Andreaea Minuta: A Tiny Moss with Unique Characteristics and Ecological Significance
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

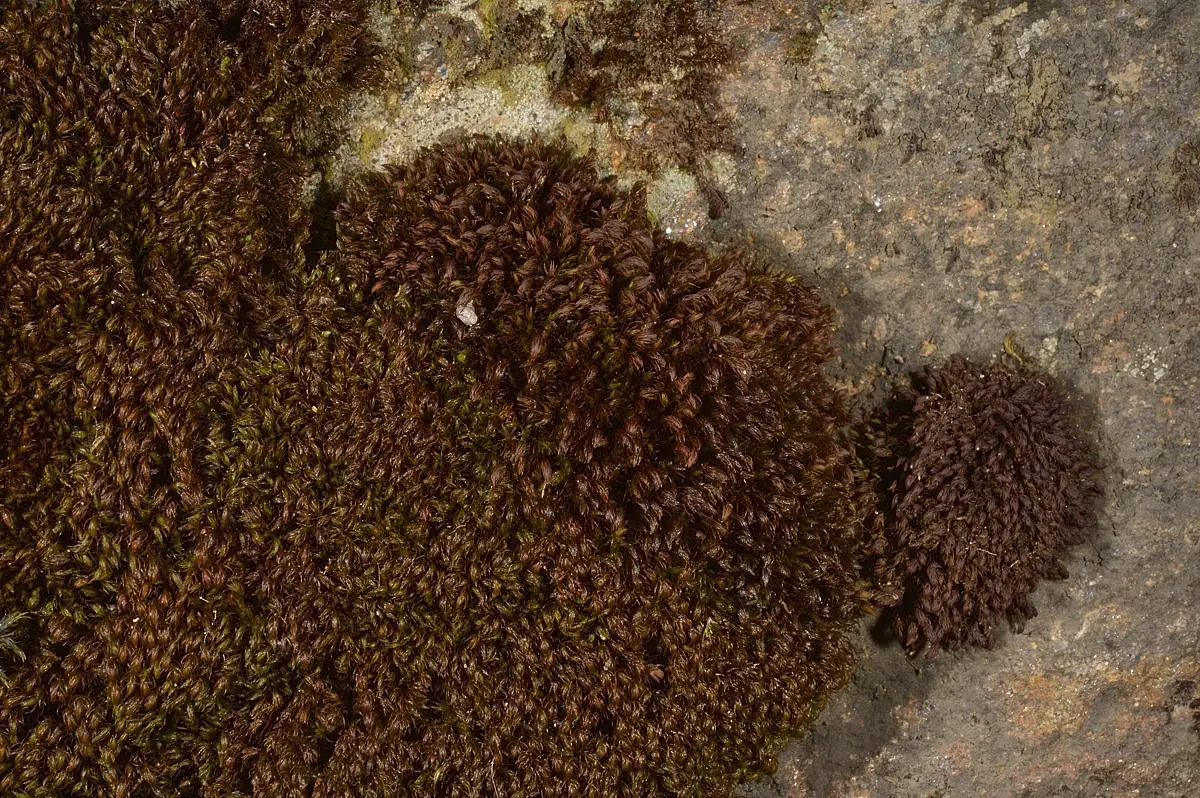
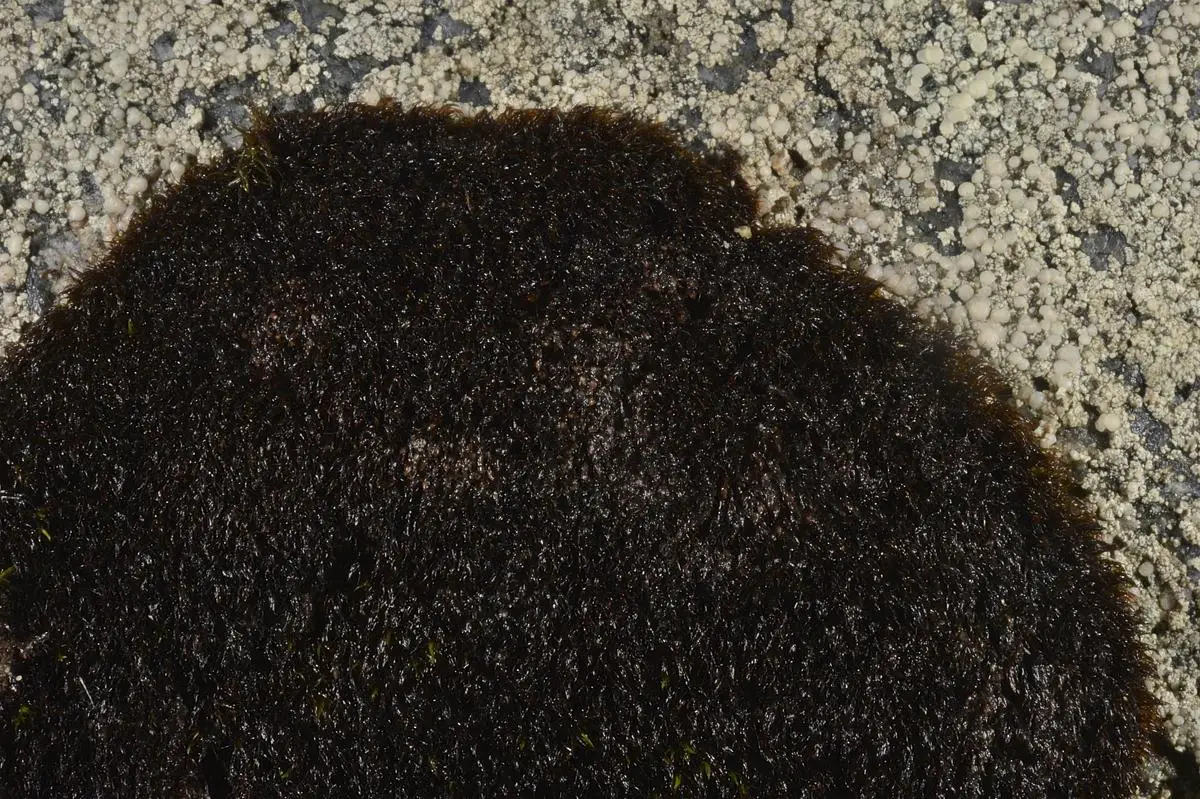
6896176628_fb25bda74b_c.jpg from: https://www.bbg.org/news/in_search_of_andreaea
Introduction
Mosses are fascinating and ancient plants that play important roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting moss species is Andreaea minuta R.Br.bis, also known simply as Andreaea. This