Metzgeria-mexicana-Steph-A-Vista-ventral-del-talo-40-B-Region-ventral-pilosa-100.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Metzgeria-mexicana-Steph-A-Vista-ventral-del-talo-40-B-Region-ventral-pilosa-100_fig2_348303329
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Metzgeria pulvinata Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating representative of the Metzgeriaceae family. Often referred to simply as Metzgeria, this unassuming yet intriguing moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Metzgeria pulvinata Steph., it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and leafy mosses. The Metzgeriaceae family, to which Metzgeria belongs, is a group of thalloid liverworts known for their unique morphological characteristics.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
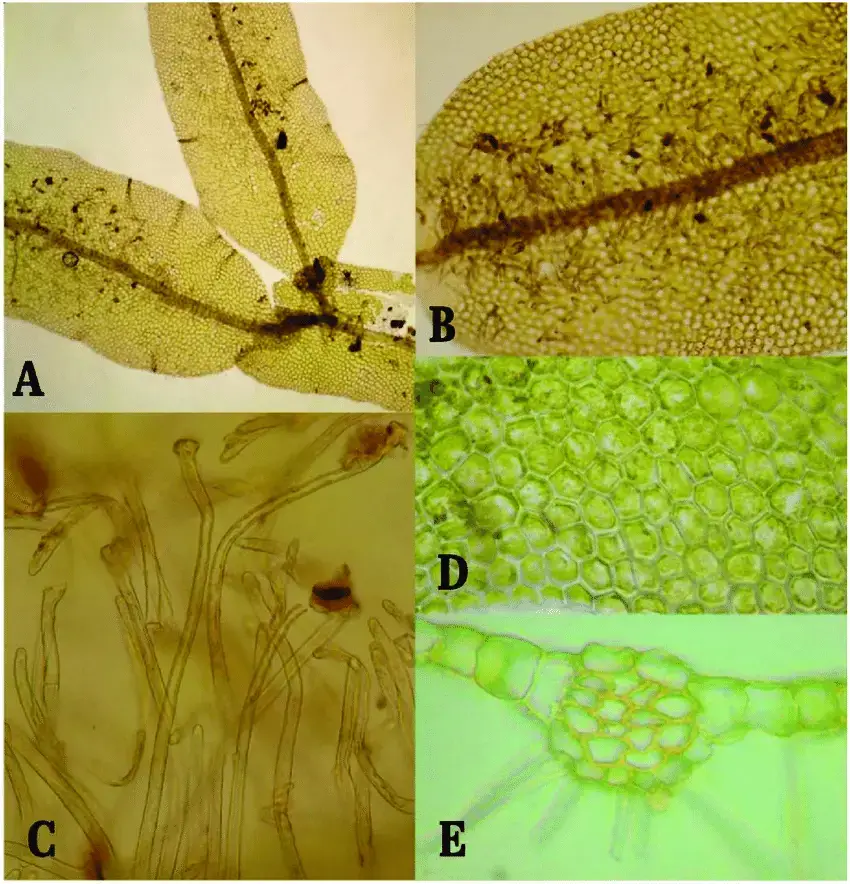
Metzgeria pulvinata Steph. is a thalloid liverwort, meaning it lacks distinct stems and leaves. Instead, it possesses a flattened, ribbon-like structure called a thallus. This thallus is typically

