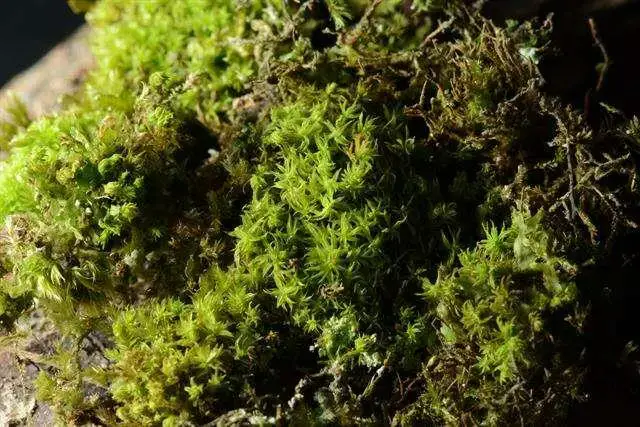

913.129258.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/3768/media?page=2
Discovering the Fascinating World of Zygodon subrecurvifolius Broth. Moss
Zygodon subrecurvifolius Broth., commonly known as Zygodon moss, is a captivating species of moss belonging to the Orthotrichaceae family. As a member of the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class, this tiny but mighty plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the intriguing world of Zygodon subrecurvifolius and explore its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological importance.
Background on Bryophytes
Before we delve into the specifics of Zygodon subrecurvifolius, let’s briefly discuss the group it belongs to: bryophytes. Bryophytes are