tiny but mighty moss belongs to the Andreaeaceae family and has some unique characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Andreaea minuta and explore its morphology, habitat, distribution, and ecological significance.
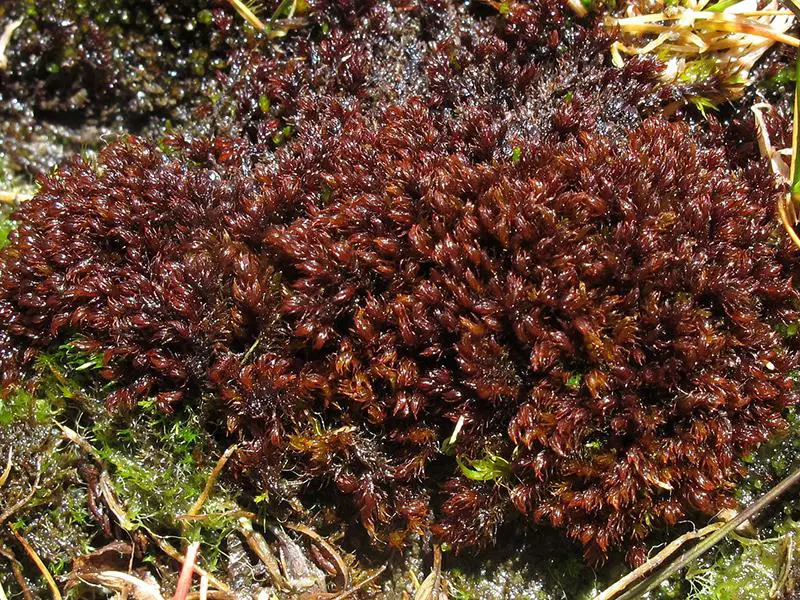

andreaea_nivalis.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Andreaeaceae/andreaea-nivalis/en/
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the specifics of Andreaea minuta, let’s briefly review what mosses are.