24522379556_1b0503109f_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/bushman_k/24522379556
green in color and can grow up to several centimeters in length. One of the distinguishing features of Metzgeria is the presence of midrib, a raised central region along the thallus that aids in water conduction and structural support.
Global Distribution and Habitat
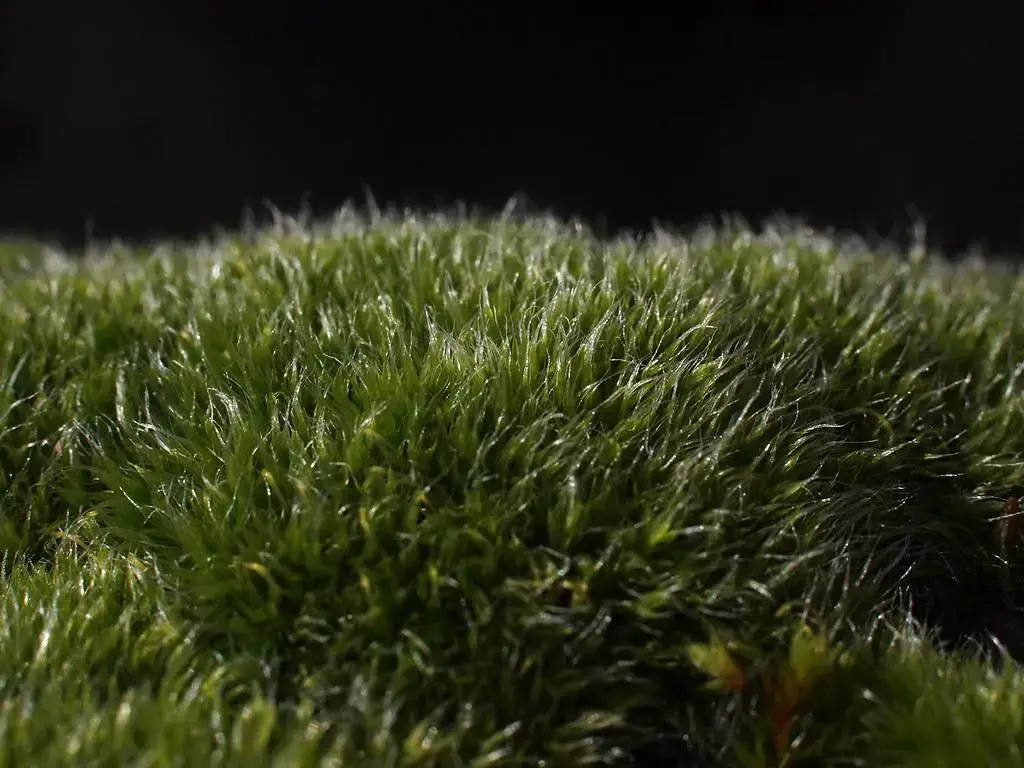
Metzgeria pulvinata Steph. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in moist and shaded environments, often found growing on the bark of trees, rocks, or soil in forests and woodlands. This moss prefers cool, humid conditions and is commonly encountered in areas with high rainfall or near streams and waterfalls.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Metzgeria pulvinata Steph. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It contributes to the overall biodiversity of the forest floor and serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms. Additionally, this moss possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to thrive in its preferred environments.
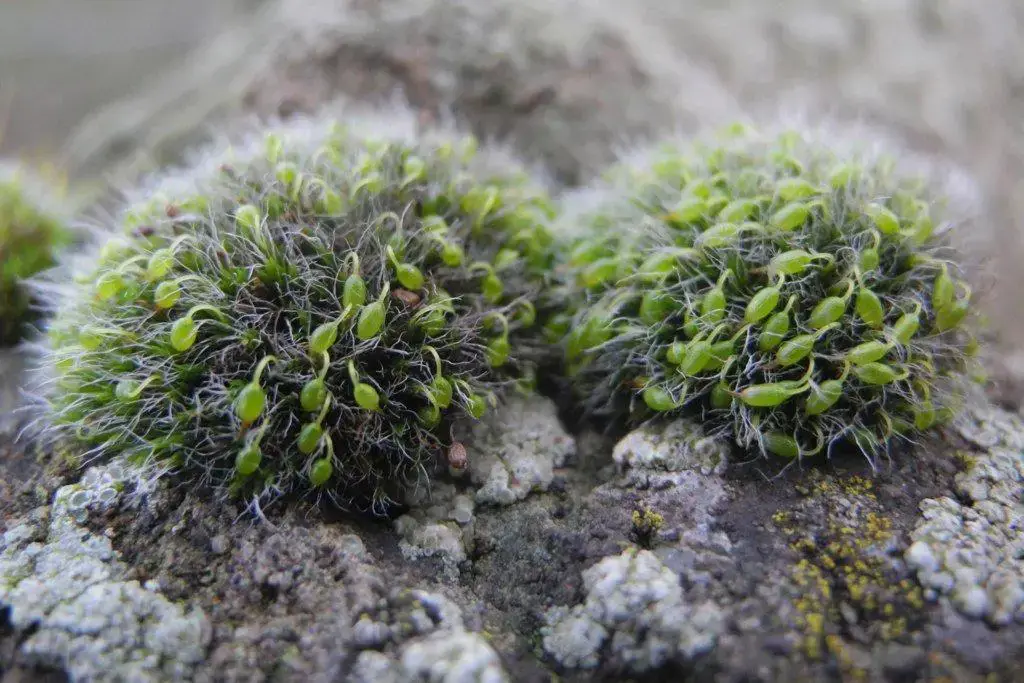
One notable adaptation is the presence of

