Eobryum-hildebrandtii-MuellHal-RHZander-A-Dry-habit-B-Moist-habit-C-E-Leaves.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Eobryum-hildebrandtii-MuellHal-RHZander-A-Dry-habit-B-Moist-habit-C-E-Leaves_fig1_353979761
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal., belonging to the Bruchiaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of the plant kingdom. Bryophytes, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have survived for millions of years, adapting to various environments and playing crucial roles in ecosystems worldwide.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Leptophascum-leptophyllum-MuellHal-JGuerra-MJCano-A-dry-plant-B-wet-plant.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Leptophascum-leptophyllum-MuellHal-JGuerra-MJCano-A-dry-plant-B-wet-plant_fig2_339071342
The Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are typically less than an inch tall, adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that are often twisted when dry. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its
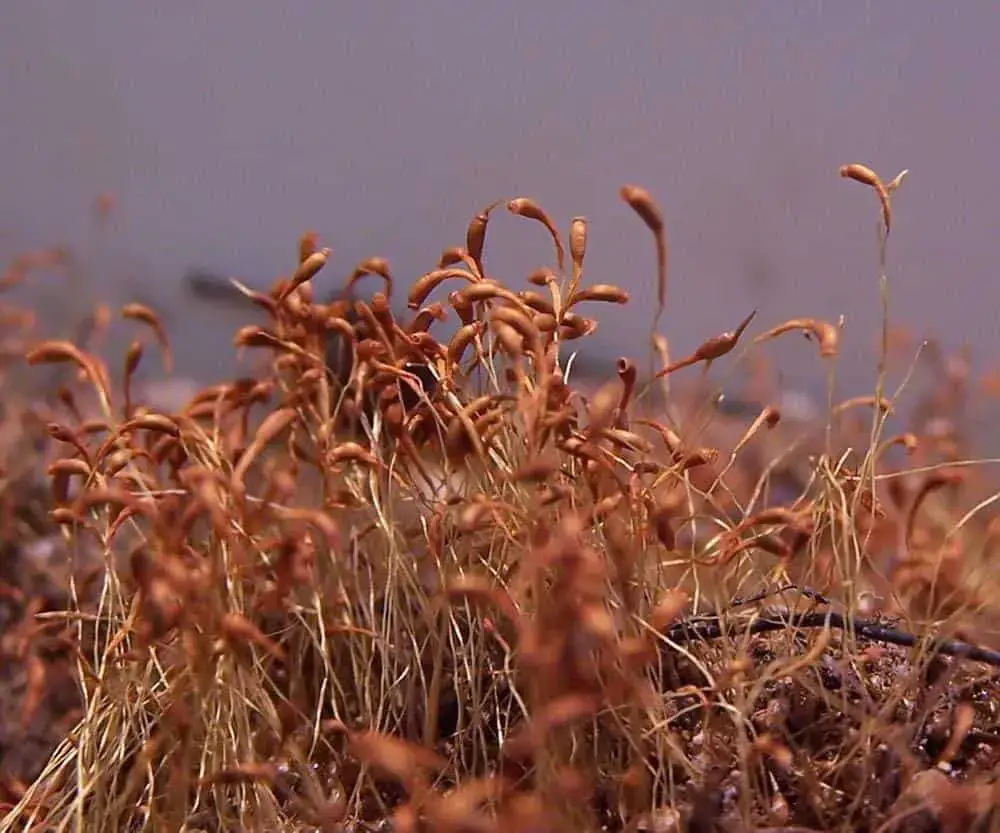

