Telaranea: A Tiny Moss with a Big Role in Forests
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
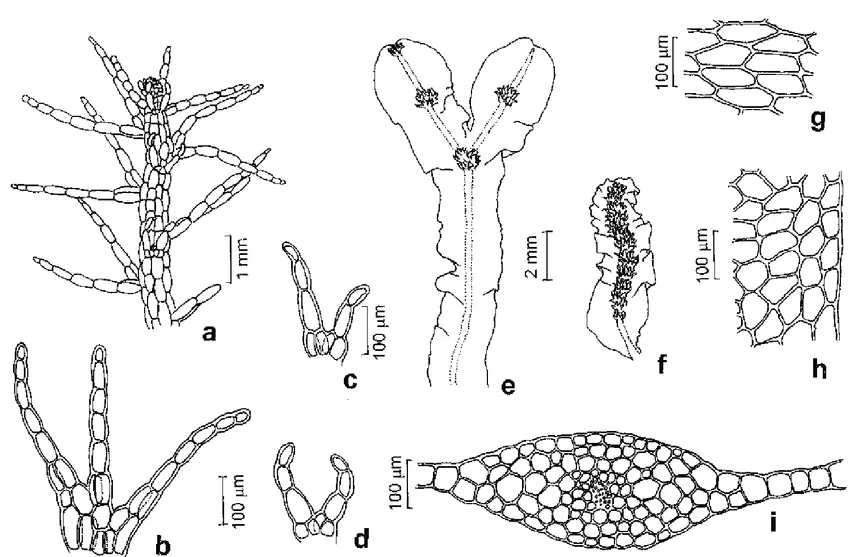
a-d-LEPIDOzIACEAE-Telaranea-nematodes-a-aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-filidio-c-d.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-d-LEPIDOzIACEAE-Telaranea-nematodes-a-aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-filidio-c-d_fig9_275609887
Telaranea meridiana: A Tiny Moss with a Big Story
Telaranea meridiana (E.A.Hodgs.) E.A.Hodgs., commonly known as Telaranea, is a fascinating species of moss belonging to the Lepidoziaceae
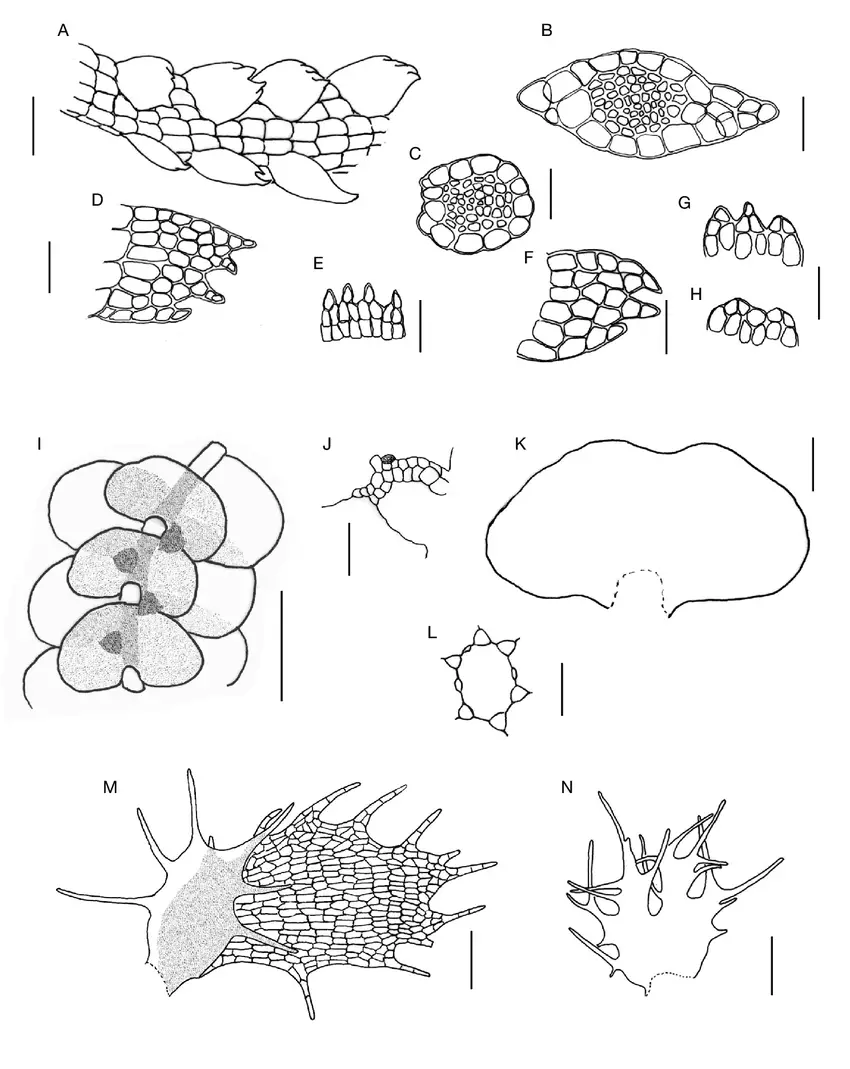
A-H-Telaranea-parvifolia-Steph-JJEngel-GLMerr-A-shoot-dorsal-view-B-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-H-Telaranea-parvifolia-Steph-JJEngel-GLMerr-A-shoot-dorsal-view-B-C_fig1_354662558
family. Despite its diminutive size, this little plant has captured the attention of botanists and enthusiasts alike. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Telaranea and explore what makes it so special.