12065863936_06fe045168_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/41066614@N05/12065863936/
rhizoids

grimmia-pulvinata-wild-moss-2A0MJR5.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/grimmia-pulvinata-wild-moss-image327450793.html
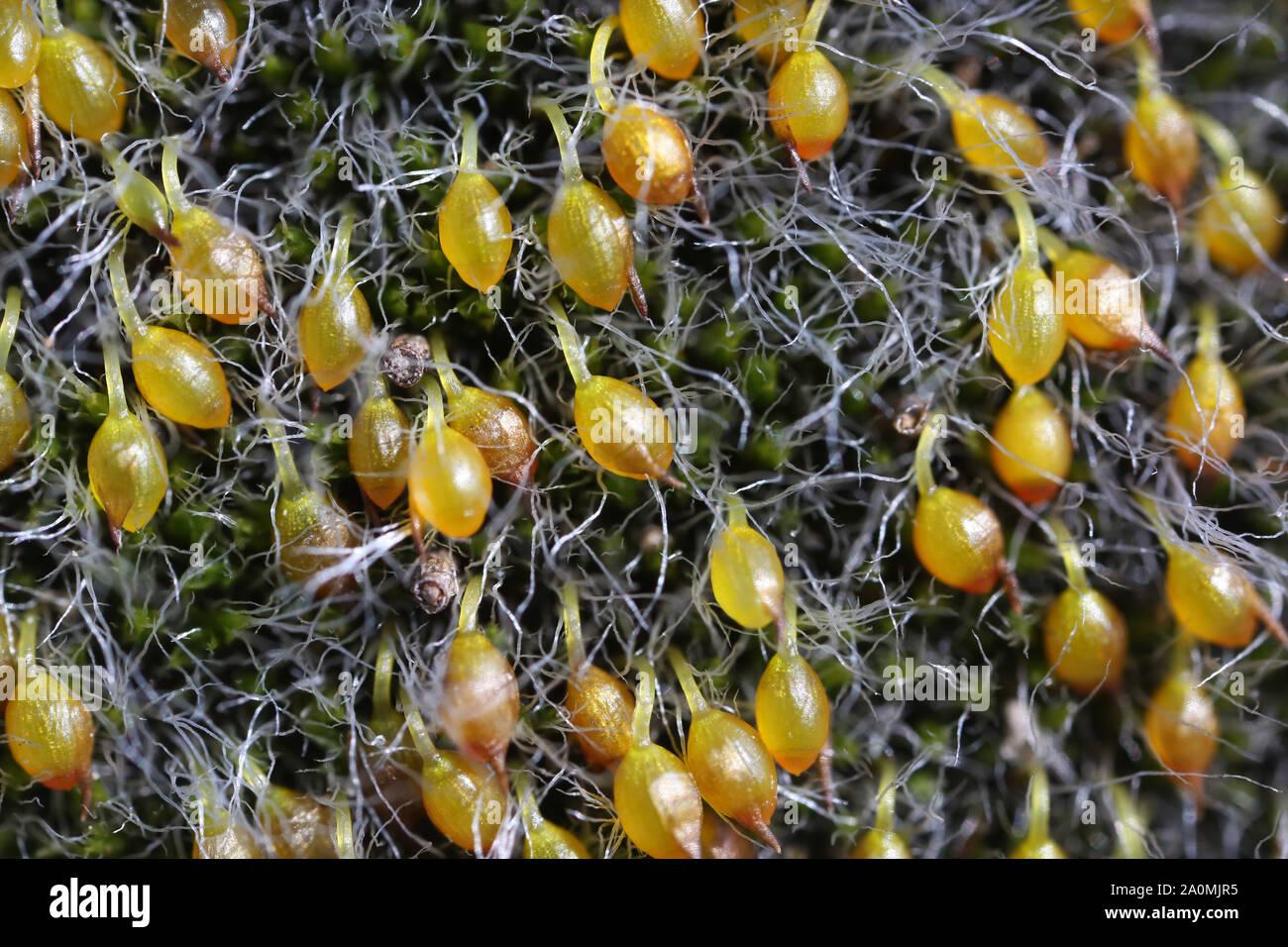
, which are hair-like structures that anchor the thallus to the substrate and facilitate water and nutrient absorption. Metzgeria also exhibits a unique reproductive strategy involving the production of specialized structures called
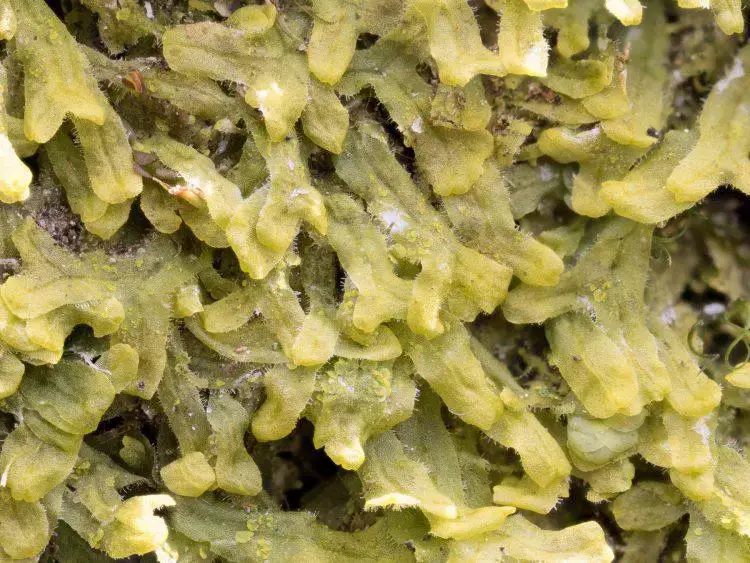

