
209684.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4818
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Ditrichum lineare (Sw.) Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Ditrichaceae family. Often referred to simply as Ditrichum, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive marvel and uncover its secrets.
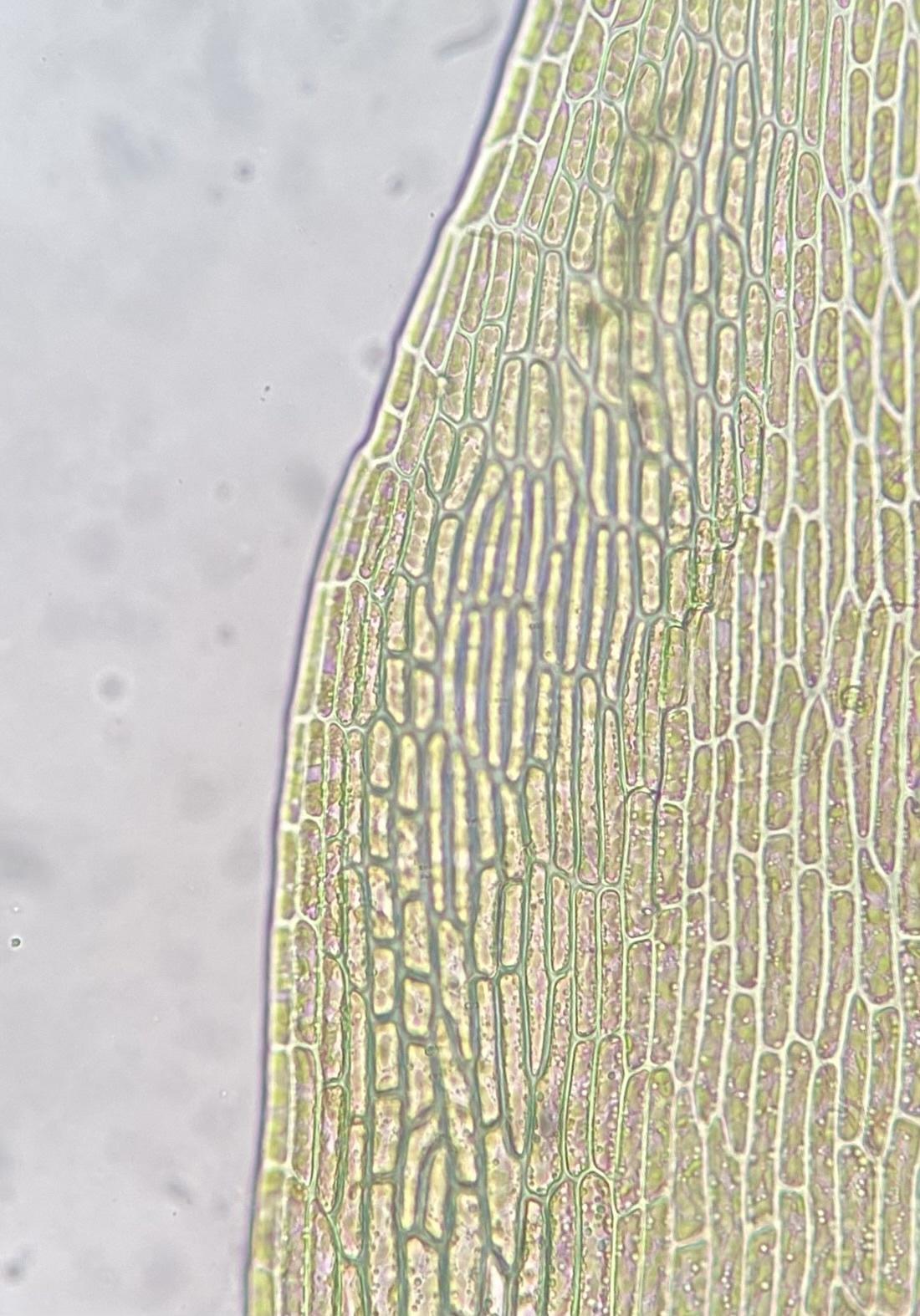
original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/5282343
Background
Before we explore the intricate details of Ditrichum lineare, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
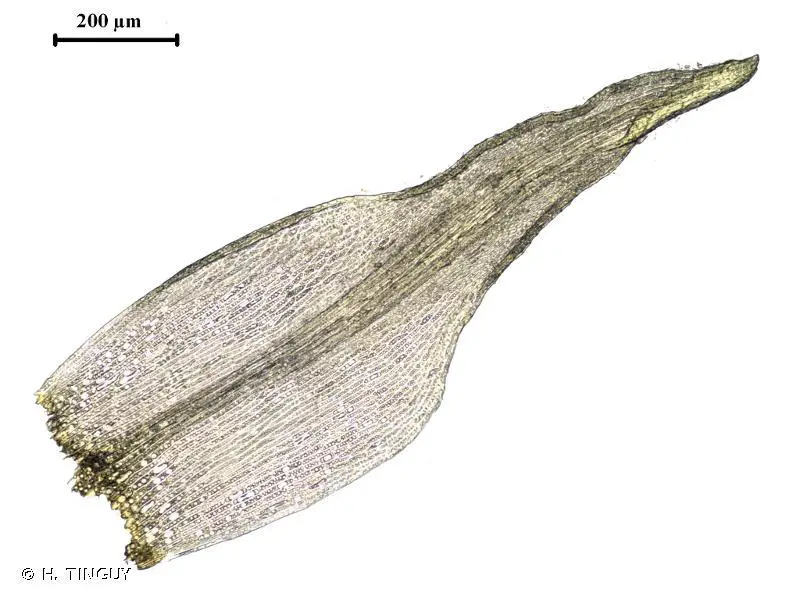
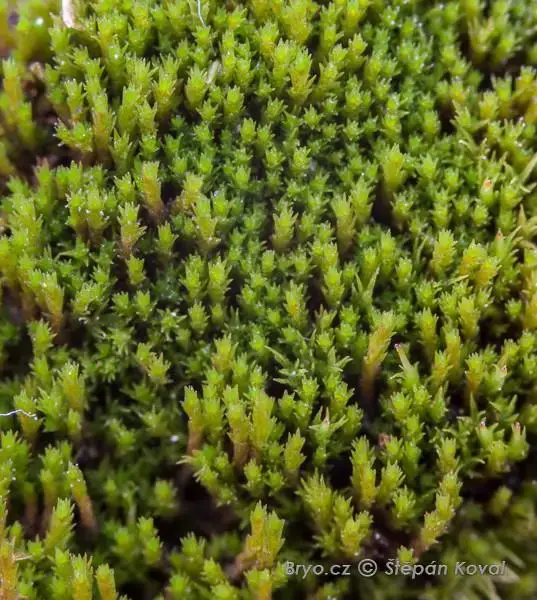
Ditrichum lineare is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems, typically reaching heights of 1-3 cm, are adorned with narrow, linear leaves that are often twisted when dry. The leaves are characterized by their distinctive

2427_Ditrichum_lineare_2010_11_17_9863.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=ditrichum_lineare&id=2427
costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short, hair-like structure known as the awn.
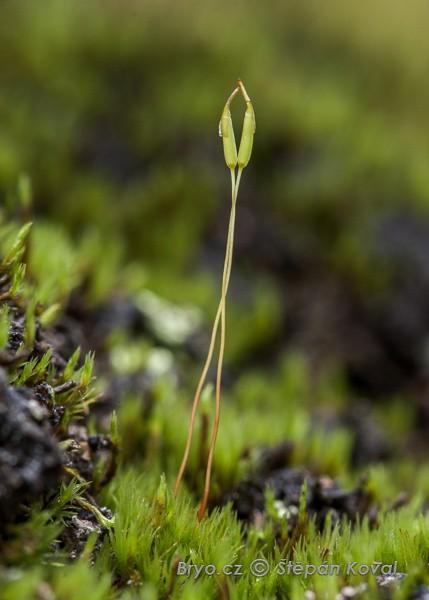
One of the most remarkable features of Ditrichum lineare is its capsule, which is cylindrical in shape and often slightly curved. This capsule is supported by a long, slender seta (stalk) and is topped with a conical operculum (lid). When the operculum detaches, it reveals a peristome – a delicate fringe of teeth that aids in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Ditrichum lineare is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents across the globe. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from acidic soils in forests and heathlands to disturbed areas such as roadsides and abandoned quarries. This moss is particularly well-adapted to colonizing bare, mineral-rich soils, often acting as a pioneer species in the early stages of ecological succession.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,

2425_Ditrichum_lineare_2009_07_12_8063.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=ditrichum_lineare&id=2425
Ditrichum lineare plays a vital role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for a diverse array of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Ditrichum lineare is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating remarkable resilience in harsh environments.