non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead absorbing water and nutrients directly through their cell surfaces. Bryophytes are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide and play crucial roles in ecosystems, such as soil stabilization, water retention, and providing shelter for small organisms.
Morphology and Identification
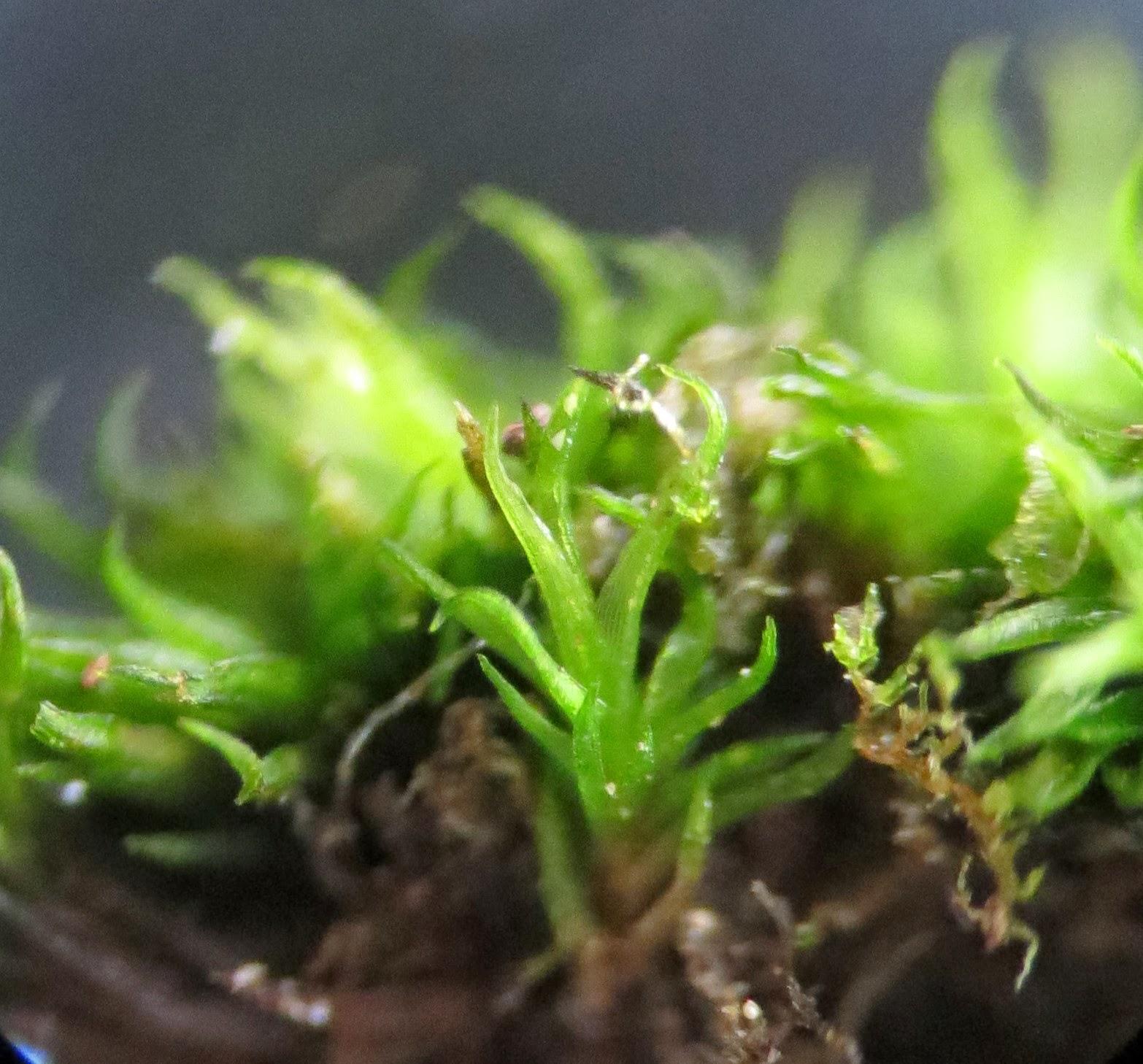

Zygo.Virid.2014-03-10-135.jpg from: https://bryobits.blogspot.com/2014/03/moss-gallery-v-z.html
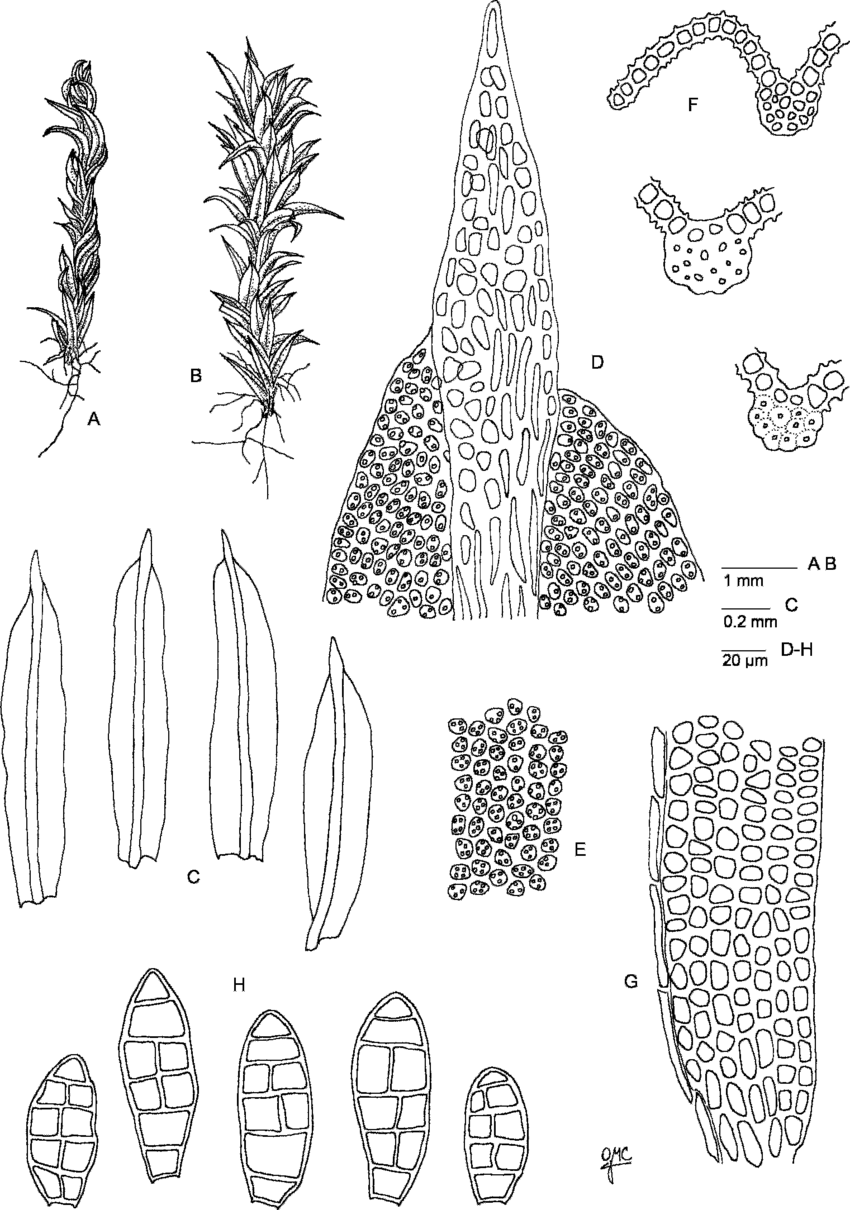
Zygodon subrecurvifolius is a small, cushion-forming moss that typically grows in dense tufts. Its stems are erect, reaching heights of 5-15 mm, and are covered in small, ovate leaves. The leaves are 0.8-1.2 mm long and have a distinct, recurved apex, which gives the species its name “subrecurvifolius.” The leaf margins are entire, and the midrib extends to the leaf tip.