Metzgeria-crassipilis-750×563.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/liverwort-metzgeria-crassipilis/
gemmae cups, which contain asexual reproductive units called gemmae.
Case Study: Metzgeria in the Pacific Northwest
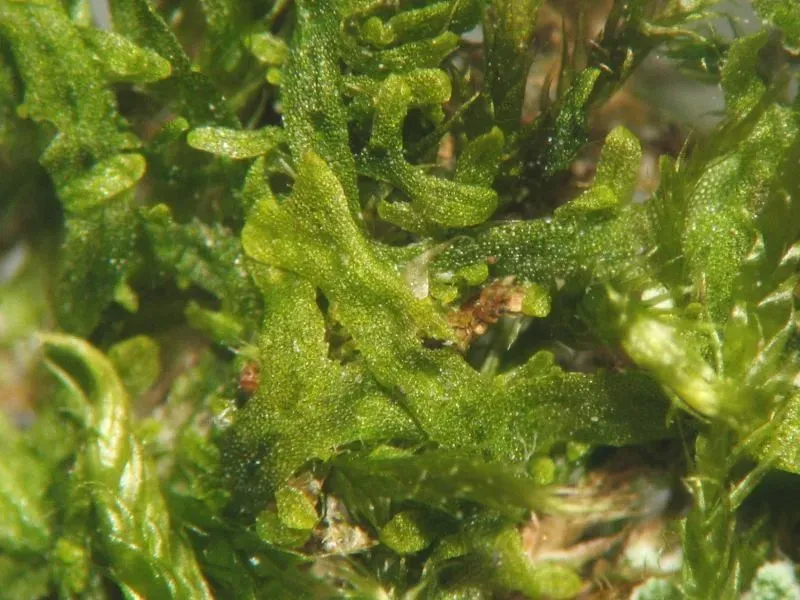

153692419727032352.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/pt/wiki/Metzgeria_furcata.html
In the lush and temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest, Metzgeria pulvinata Steph. thrives in abundance. Here, it carpets the trunks of towering conifers and blankets the forest floor, creating a verdant tapestry. Researchers have studied the intricate relationships between Metzgeria and other organisms in this ecosystem, revealing its importance as a food source and habitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms.