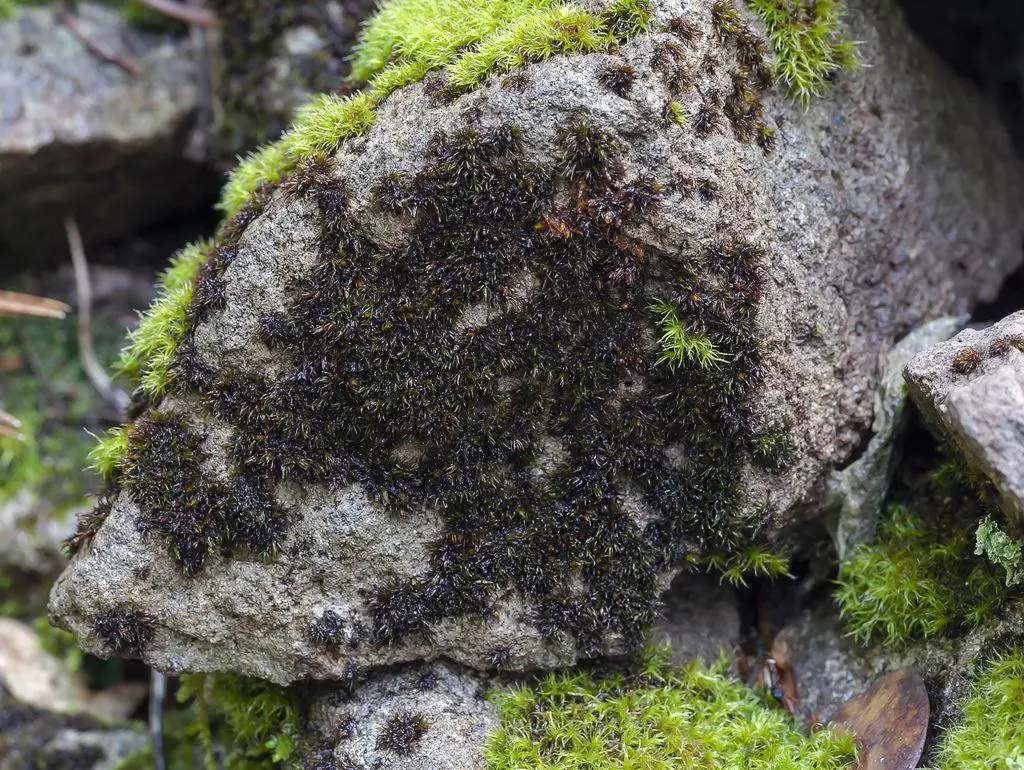

80456_orig.jpg from: https://idfg.idaho.gov/species/taxa/34877
Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves like other land plants. Instead, they have rhizoids that anchor them and absorb water and nutrients. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in moist habitats worldwide, from the Arctic to the tropics.
