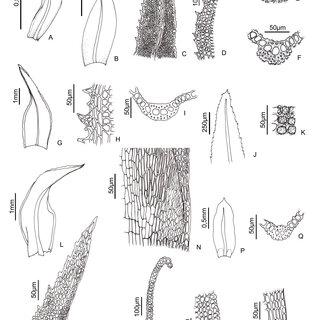
Leptodontium-flexifolium-Dicks-ex-With-Hampe-in-Lindb-A-B-Leaves-C-Leaf-apex-D_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Trichostomum-termitarum-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-A-Leaf-B-Leaf-apex-C-Marginal_fig11_296705710
Trichostomum prionodon: The Fascinating Moss of the Pottiaceae Family
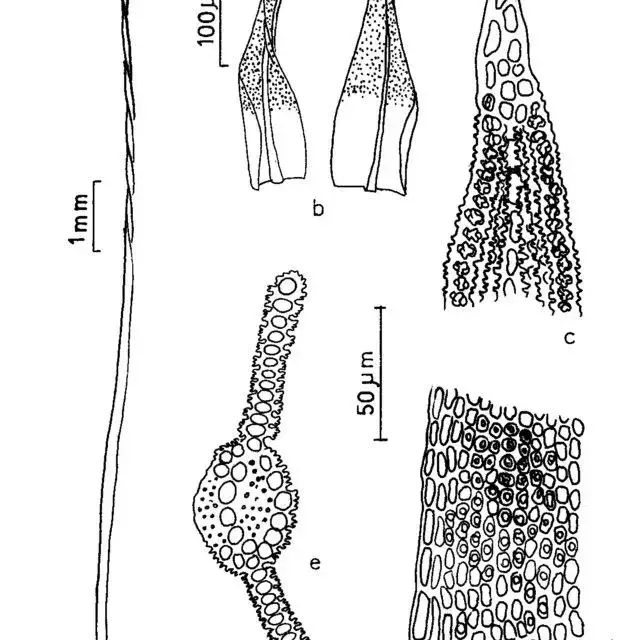
Figura-13-Trichostomum-tenuirostris-Hook-Taylor-Lindb-a-Aspecto-geral-do_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-10-Macromitrium-podocarpi-Muell-Hal-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-Filidios_fig8_259822623
Introduction
Trichostomum prionodon Müll.Hal., commonly known as Trichostomum moss, is a captivating species belonging to the Pottiaceae family of mosses. This tiny but mighty plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems and boasts unique adaptations that allow it to thrive in various habitats worldwide. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of Trichostomum prionodon and explore its morphology, distribution, ecological roles, and more.
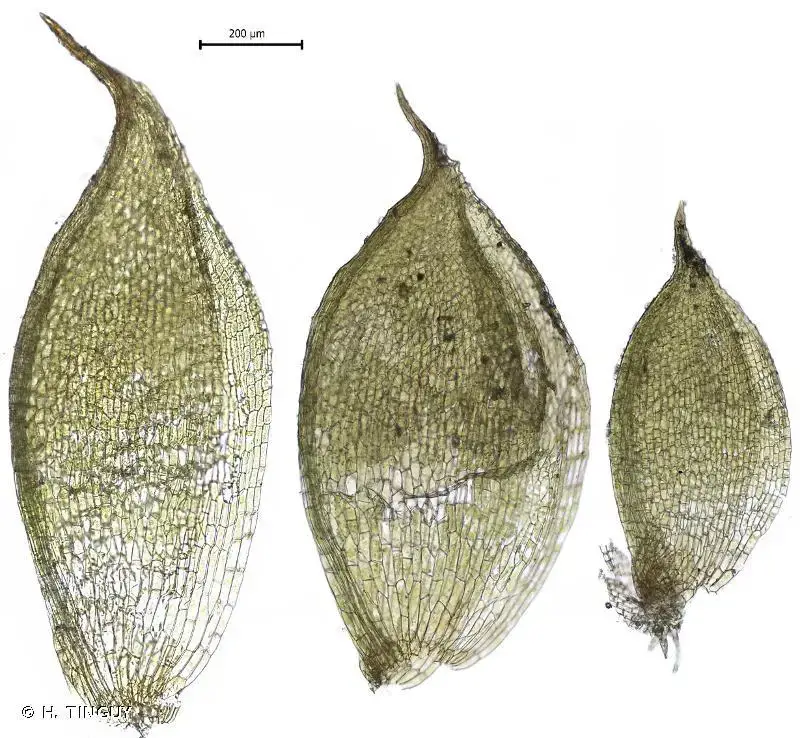

