
2021-09-12-11-28-02.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/racomitrium-aquaticum/
Introduction
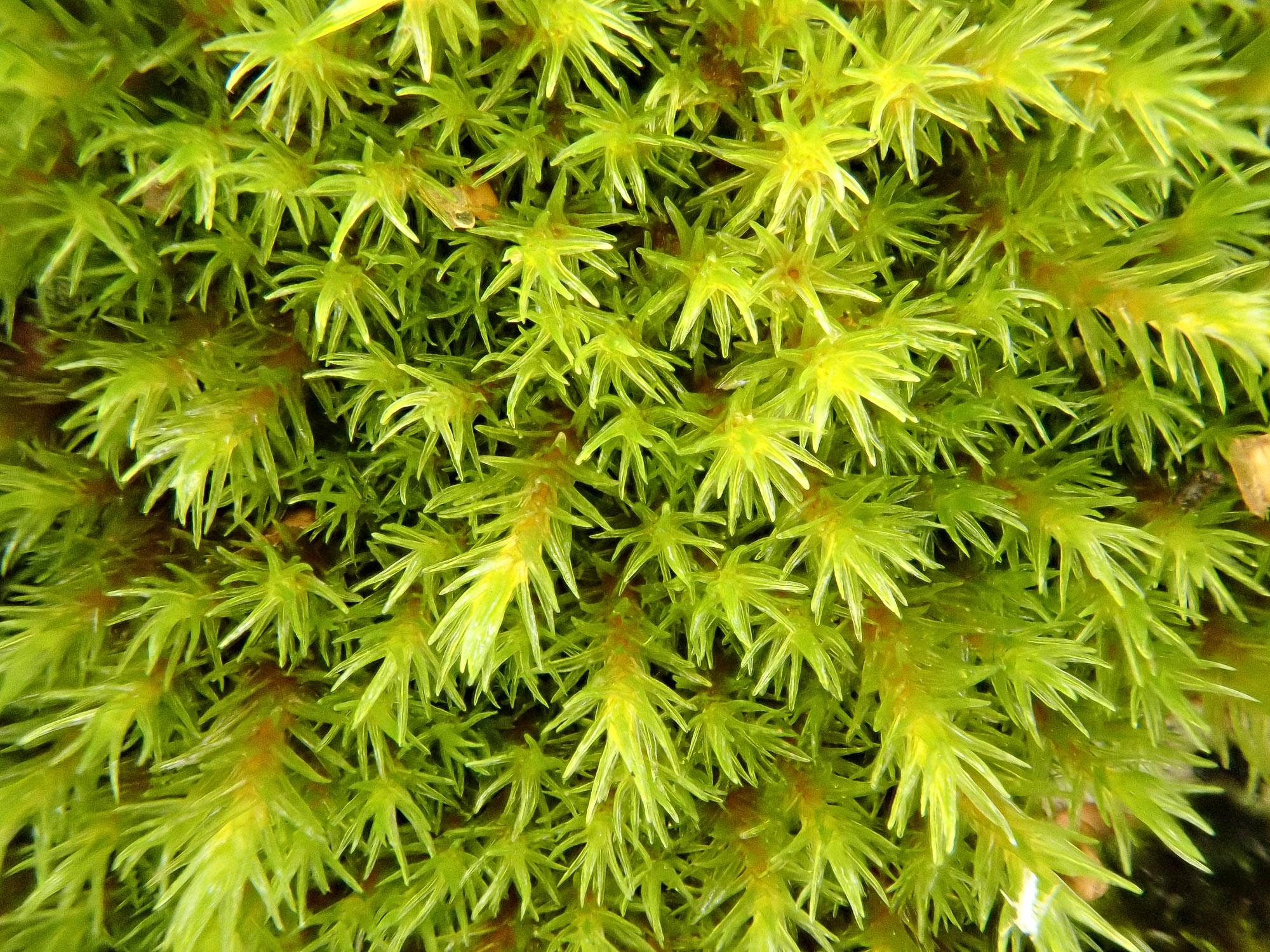
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of Racomitrium aquaticum (Brid. ex Schrad.) Brid., a remarkable moss species that belongs to the
198508.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5573
Grimmiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Racomitrium, this unassuming yet fascinating bryophyte (a non-vascular plant) has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Racomitrium aquaticum, it’s essential to understand its place within the grand scheme of plant life. As a member of the Bryophyta division and the Bryopsida class, this moss species represents a crucial link in the evolutionary chain, bridging the gap between the simplest and most complex forms of plant life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
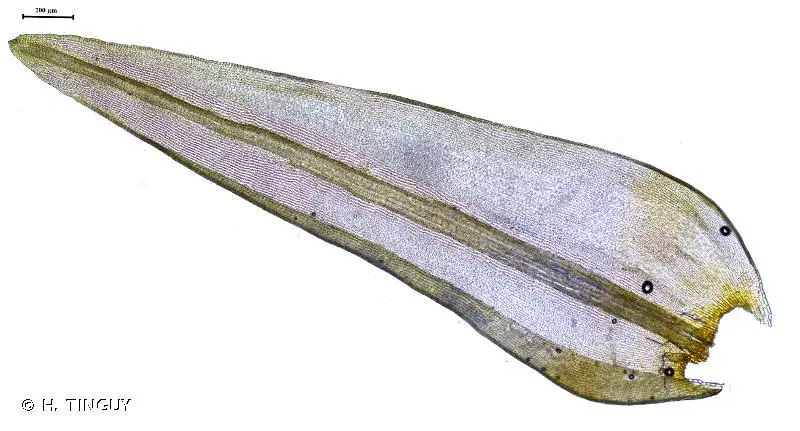
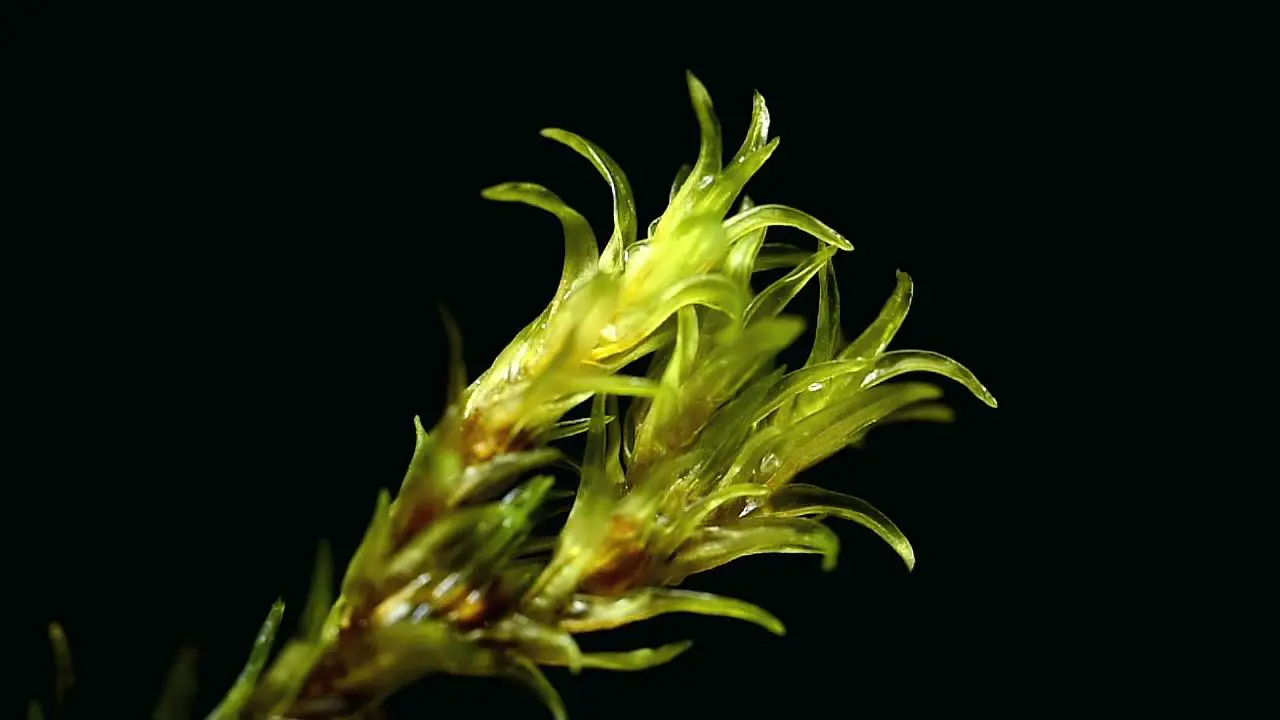
Racomitrium aquaticum is a tufted moss that forms dense, cushion-like mats. Its stems are erect and branched, typically reaching heights of 2-5 centimeters. The leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and possess a distinctive hairpoint at the tip, which aids in water conduction and retention. The capsules, which contain the spores, are cylindrical and often curved, adding to the moss’s unique appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species can be found across various regions of the world, thriving in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bvNLoBxqZCQ
Racomitrium aquaticum is particularly fond of cool, moist habitats, such as stream banks, waterfalls, and rocky outcrops in mountainous areas. Its ability to withstand periodic submersion and desiccation makes it a true survivor in the ever-changing world of bryophytes.