tiny but mighty plant is worth taking a closer look at. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce moss and explore what makes it so fascinating.
Background
Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce is a species of leafy liverwort, which are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. It belongs to the class Jungermanniopsida. The species was first described by British botanist Richard Spruce in 1885. Lepidozia mosses can be found in many parts of the world, from Europe to Asia to the Americas.
Morphology and Identification
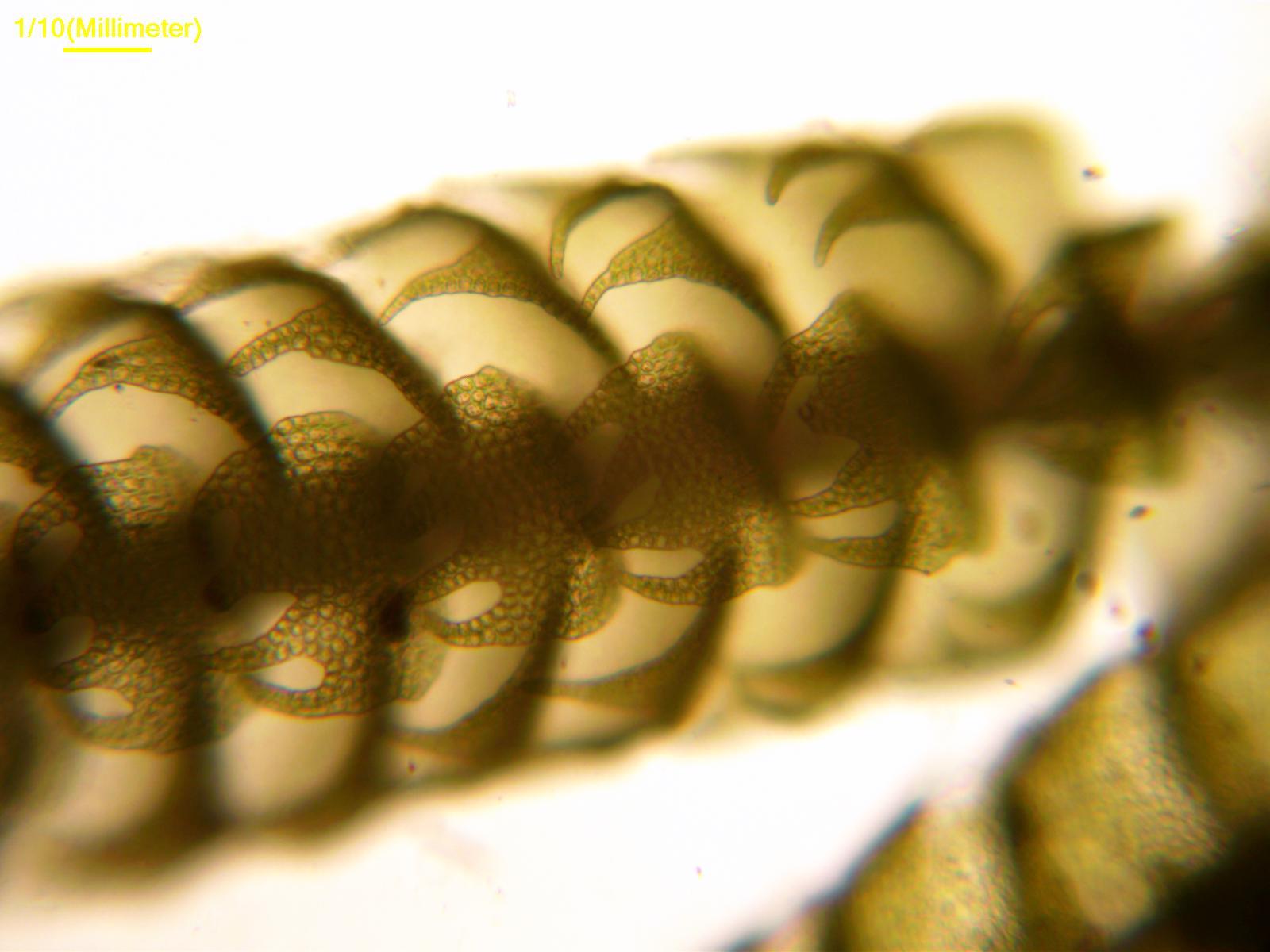
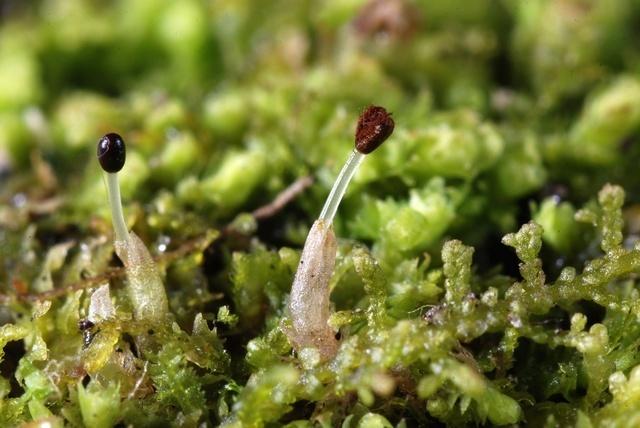
Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce is a small moss, typically growing in dense mats. The shoots are pinnately branched and the leaves are deeply divided into narrow lobes. The underleaves (modified leaves on the underside of the stem) are much smaller than the lateral leaves. Lepidozia has reddish stems that help distinguish it from similar species. The moss produces small, spherical capsules on long stalks.

Lepidozia%2Bpearsonii%2BTynygroes%2B48%2BSDSB.JPG from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2015/01/meirionydd-fun.html
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce has a wide global distribution, found in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It typically grows in damp, shaded environments such as on rocks, logs, and tree bases in forests. In some areas, it is considered an indicator species of ancient woodland habitats. Lepidozia is able to tolerate a range of conditions but prefers high humidity.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides shelter and habitat for micro-organisms and invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter
- Serves as a pioneer species in ecological succession
Lepidozia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Efficient water transport via capillary action between its leaves
- Ability to dry out and rehydrate quickly
- Asexual reproduction through fragmentation

32462051332_8f8b153a0d_n.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/61583856@N06/32462051332
Lepidozia2.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/salmonberry/walkin-in-the-woods-2/

Lepidozia-cupressina-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lepidozia-reptans/

lepidozia_reptans.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/lepidoziaceae/index.html

45555_1839_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/lepidozia-pearsonii-1839

1d9b337b71b1bbd7ed4399aa9f321a4a.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/the-sprucefir-moss-spider-is-an-endangered-species-of-spider-found-at-high-elevations-in-the-souther–449867450274659731/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Taxonomy | Marchantiophyta, Jungermanniopsida, Lepidoziaceae |
| Growth Form | Small, pinnately branched, dense mats |
| Leaves | Deeply divided into narrow lobes |
| Stems | Reddish, help with identification |
| Capsules | Small, spherical, on long stalks |
| Habitat | Damp, shaded environments in forests |
| Distribution | Wide global range across multiple continents |
| Ecological Roles | Moisture retention, erosion prevention, shelter, nutrient cycling |
| Adaptations | Efficient water transport, desiccation tolerance, fragmentation |
Conclusion
Lepidozia pearsonii Spruce may be small, but this mighty moss is an important part of ecosystems around the world. From its distinctive morphology to its ecological roles and adaptations, Lepidozia has many fascinating features. Next time you’re walking through the woods, take a moment to appreciate the complex world of mosses under your feet. What other secrets might these ancient plants hold?

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/298311