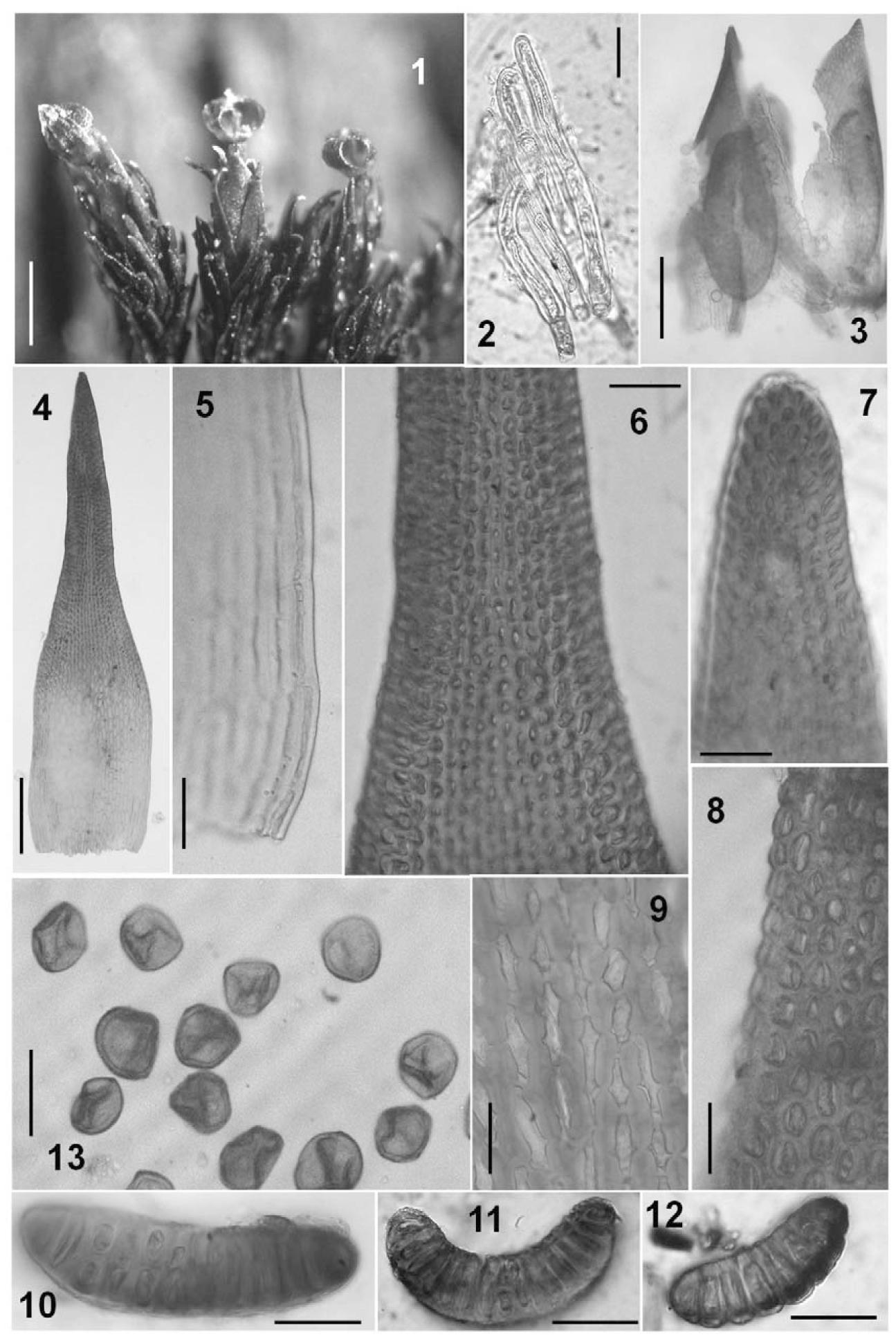
Andreaea minuta: Small but Mighty
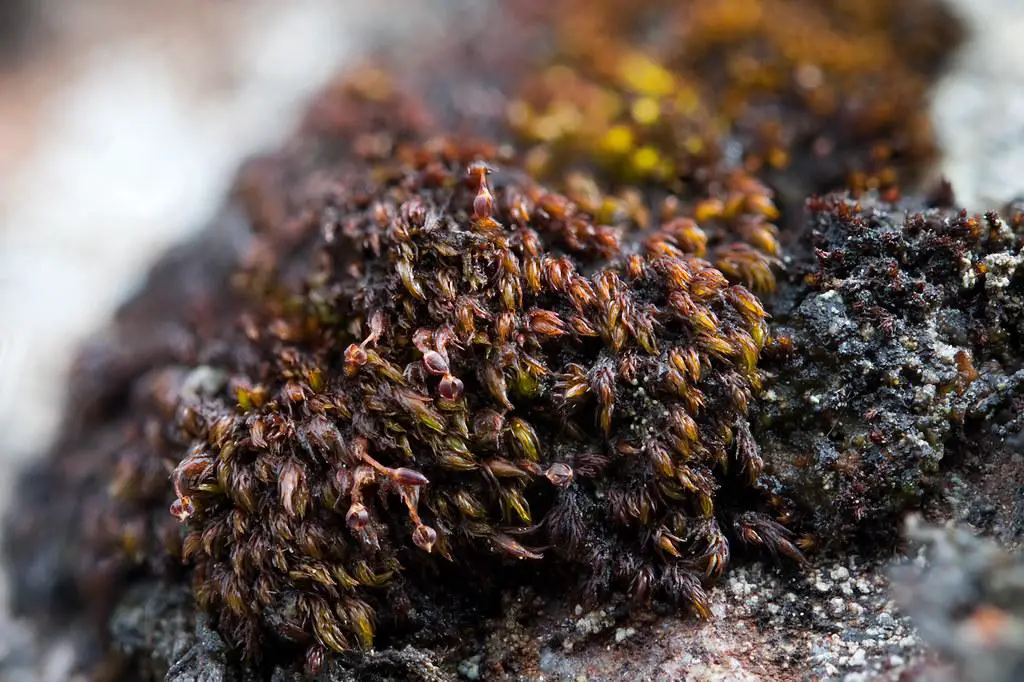
Andreaea minuta is a very small moss, typically only 2-5 mm tall. Its scientific name reflects this, as “minuta” means minute or tiny. Despite its diminutive size, Andreaea packs a lot of interesting features into its compact form:
- Morphology