368171.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4862
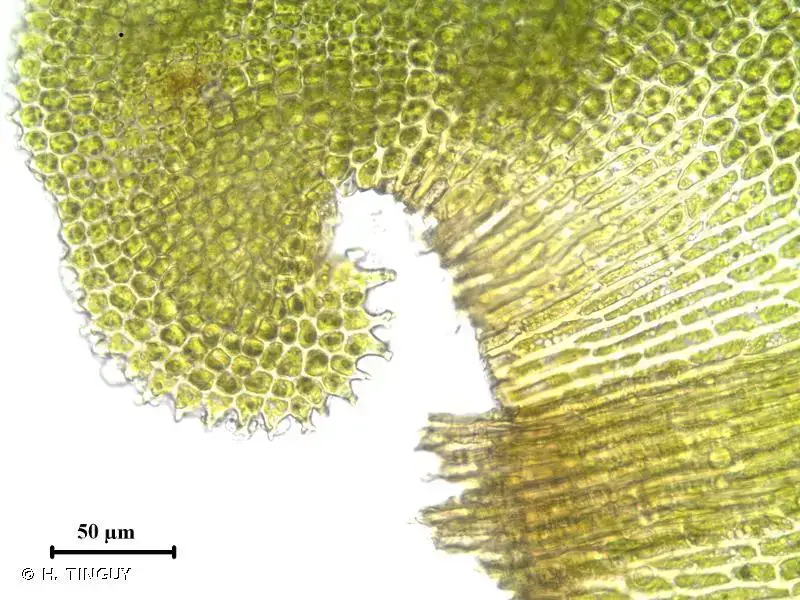

200154.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5182
Background
Trichostomum prionodon is a moss species that falls under the