One of the most distinguishing features of Zygodon subrecurvifolius is its sporophyte (the spore-producing structure). The sporophyte consists of a capsule on a short seta (stalk) that emerges from the top of the leafy gametophyte. The capsule is cylindrical, 1.5-2 mm long, and has 8 longitudinal ridges. When mature, the capsule opens via 8 triangular teeth to release the spores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Zygodon subrecurvifolius has a wide global distribution, found on several continents:
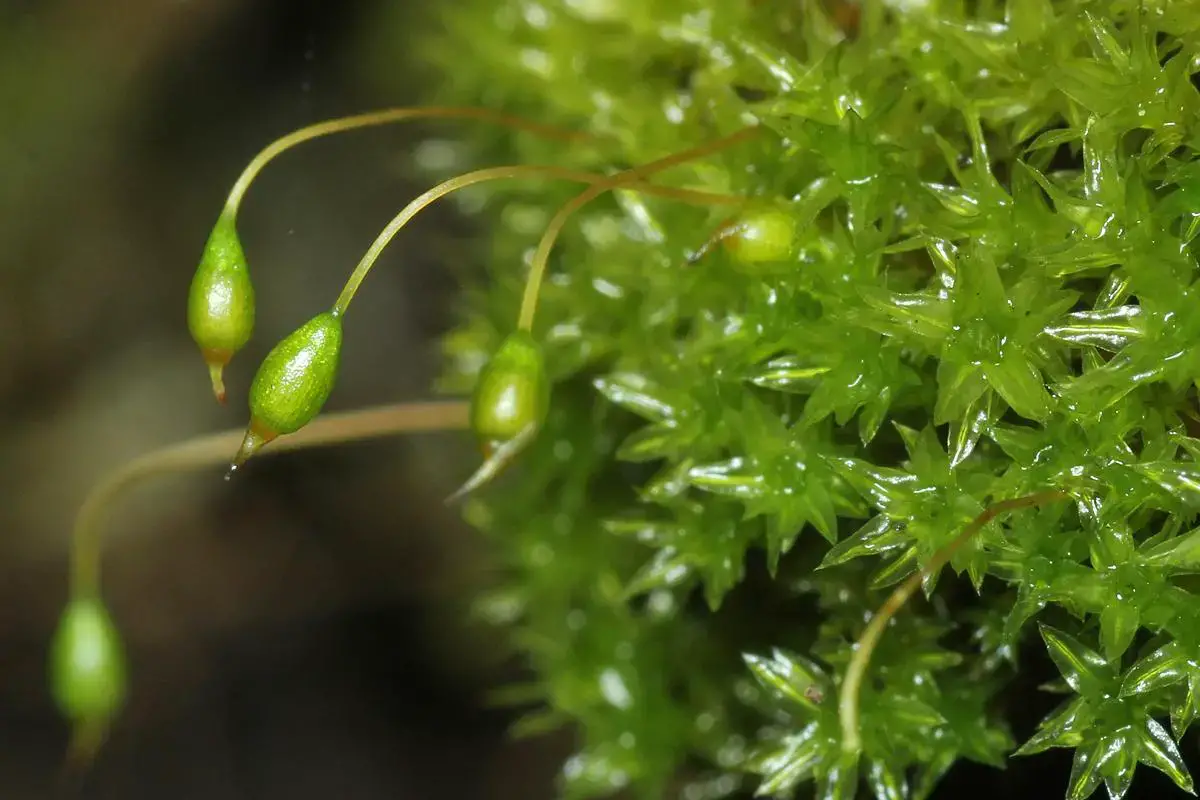

Zygodon+conoideus+var.+conoideus+01feb13+(2a).jpg from: https://goweros.blogspot.com/2013/02/an-adaptable-epiphyte.html
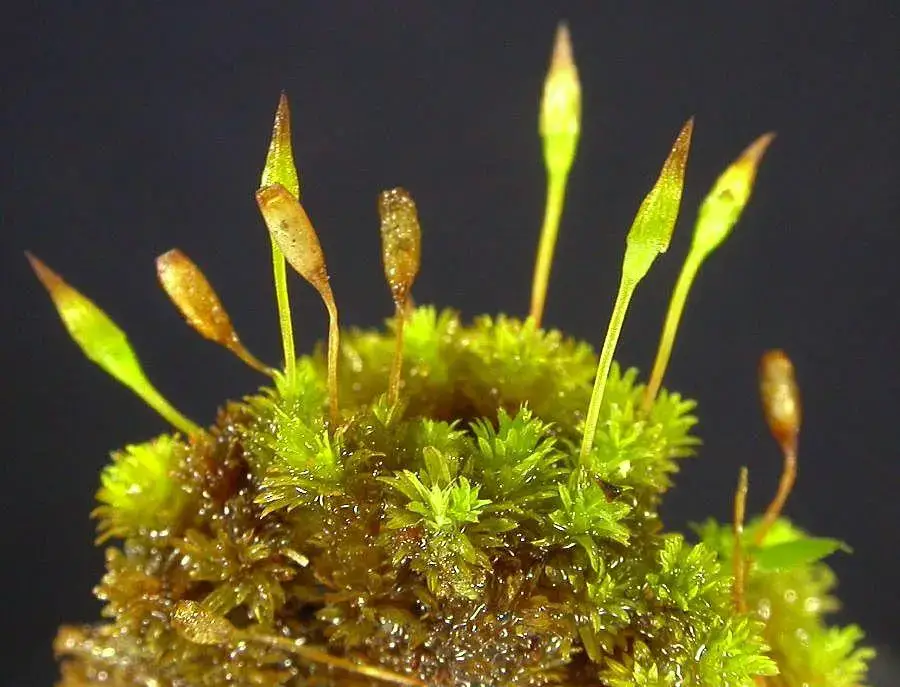