Background on Telaranea Moss
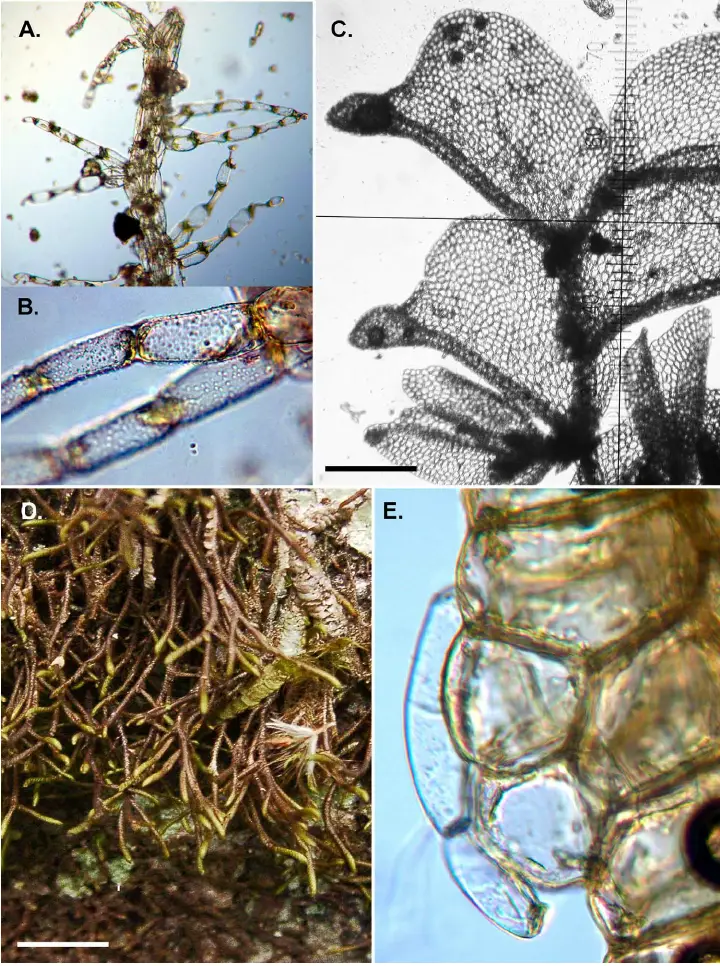

A-B-Telaranea-rosarioana-M-von-Konrat-J-E-Braggins-A-Naikatini-06-7-13-A.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-B-Telaranea-rosarioana-M-von-Konrat-J-E-Braggins-A-Naikatini-06-7-13-A_fig4_266465597
Telaranea is a genus of leafy liverworts in the Marchantiophyta division, Jungermanniopsida class. The genus contains over 100 species found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. T. meridiana was first described by E.A. Hodgson in 1956 based on specimens collected in New Zealand.
Morphology and Identification
Telaranea meridiana is a tiny moss, typically growing in dense mats. Its leaves are deeply divided into hair-like segments, giving it a delicate, feathery appearance. The leaves are arranged in two rows along the stem. Sporophytes (spore-producing structures) are rare and have only been observed a few times.
Identifying T. meridiana requires careful examination under a microscope. Key features to look for include:
- Deeply divided, unistratose leaves
perglossario.png from: https://eratostene.vialattea.net/wpe/glossario/linea-meridiana/
- Leaf lobes ending in a single elongated cell
- Underleaves absent
- Rhizoids scarce
Global Distribution and Habitat
T. meridiana has a scattered distribution in the Southern Hemisphere. It has been recorded in:
- New Zealand
- Australia
- South Africa
- Chile
- Argentina
This tiny moss typically grows on damp, shaded soil, rocks, and rotting logs in forests from lowland to montane elevations. It prefers humid microclimates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other bryophytes, Telaranea plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Helps retain moisture in the soil
- Provides shelter for micro-invertebrates
- Acts as a pioneer species in disturbed habitats
- Contributes to nutrient cycling
Telaranea has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its niche:
- Small size minimizes water loss
- Hair-like leaf segments increase surface area for moisture absorption
0c75cf8a9befcf9d112f1d1c81415c46.jpg from: https://ambienttrend.blogspot.com/2022/02/planos-de-hodge-y-lee.html
- Tolerates low light levels on the forest floor
- Reproduces primarily via fragmentation rather than spores
221565.jpg from: https://www.udocz.com/apuntes/221565/planos-de-hodge
la-meridiana-con-le-tracce-delle-lettere-rimosse.jpg from: https://www.brindisireport.it/cronaca/meridiana-firmata-la-soprintendenza-scrive.html
244024.jpg from: https://fity.club/lists/suggestions/planos-de-hodge/
Meridiana-Orizzontale-scaled.jpg from: https://parcoastronomico.it/meridiane/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Genus | Telaranea |
| Species | T. meridiana |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Leaf shape | Deeply divided into uniseriate segments |
| Underleaves | Absent |
| Habitat | Damp soil, rocks, logs in forests |
| Distribution | Scattered in Southern Hemisphere |
Conclusion
Telaranea meridiana may be small, but it is a prime example of how even the tiniest organisms can have fascinating stories to tell. Through its specialized adaptations and ecological roles, this unassuming moss has found a successful niche in forest habitats across the Southern Hemisphere.
The next time you’re out for a hike in New Zealand or Chile, take a moment to appreciate the miniature world of mosses at your feet. You just might spot a patch of Telaranea meridiana going about its quiet yet important business in the ecosystem. What other secrets might these small but mighty plants hold?

una-meridiana-antica-95259823.jpg from: https://it.dreamstime.com/fotografia-stock-una-meridiana-antica-image95259823