Case Studies/Examples
Ditrichum lineare has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological significance and adaptations. For instance, researchers have investigated its role in soil stabilization and revegetation efforts in areas affected by mining activities or natural disasters. Additionally, its ability to tolerate heavy metal contamination has made it a valuable bioindicator for monitoring environmental pollution levels.
Technical Table
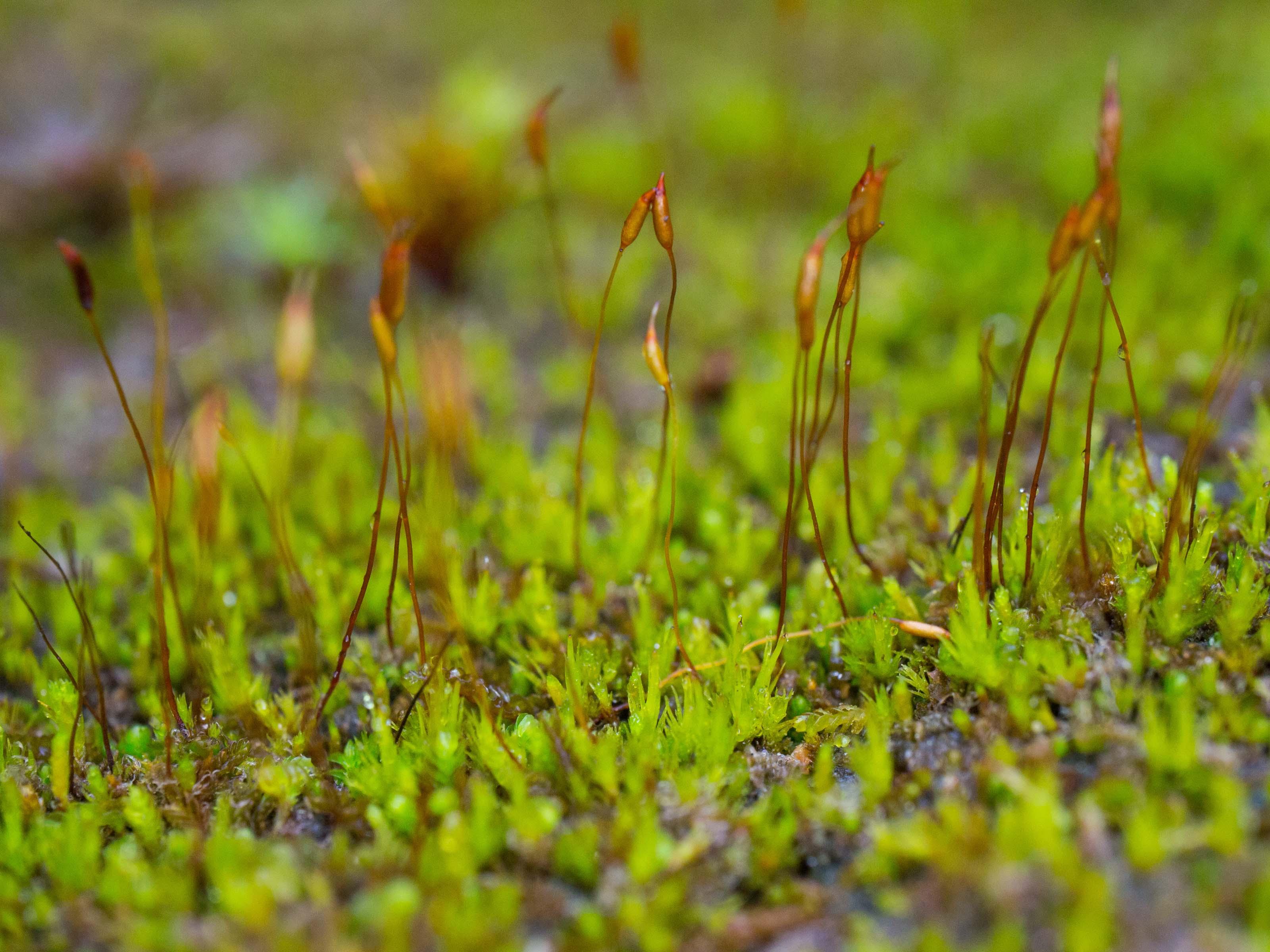

ditrichum_lineare.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/ditrichaceae/index.html