DT_Zygodon_intermedius.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/47_Orthotrichaceae_images.html
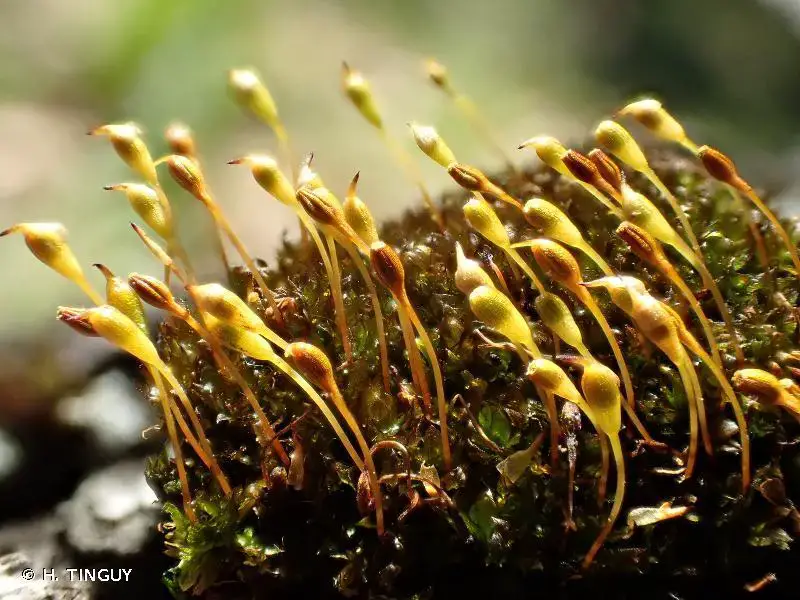

203864.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5065
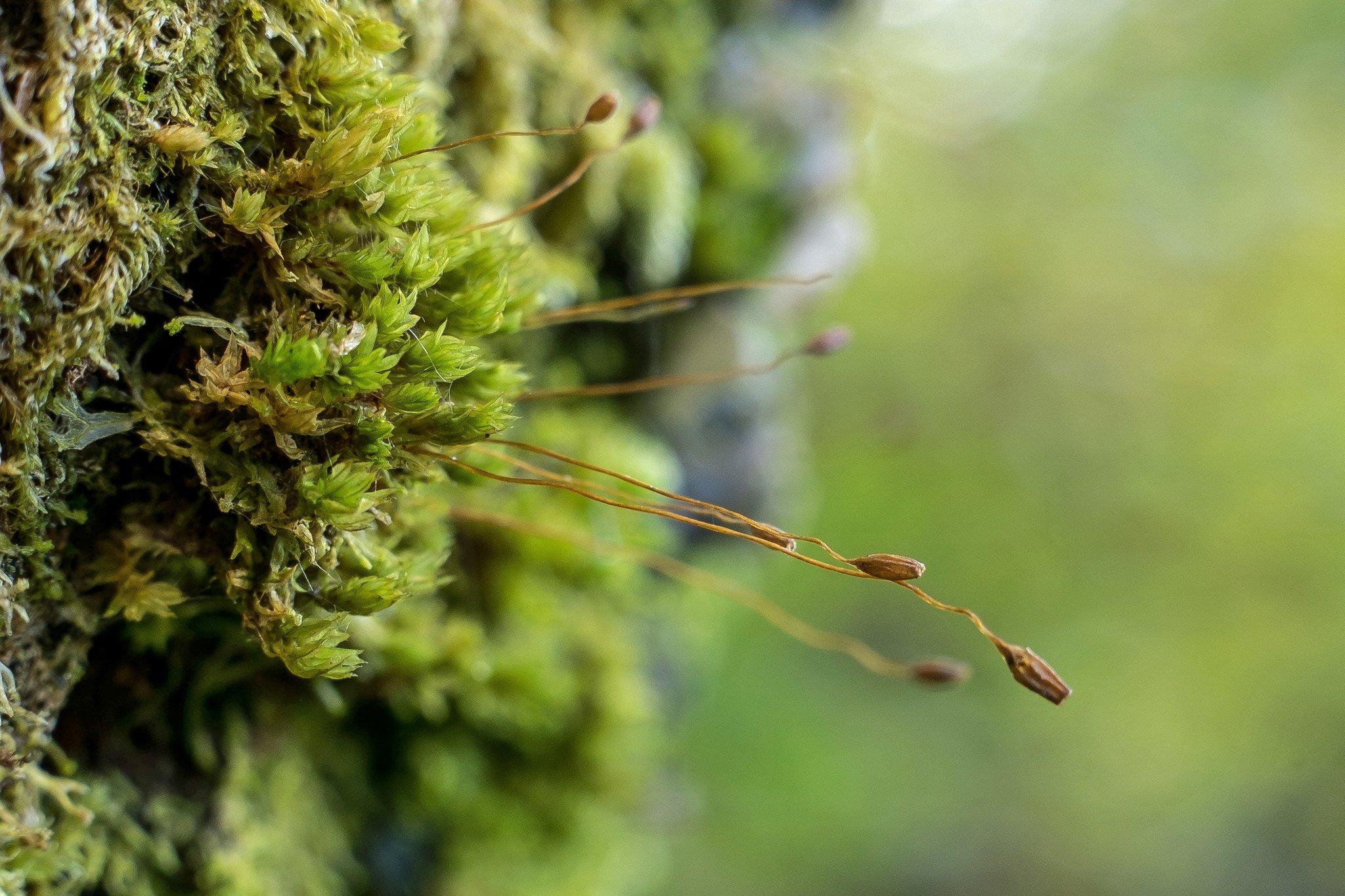

SP+-+Zygodon-conoideus+or+Lesser+Yoke+moss+Stan+Phillips.jpg from: https://savingscotlandsrainforest.org.uk/blog/bryophytes-back-to-basics
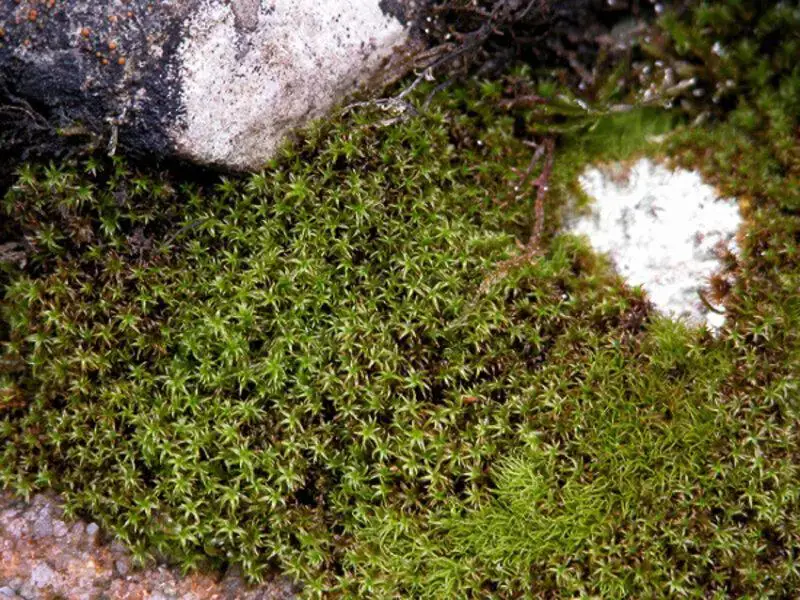

01-09-zygograc-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/zygodon-gracilis/
| Continent | Countries/Regions |
|---|---|
| Europe | UK, Ireland, France, Spain, Portugal, Italy |
| Africa | Macaronesia (Azores, Madeira, Canary Islands) |
| Asia | China, Japan, Taiwan |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand |
