
sphaeranthus-randii-s-moore-sphaeranthus-randii-s-moore-2BXEJ53.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/sphaeranthus-randii-s-moore-sphaeranthus-randii-s-moore-image360509999.html
Cephalozia randii S.W.Arnell: A Fascinating Moss of the Cephaloziaceae Family
Introduction
Today we’re diving into the intriguing world of Cephalozia randii S.W.Arnell

Riccia-teneriffae-SWArnell-SEM-image-of-proximal-face-of-spore-from-the-holotype-S.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Riccia-teneriffae-SWArnell-SEM-image-of-proximal-face-of-spore-from-the-holotype-S_fig2_272253996
, a small but mighty moss species of the Cephaloziaceae family, also commonly referred to simply as Cephalozia. This diminutive plant may be easily overlooked, but it plays important ecological roles and has some remarkable adaptations. Let’s explore this fascinating bryophyte!
Background on Cephalozia Mosses
The genus Cephalozia contains around 30 species of leafy liverworts in the order Jungermanniopsida and division Marchantiophyta. These small mosses are found in many parts of the world, typically growing on soil, rocks, logs, or even other mosses. Cephalozia randii is one notable species.
Morphology and Identification
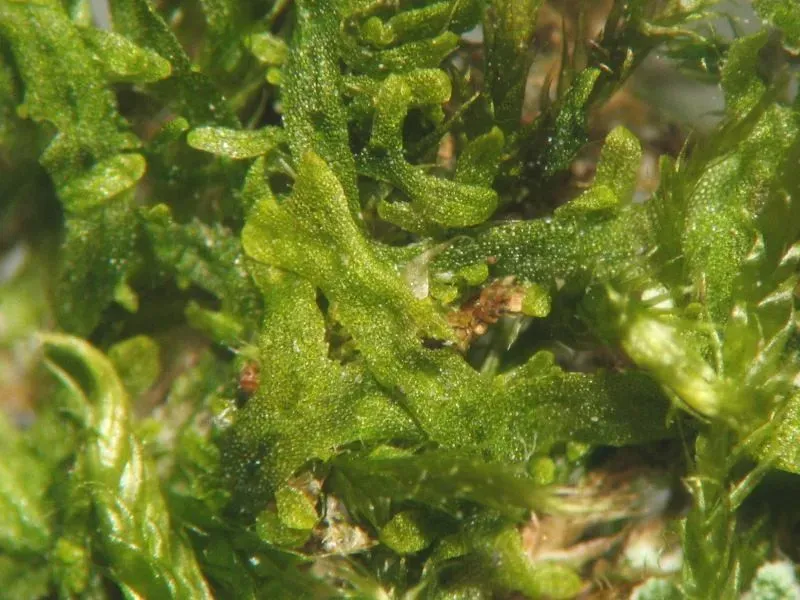
C. randii forms small, dense mats of delicate shoots. The leaves are deeply divided into two lobes and lack underleaves, giving the plant a distinctive appearance under magnification. Rhizoids are sparse. The species is dioicous, with separate male and female individuals. Sporophytes are uncommon.
Identification of Cephalozia mosses to species can be challenging and often requires microscopic examination of leaf cell details and perianths. However, C. randii

euphrasia-randii-ha-gmittelhauser.jpg from: https://gobotany.nativeplanttrust.org/species/euphrasia/randii/
has some distinguishing characteristics, including the shape and orientation of its leaf lobes.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Cephalozia randii has a scattered global distribution, being reported from Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It grows in a variety of habitats including on soil, humus, decaying logs, and rock surfaces, often in damp, shaded sites in woodlands and forests. The species seems to have a preference for acidic substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other bryophytes, C. randii plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides shelter and food for micro-organisms and invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling and soil formation as it grows and decays
This tiny moss has adaptations that allow it to thrive in its niche:

Cephalozia_catenulata_2.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Cephalozia_catenulata.html
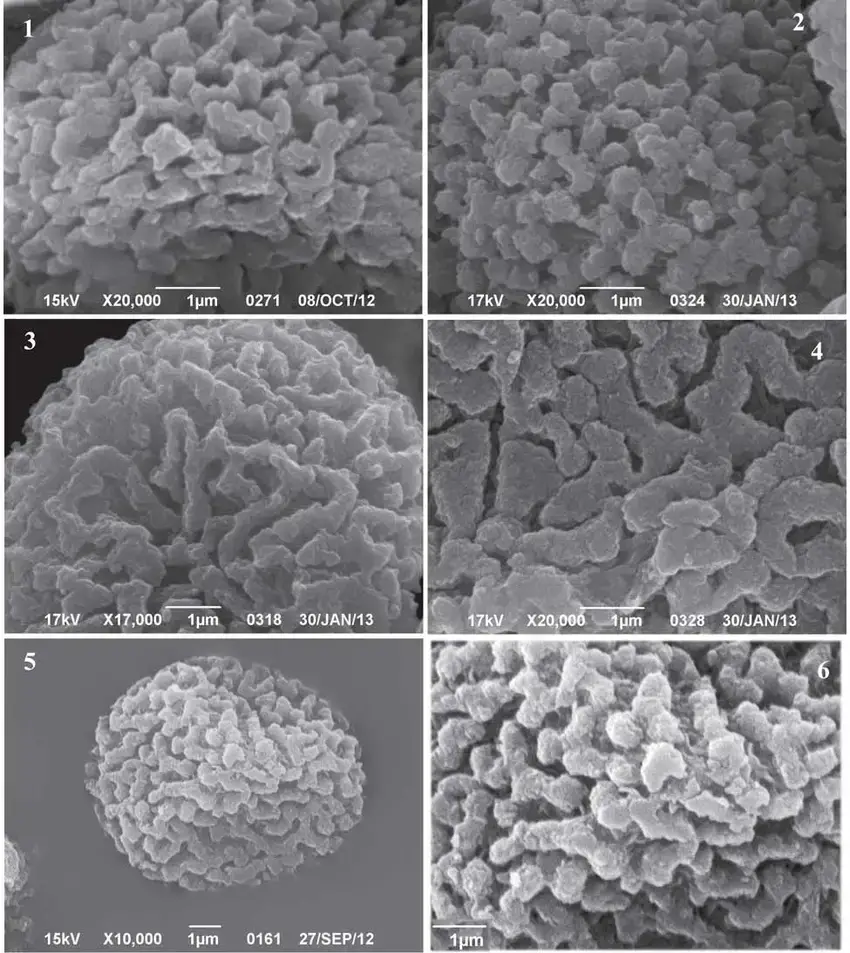
Spore-surface-structure-of-Cephalozia-leucantha-1-C-catenulata-s-str-2-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Spore-surface-structure-of-Cephalozia-leucantha-1-C-catenulata-s-str-2-C_fig3_302166884
- Small size is advantageous in harsh conditions with limited resources
- Leaf lobes help increase surface area for moisture and nutrient uptake
- Rhizoids anchor the plant to its substrate
- Reproduction via spores allows long-distance dispersal
Conclusion

cephalozia-bicuspidata-e-144737-474750-3627-M0RY6W.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/cephalozia.html

4607278054_f4e6ed8dfd_z.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/32503151@N05/4607278054
Cephalozia randii may be small, but this mighty moss is a fascinating and ecologically important species. Its unique morphology, widespread distribution, and important ecosystem functions make it a worthy subject of study and appreciation. Next time you’re out in the woods, take a moment to search for this tiny gem! What other miniscule marvels of the plant kingdom have you encountered?

153692419727032352.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/pt/wiki/Metzgeria_furcata.html

fe8786.jpg from: https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/showimage/243804/

d6f618db91e93931042f9a9c2bcf4fd8–mountain.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.co.uk/pin/cephalozia-catenulata–308637380693938768/