Oxystegus-tenuirostris-4-150×85.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-trichostomum-tenuirostre/
Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. The Pottiaceae family, to which it belongs, is one of the largest moss families, with over 1,500 species distributed across the globe. Trichostomum mosses are known for their small size and their ability to colonize a wide range of substrates, from rocks and soil to tree bark and even man-made structures.
Morphology and Identification
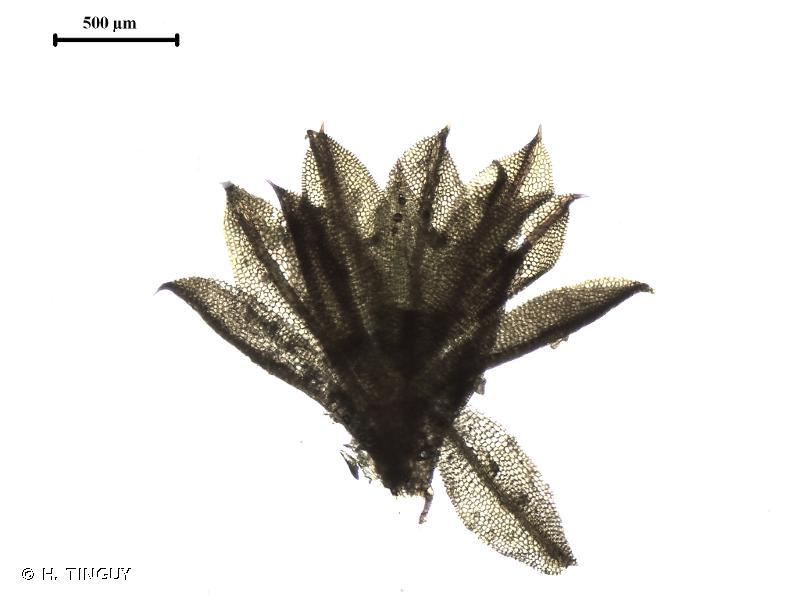
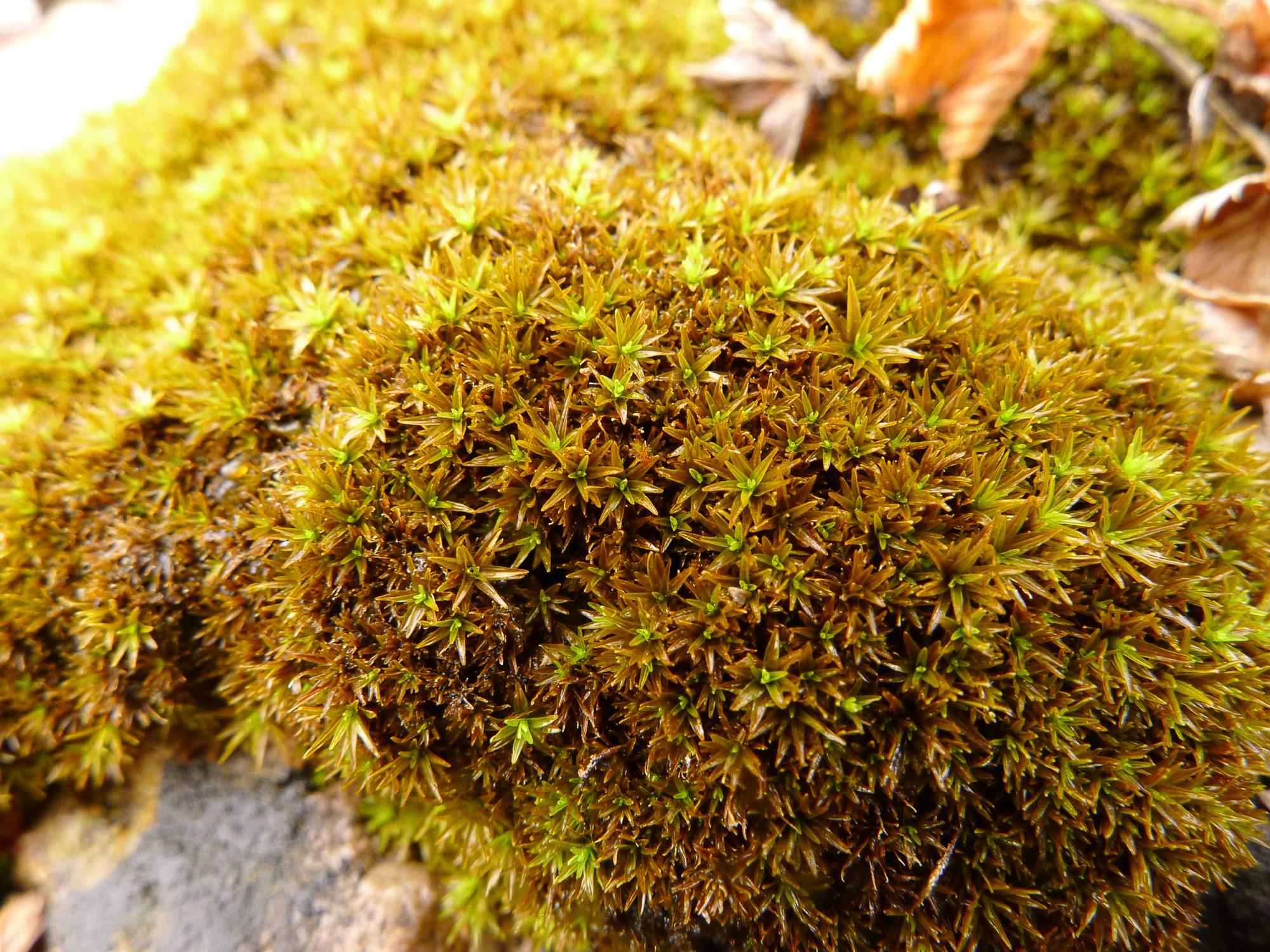
Trichostomum prionodon is characterized by its small, compact cushions or tufts, which typically measure between 0.5 to 2 cm in height. The leaves are lanceolate to linear-lanceolate in shape, with a pointed apex and recurved margins. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is the presence of elongated, hyaline hair-points at the leaf tips, which give the cushions a hoary appearance when dry.