This moss species typically grows on the bark of trees (epiphytic) or on rocks (epilithic) in humid environments. It prefers partial shade and can be found in forests, woodlands, and even urban areas with suitable substrates and moisture levels.
Zygodon-stirtonii-A-Habit-when-dry-B-Habit-when-moist-C-Leaves-D-Leaf-apex-E.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Zygodon-stirtonii-A-Habit-when-dry-B-Habit-when-moist-C-Leaves-D-Leaf-apex-E_fig7_232664005
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other bryophytes, Zygodon subrecurvifolius plays essential roles in its ecosystems:
Water retention: The dense cushions formed by this moss help to trap and retain moisture, contributing to local humidity levels and supporting other organisms.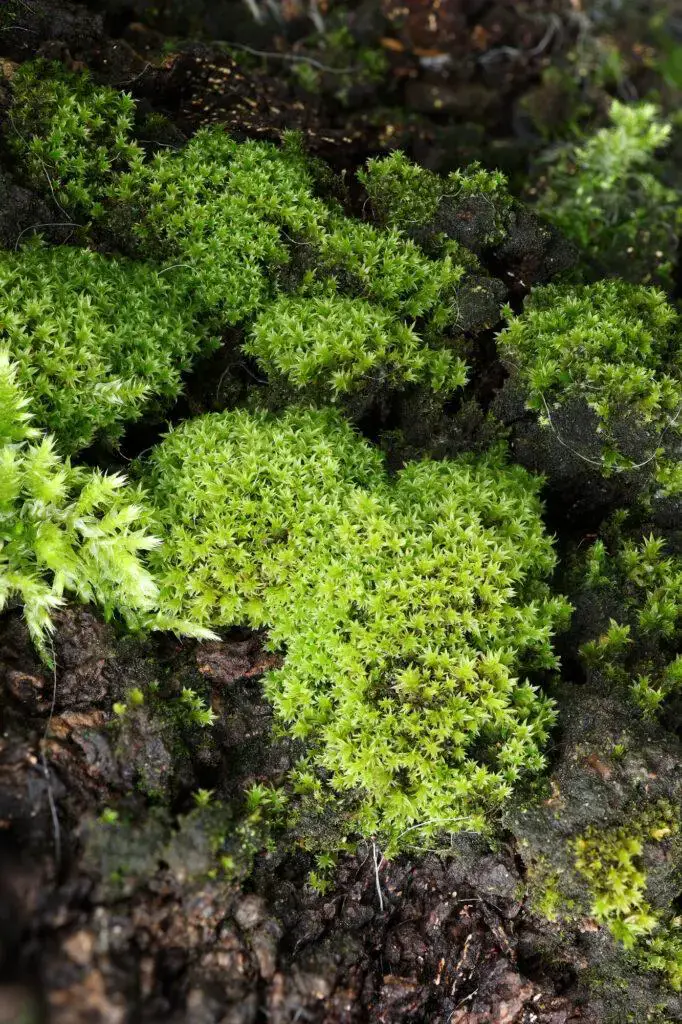
2020-08-15-12-02-15-682×1024.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/zygodon-viridissimus/
