
2174e69b73594fa0c620e8af5924f136.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/bf7e5eeaf8a578b6413d823dbe679935
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of Willia austroleucophaea (Besch.) Broth., a captivating moss species from the Pottiaceae family, commonly known as Willia. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of the Bryophyta (mosses) kingdom.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Willia austroleucophaea, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These ancient plants have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Mosses are classified as Bryopsida, a division within the Bryophyta phylum, and play crucial roles in various ecosystems worldwide.
Main Content
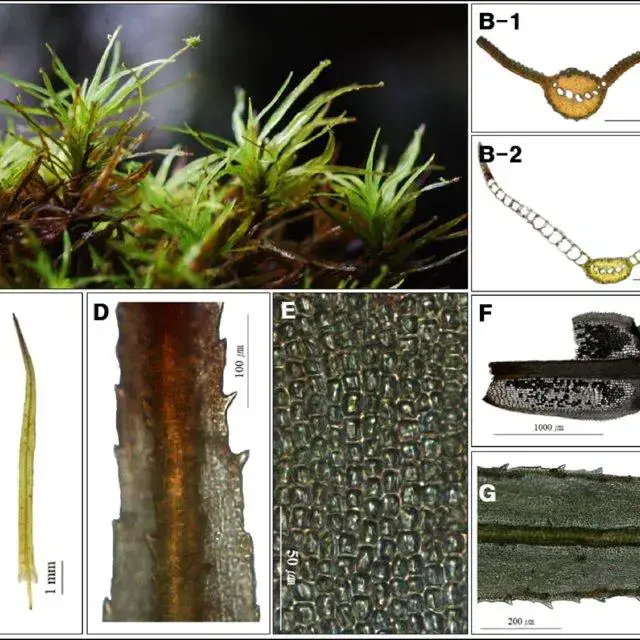
Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_fig1_283888063
Morphology and Identification
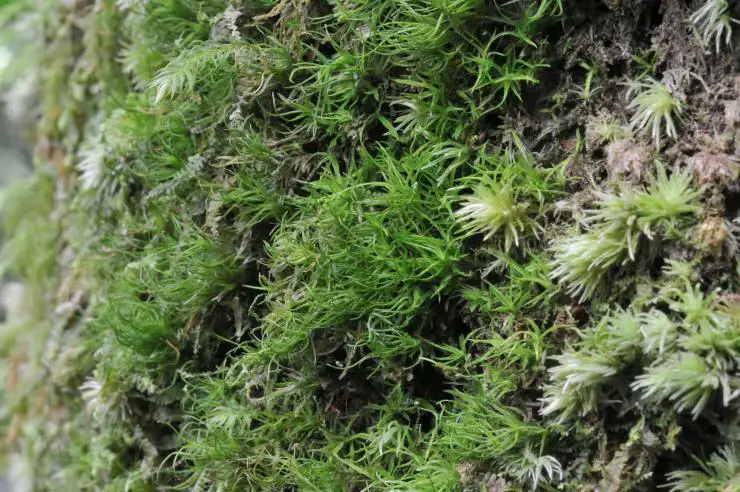
Willia austroleucophaea is a small, acrocarpous moss species, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow vertically from the tips of the gametophytes (leafy shoots). Its delicate leaves are typically lanceolate

B094-02_0.jpg from: http://taibif.tw/zh/namecode/200877

7518e22576ca8e839c67d85849c8b9dc.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.jp/pin/557390891371735155/
(lance-shaped) and spirally twisted when dry, a characteristic that aids in water retention. The calyptra (a cap-like structure covering the developing sporophyte) is cucullate (hood-shaped), and the capsules (spore-bearing structures) are cylindrical and erect.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe, including Australia, New Zealand, South America, and Antarctica. It thrives in diverse habitats, from coastal areas

Figura-12-Trachycarpidium-verrucosum-Besch-Broth-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-12-Trachycarpidium-verrucosum-Besch-Broth-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito_fig10_259822623
to alpine regions, often found growing on soil, rocks, or tree bark. Willia austroleucophaea is particularly well-adapted to harsh environments, making it a resilient pioneer species in disturbed or newly formed habitats.

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iqVOncK2Cig
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