trematodon_boasii.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Bruchiaceae/trematodon-boasii/en/
capsule, which is cylindrical in shape and slightly curved, resembling a miniature banana.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This fascinating moss species can be found across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from moist, shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and quarries. The Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal. is a true survivor, able to adapt to diverse environmental conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, the Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and helping to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion. They also contribute to the formation of microhabitats, providing shelter and moisture for other organisms, such as insects and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the leaves curl inward, protecting the delicate inner tissues from drying out. When moisture returns, the leaves unfurl, allowing the moss to resume its photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest in North America, researchers discovered that the Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal. played a crucial role in the regeneration of the forest floor after a disturbance. The moss quickly colonized the bare soil, creating a suitable environment for the establishment of other plant species, ultimately contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do_fig13_259822623
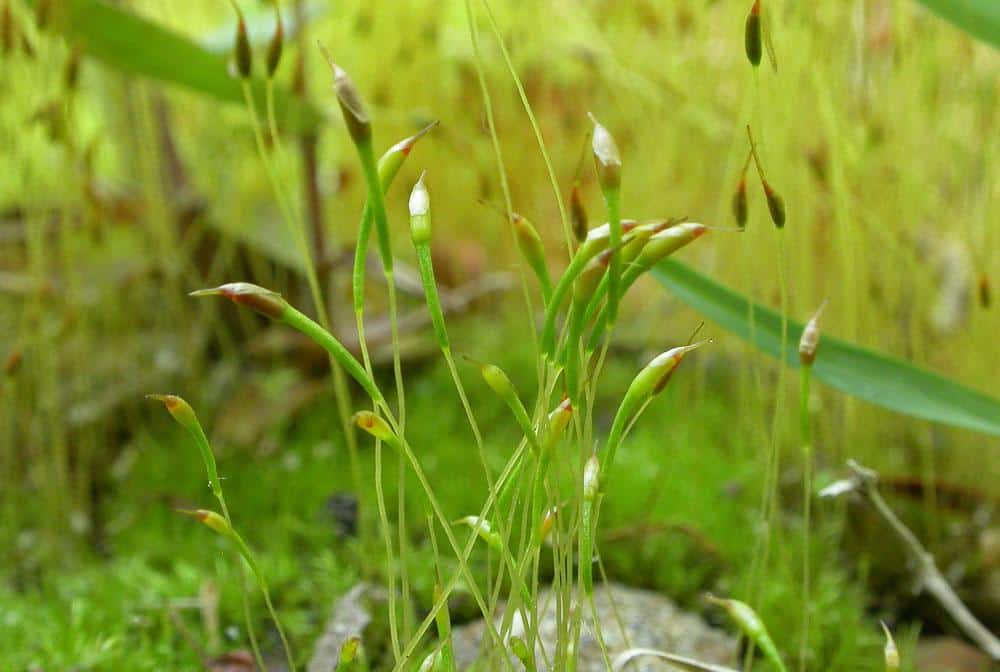

Trematodon-longicollis-2.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/new_species_trematodon_longicollis/
Anomodon-pseudotristis-Muell-Hal-Kindb-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-shoot-C-Branch_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Anomodon-pseudotristis-Muell-Hal-Kindb-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-shoot-C-Branch_fig5_356611709
Technical Table

168942.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/963689/tab/fiche

Trachyphyllum-dusenii-Muell-Hal-ex-Broth-Broth-A-Habito-B-Hoja-C-Celulas-alares_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribucion-de-Trachyphyllum-dusenii-Muell-Hal-ex-Broth-Broth-en-el-Neotropico_fig5_318583545
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Bruchiaceae |
| Genus | Trematodon |
| Species | hildebrandtii |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical, curved |
Conclusion
The Trematodon hildebrandtii Müll.Hal. is a true testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. Despite its unassuming appearance, this moss plays a vital role in ecosystems worldwide, contributing to soil stabilization, microhabitat formation, and overall biodiversity. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems lie waiting to be discovered, even in the smallest and most overlooked corners of our planet?

226058.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/770935
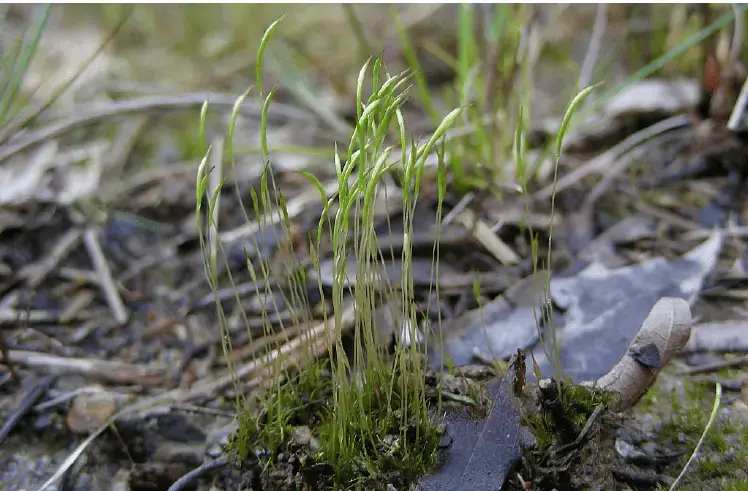

Trematodon-longicollis-on-a-wet-roadside-bank.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Trematodon-longicollis-on-a-wet-roadside-bank_fig2_237475882