andreaea_obovata.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Andreaeaceae/andreaea-obovata/en/
: The leaves are short, concave, and tightly overlapping, giving the moss a scaly appearance. They lack a midrib and are usually dark reddish-brown.
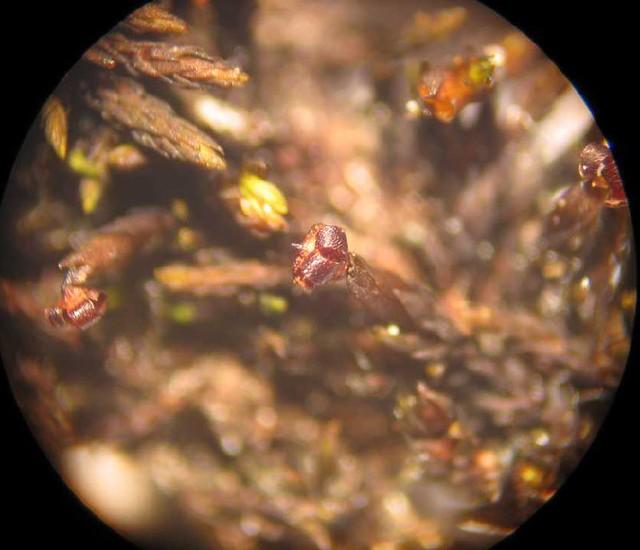
- Capsule: The spore capsule is small, round, and lacks a lid (operculum). It splits open along 4-8 vertical lines to release the spores.