Nutrient cycling: As Zygodon subrecurvifolius decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil, supporting the growth of other plants.
Habitat provision: The small spaces between the moss plants provide shelter and microhabitats for various invertebrates, such as mites, springtails, and tardigrades.
To thrive in its preferred environments, Zygodon subrecurvifolius has developed several adaptations:
- Desiccation tolerance: This moss can survive periods of drought by entering a dormant state and quickly reviving when moisture becomes available again.
- Efficient water uptake: The small, dense leaves of Zygodon subrecurvifolius allow for efficient water absorption and retention.
- Asexual reproduction: In addition to producing spores, this moss can also reproduce asexually through fragmentation, ensuring its survival and spread in suitable habitats.
Conclusion
Zygodon subrecurvifolius Broth. may be small, but it is a fascinating and important component of the ecosystems it inhabits. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a captivating subject for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. The next time you find yourself in a humid forest or woodland, take a closer look at the tree bark or rocks – you might just spot a patch of Zygodon moss quietly thriving in its niche.
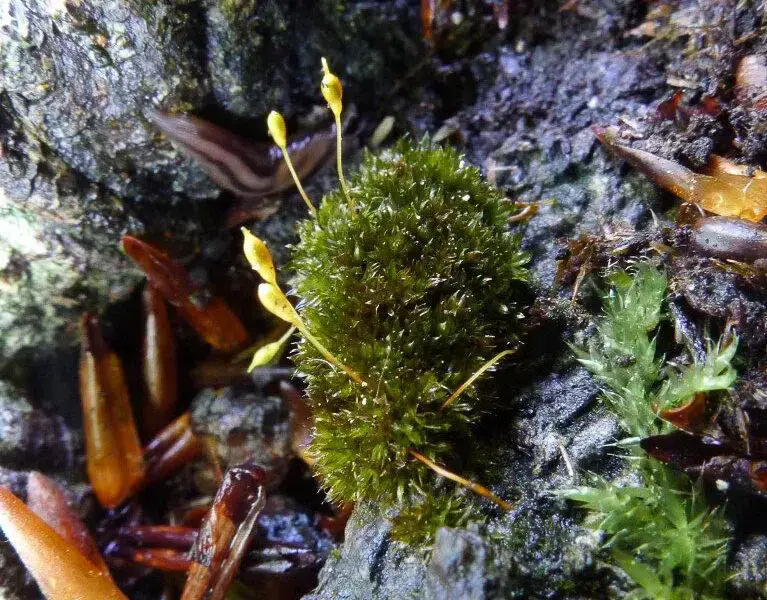

VC11-zygodon-forsteri-fred-rumsey-767×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/codonoblepharon-forsteri/
What other secrets might these tiny plants hold, and how can we continue to learn from and appreciate them?