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Racomitrium aquaticum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It serves as a pioneer species, colonizing bare rock surfaces and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss acts as a natural sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps to regulate water flow and prevent soil erosion.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Racomitrium aquaticum is its ability to undergo desiccation and revive itself upon rehydration. This incredible feat is made possible by the moss’s unique cellular structure and the production of specialized compounds that protect its delicate tissues from damage during dry periods.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Racomitrium aquaticum plays a crucial role in the health of stream ecosystems. Its presence helps to stabilize stream banks, filter out sediments, and provide habitat for a diverse array of aquatic invertebrates, which in turn serve as food sources for larger organisms, such as fish and amphibians.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Grimmiales |
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Genus | Racomitrium |
| Species | Racomitrium aquaticum (Brid. ex Schrad.) Brid. |
| Common Name | Aquatic Racomitrium Moss |
| Growth Form | Tufted, cushion-like mats |
| Stem | Erect, branched, 2-5 cm tall |
| Leaves | Narrow, lance-shaped, with hairpoint |
| Capsules | Cylindrical, often curved |
| Habitat | Cool, moist environments, stream banks, waterfalls, rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
Conclusion
Racomitrium aquaticum is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. Its ability to thrive in both aquatic and terrestrial environments, its ecological significance, and its remarkable desiccation tolerance make it a fascinating subject of study for moss enthusiasts and scientists alike.
As we bid farewell to this captivating moss species, a thought-provoking question lingers: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, what role can we play in preserving and appreciating the often overlooked wonders of nature, like the humble Racomitrium aquaticum?