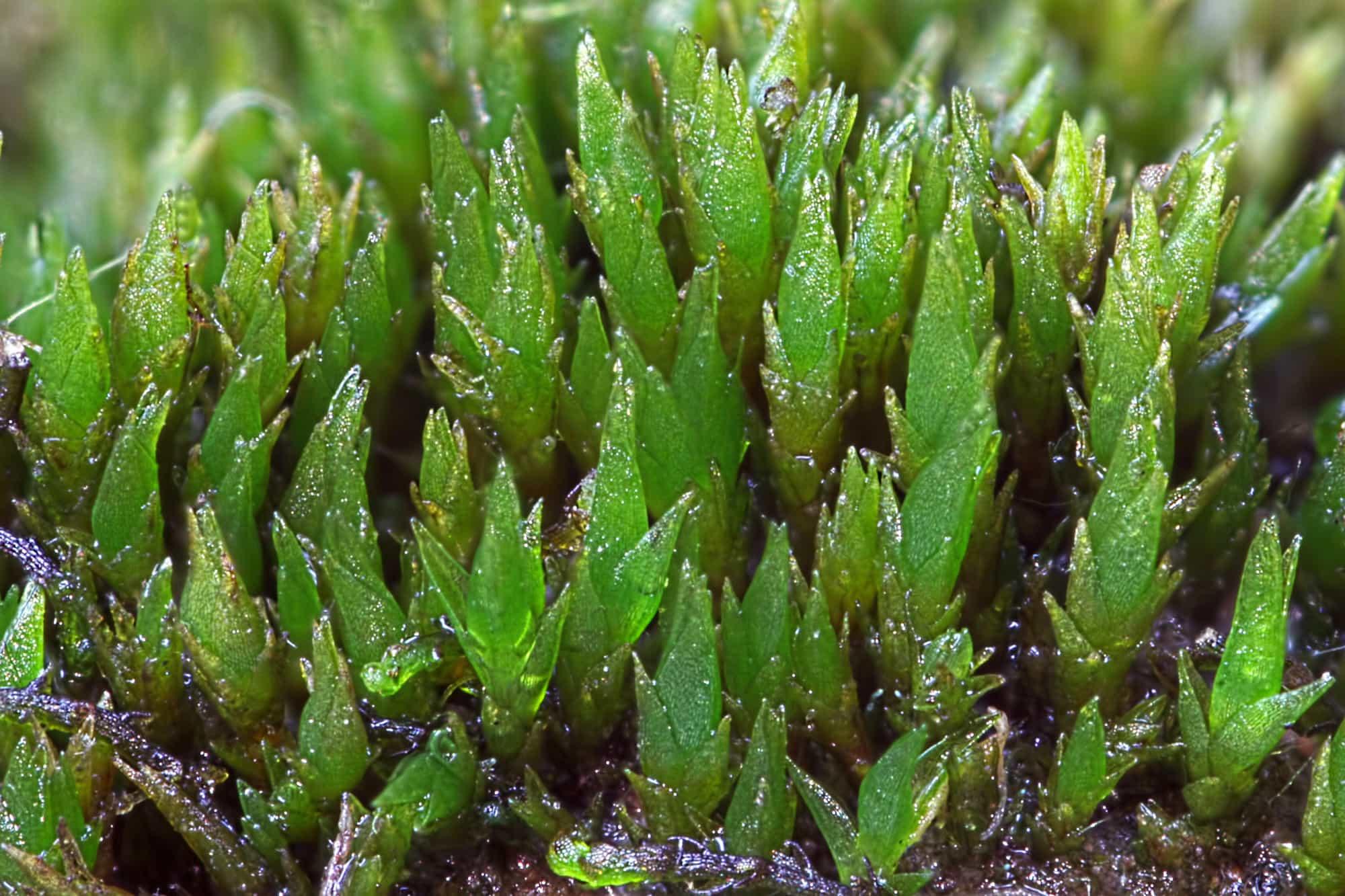

Ditrichum-cornubicum-Des-Callaghan.jpg from: https://naturebftb.co.uk/ditrichum-cornubicum-des-callaghan/
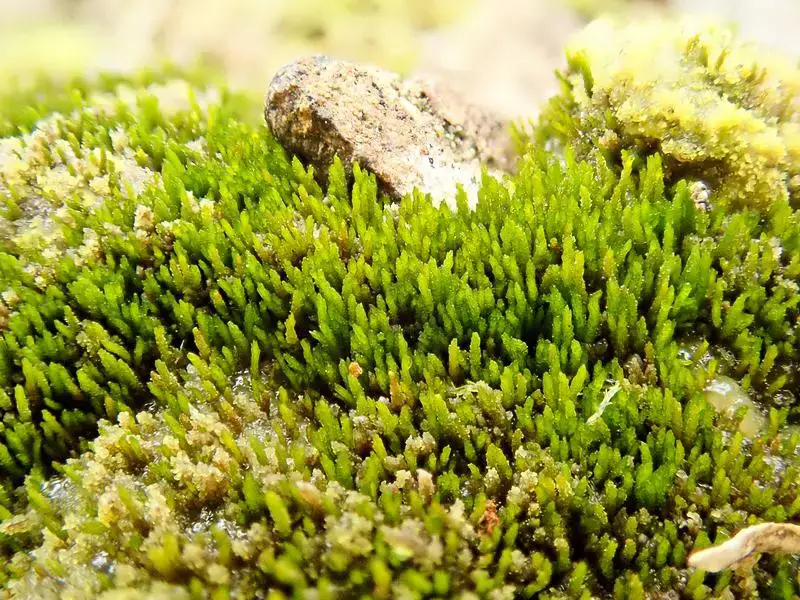

Ditrichum-plumbicola_Gwydyr-Forest-1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/ditrichum-plumbicola/
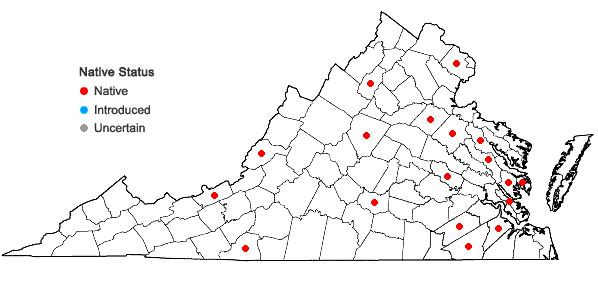
Ditrichum_lineare_4040.png from: https://vaplantatlas.org/index.php?do=plant&plant=4040
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
Order
 medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/161969-Ditrichum-lineare |
Dicranales |