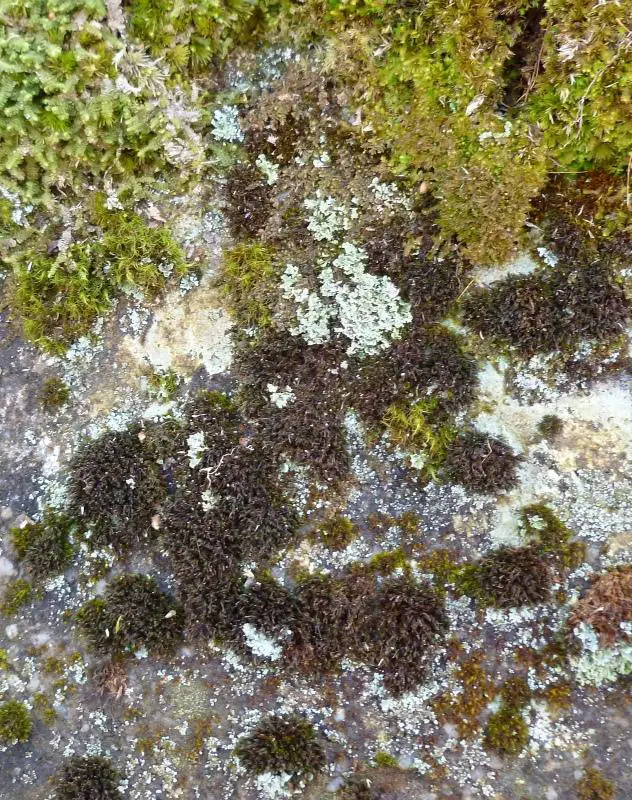
- Habitat: Andreaea minuta grows on acidic rocks, often in exposed alpine or subalpine areas. It is well-adapted to harsh conditions.
andreaea_blyttii.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Andreaeaceae/andreaea-blyttii/en/
- Distribution: This moss has a wide global distribution, found in mountainous regions of Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
Ecological Roles
Like other mosses, Andreaea plays some key roles in its ecosystem:
- Pioneer species: As Andreaea can grow on bare rock surfaces, it is often one of the first species to colonize disturbed or new areas. Over time, it helps build up organic matter for other plants to grow.
f01_271.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/cryptogamie-bryologie/volume-33/issue-3/cryb.v33.iss3.2012.271/Andreaea-flexuosa-R-Brown-Bis-subsp-luisieri-Sérgio-et-Sim/10.7872/cryb.v33.iss3.2012.271.full
- Erosion control: The dense mats formed by Andreaea help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
- Water retention: Mosses are excellent at absorbing and retaining water, which helps regulate moisture in their environment.
- Carbon cycling: Although small, mosses make a big cumulative contribution to carbon uptake and storage worldwide.