moss_Grimmia_pulvinata_col_120220_0113c.jpg from: https://www.wansteadwildlife.org.uk/WILDLIFE/liverworts_and_mosses/moss_Grimmia_pulvinata.htm
Technical Table

grey-cushion-moss-grimmia-pulvinata-E618XT.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-grey-cushion-moss-grimmia-pulvinata-72558384.html
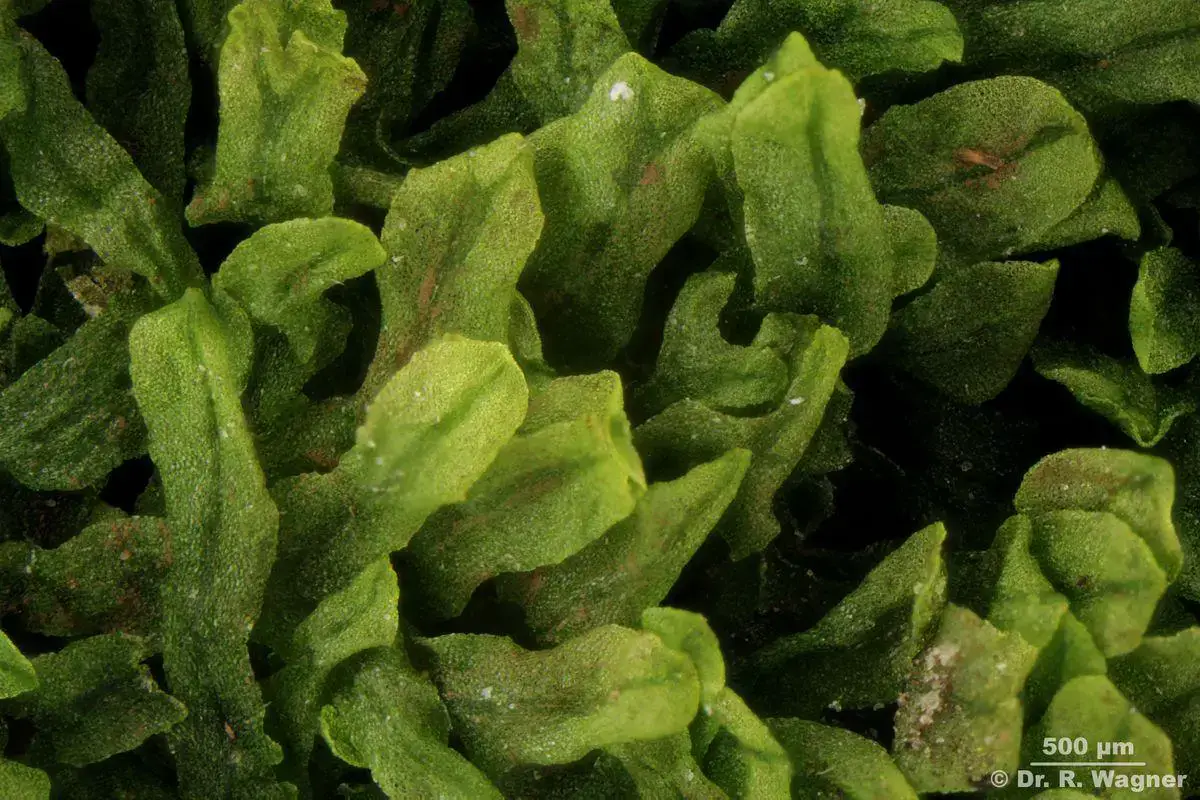

1200-Metzgeria_furcata-25x.jpg from: https://www.lichenes.de/metzgeria-furcata/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Metzgeriaceae |
| Genus | Metzgeria |
| Species | pulvinata Steph. |
| Thallus | Flattened, ribbon-like |
| Midrib | Present, raised central region |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
| Reproduction | Sexual and asexual (gemmae cups) |
Conclusion

grey-cushioned-grimmia-moss-grimmia-pulvinata-CY68XA.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-grey-cushioned-grimmia-moss-grimmia-pulvinata-51155170.html
Metzgeria pulvinata Steph., a humble yet fascinating moss, has captured the hearts and minds of bryophyte enthusiasts worldwide. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a captivating subject of study. As we continue to explore the intricate world of mosses, Metzgeria serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and adaptations found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you venture into a lush forest, you’ll pause to appreciate the verdant tapestry woven by this remarkable moss.
Ponder this: In the grand tapestry of life, what other hidden wonders await our discovery, nestled within the intricate details of the natural world?