Family
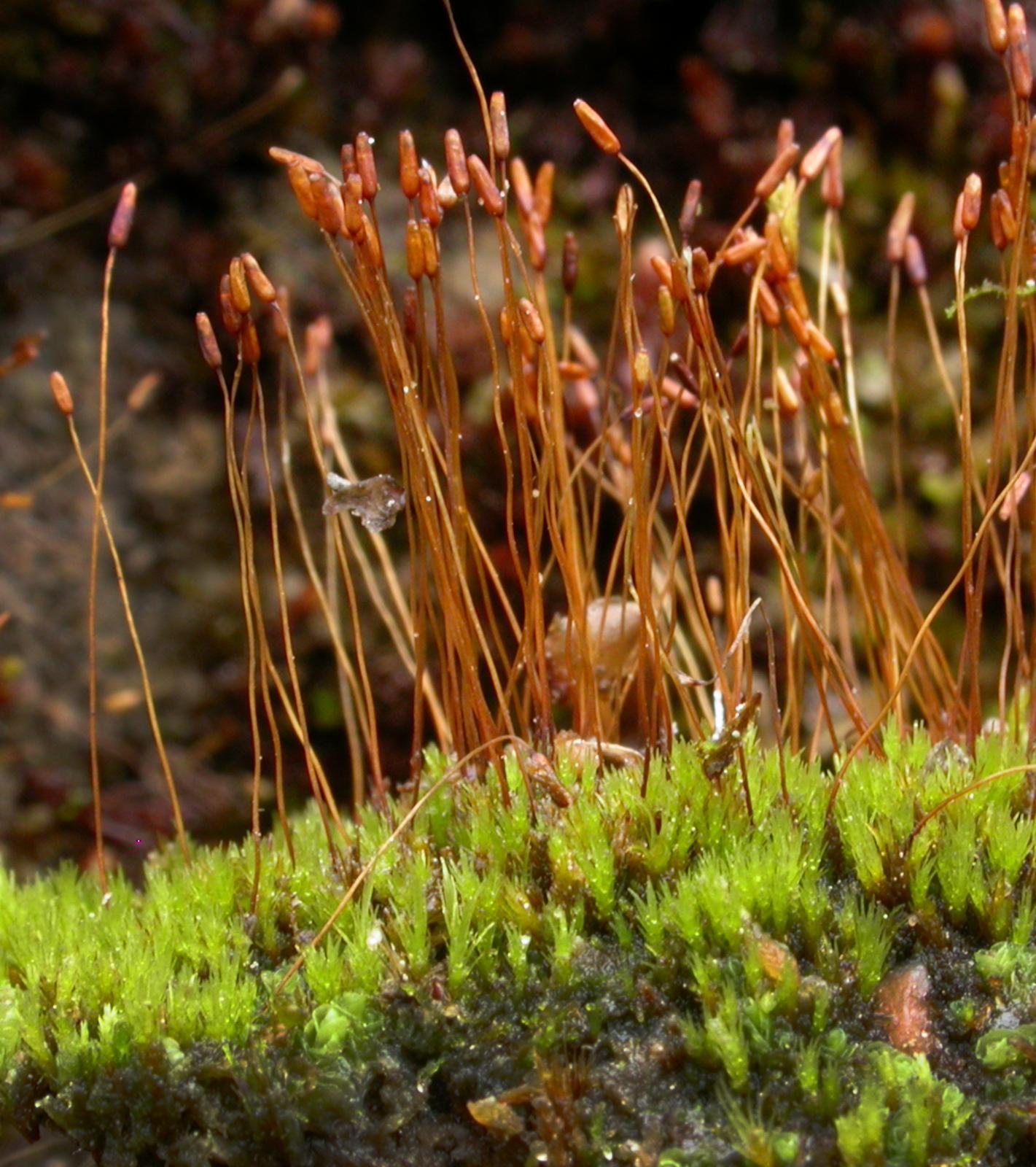 49427_2105_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/artinformation/taxa/ditrichum-lineare-2105/galleri |
Ditrichaceae |
| Genus | Ditrichum |
| Species | Ditrichum lineare (Sw.) Lindb. |
| Common Name | Ditrichum Moss |
| Habitat | Acidic soils, disturbed areas, forests, heathlands |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
| Growth Form | Dense cushions or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Linear, twisted when dry |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, slightly curved |
| Peristome | Present, fringe of teeth |
Conclusion
The Ditrichum lineare (Sw.) Lindb. moss, or simply Ditrichum, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this tiny bryophyte plays a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as a pioneer species and contributing to soil formation and stabilization. Its ability to withstand desiccation and colonize harsh environments is truly awe-inspiring.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve the delicate balance of ecosystems, ensuring that remarkable species like Ditrichum lineare continue to thrive and enrich our planet?