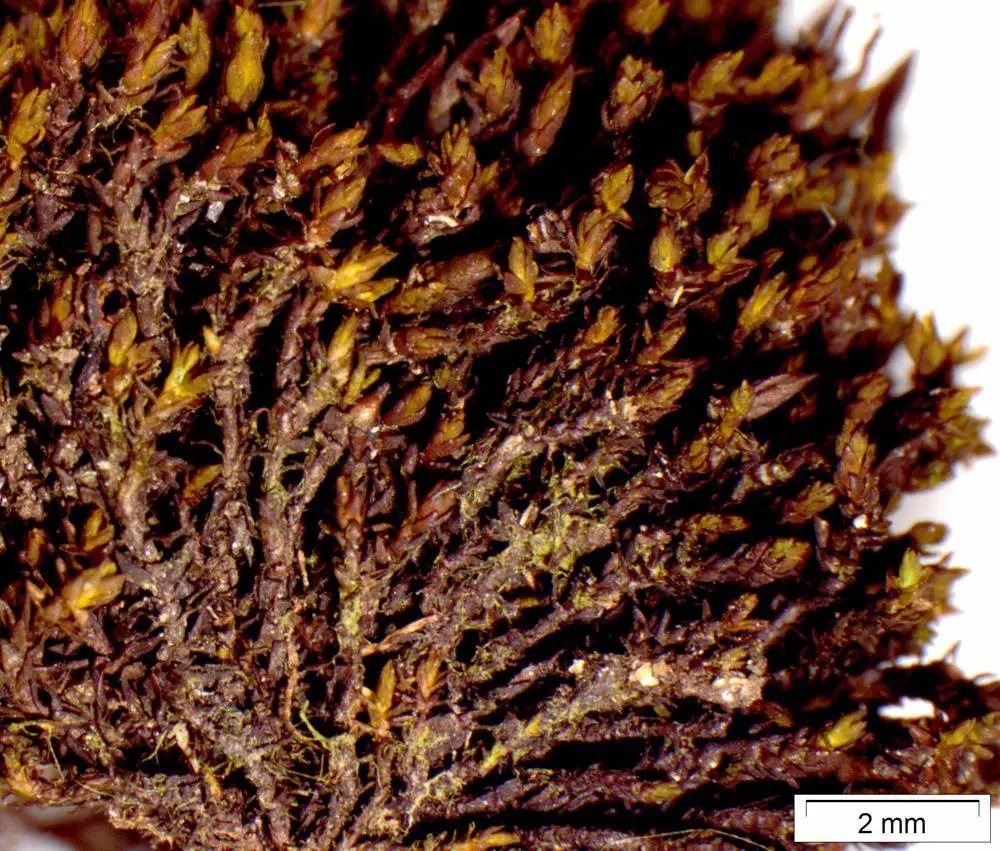

Andreaea_rupestris_26261__0.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxon=157761
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Size
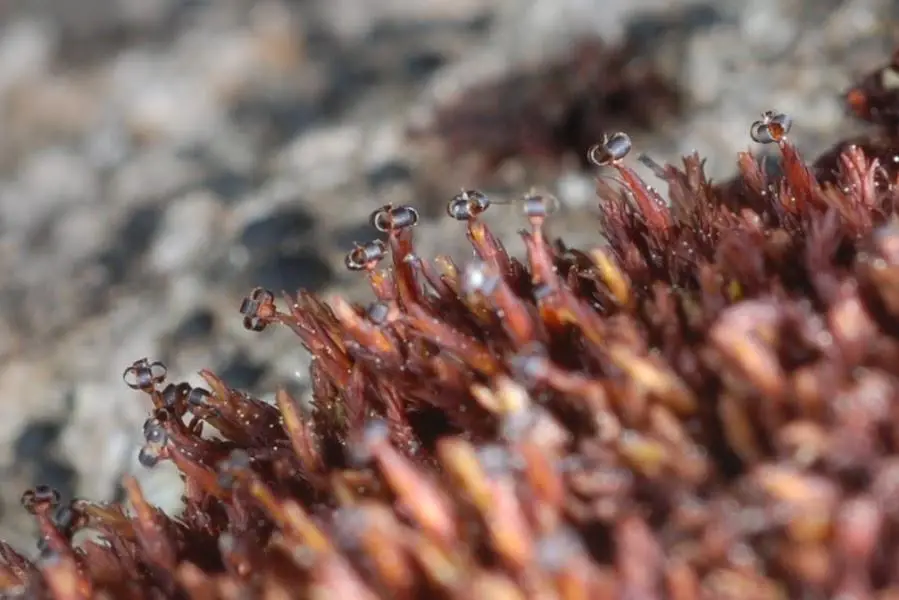 NK_Andreaea_mutabilis_possibly.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/55_Andreaeaceae_images.html |
2-5 mm tall |
| Leaves | Short, concave, overlapping, reddish-brown |
Capsule
 14417121659_36130c96e4_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/14417121659 |
Small, round, lacks lid, splits open |
| Habitat | Acidic rocks in alpine areas |
| Distribution | Mountainous regions worldwide |
Conclusion
Andreaea minuta may be a tiny moss, but it has an outsized ecological impact. From pioneering bare environments to preventing erosion and cycling carbon and water, this mighty moss plays a valuable role. Next time you’re in the mountains, take a closer look at the rocks – you may just spot a patch of Andreaea making a living in a tough environment. As we continue to study and appreciate the importance of mosses and other small but significant species, what other mighty miniatures of the natural world deserve our attention?

791871884_82cc108f3b_z.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/9536434@N02/791871884/