3215155fbb924b5ec593c5b2f47aef7a–british-columbia.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/107875353546177899/
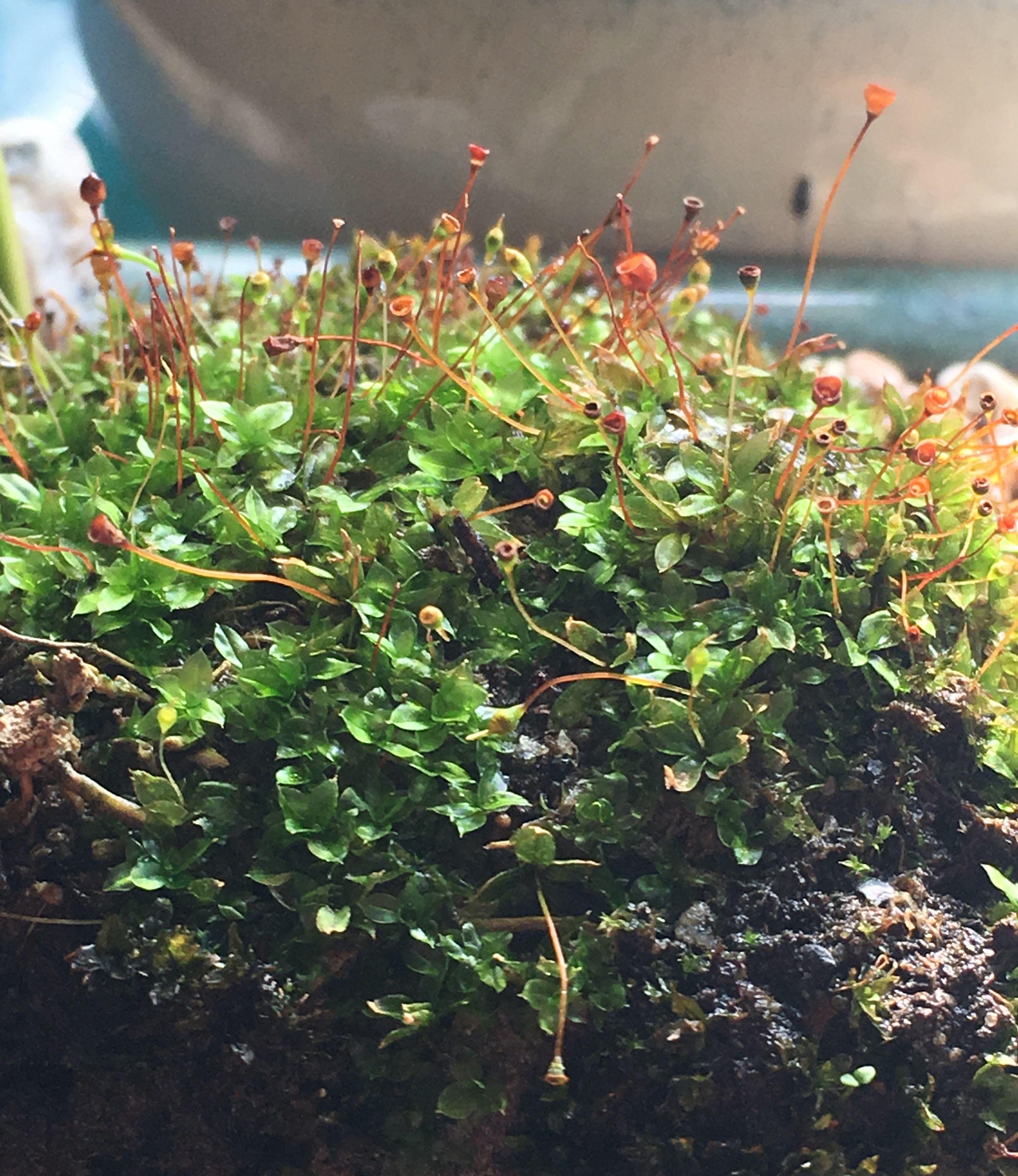
Like many mosses, Willia austroleucophaea plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, its ability to
Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
colonize bare surfaces and stabilize soil makes it an essential component of ecological succession.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Willia austroleucophaea is its desiccation tolerance. This moss can survive prolonged periods of drought by entering a state of dormancy, reviving once water becomes available again. This adaptation allows it to thrive in harsh, arid environments where other plants struggle to survive.
Case Studies/Examples
In Antarctica, Willia austroleucophaea

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283888063_Unrecorded_moss_species_from_Korean_Flora_III_Syrrhopodon_japonicus_Besch_Broth_and_Syrrhopodon_armatus_Mitt
has been observed growing in close association with other moss species, forming intricate moss carpets that provide crucial habitats for various invertebrates and microorganisms. These moss communities play a vital role in the fragile Antarctic ecosystem, contributing to nutrient cycling and primary productivity.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Division | Bryopsida |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Willia |
| Species | austroleucophaea |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, spirally twisted when dry |
| Calyptra | Cucullate (hood-shaped) |
| Capsules | Cylindrical, erect |
| Distribution | Australia, New Zealand, South America, Antarctica |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, tree bark, coastal and alpine regions |
Conclusion
Willia austroleucophaea (Besch.) Broth., or simply Willia, is a remarkable moss species that exemplifies the resilience and adaptability of the Bryophyta kingdom. From its intricate morphology to its global distribution and ecological significance, this unassuming plant has captured the imagination of bryologists and nature enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of life on our planet, Willia austroleucophaea serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty and importance of even the smallest organisms in our ecosystems.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the seemingly insignificant, what other wonders might we be missing, hidden in plain sight, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?

90cd87c0081e51684550c006a874c125.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/i-was-aiming-for-a-closeup-of-the-moss-to-better-define-its-detail-lichens-and-moss-growing-on-crystal-taken-by-robin-willia–295126581803848246/