250105.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/435838
The

Trichostomum-crispulum-0719.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/trichostomum-crispulum/
leaf cells of T. prionodon are small and rounded to quadrate in shape, with thick walls. The costa (midrib) is strong and extends to the leaf apex. Sporophytes are relatively common in this species, with cylindrical capsules borne on long, slender setae.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Trichostomum prionodon has a wide global distribution, occurring on all continents except Antarctica. It can be found in a variety of habitats, including rocky outcrops, cliffs, soil banks, and disturbed areas such as roadsides and quarries. This moss is particularly well-adapted to calcareous substrates and is often associated with limestone and chalk formations.
| Continent | Habitat |
|---|---|
| North America | Rocky outcrops, cliffs, soil banks |
| South America | Disturbed areas, roadsides |
| Europe | Calcareous substrates, limestone formations |
| Asia | Cliffs, chalk formations |
| Africa | Rocky outcrops, disturbed areas |
| Australia | Soil banks, roadsides |
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
As a pioneer species, Trichostomum prionodon plays a crucial role in the colonization and stabilization of bare substrates. Its compact cushions help to retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, creating microhabitats for other plant species to establish. This moss also contributes to the formation of soil through the accumulation of dead organic matter and the weathering of rock surfaces.
Trichostomum prionodon exhibits several adaptations that enable it to thrive in harsh environments. The hyaline hair-points on the leaf tips help to reflect excess light and protect the photosynthetic tissue from damage. The thick cell walls and small leaf size minimize water loss during periods of drought, while the strong costa provides structural support

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/169941-Trichostomum-brachydontium
and aids in water conduction.
Conclusion
Trichostomum prionodon may be small in stature, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is far from insignificant. This resilient moss serves as a pioneer species, stabilizes substrates, creates microhabitats, and contributes to soil formation. Its unique adaptations allow it to thrive in a wide range of environments, from rocky outcrops to disturbed areas, making it a true survivor in the world of bryophytes.
As we continue to study and appreciate the diversity of life on Earth, let us not overlook the humble moss, such as Trichostomum prionodon, and the vital roles they play in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. The next time you come across a small, hoary cushion of moss clinging to a rock or soil bank, take a moment to marvel at the tenacity and resilience of these extraordinary plants. Who knows what other secrets and adaptations they may be hiding in their tiny, intricate structures?

d36ce4ae460d121a18b6b04331eefb57.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/777152479423470222/
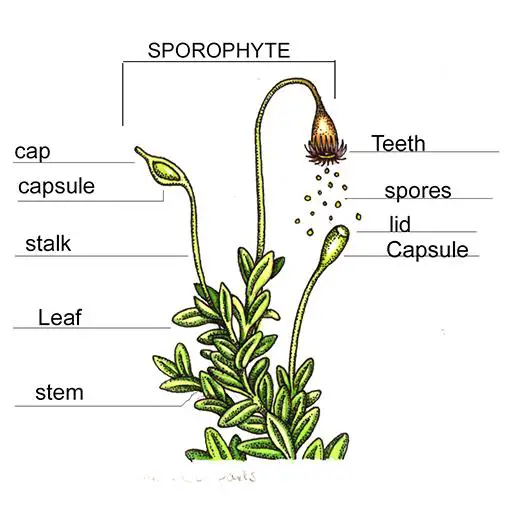
mosses-anatomy-natural-history-illustration-by-Lizzie-Harper.jpg from: https://ar.inspiredpencil.com/pictures-2023/moss-diagram