Unveiling the Enigmatic Cyrtopus: A Comprehensive Guide to Cyrtopus setosus (Hedw.) Hook.f. Moss
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
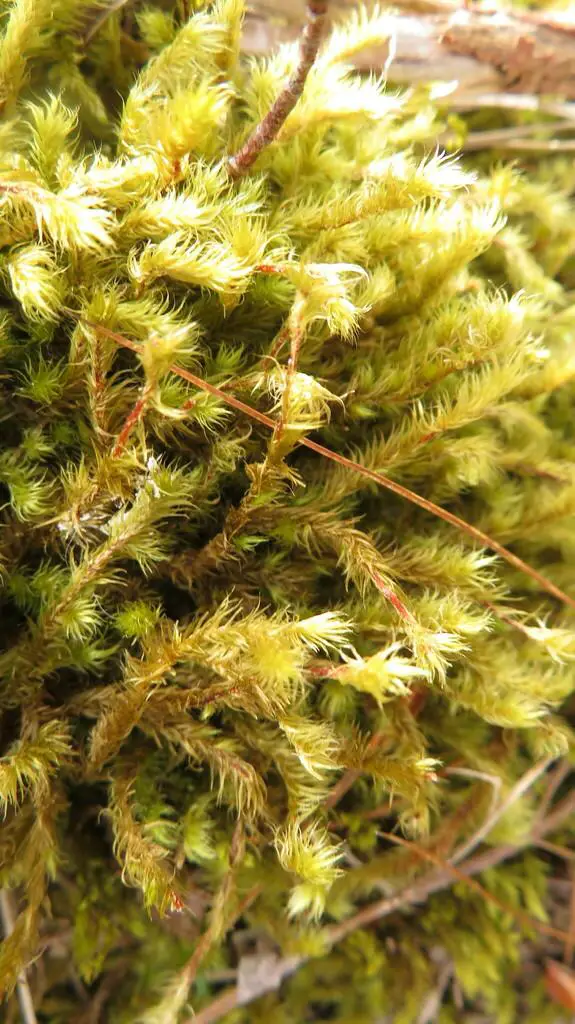

large.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/143526985
Introduction
The world of bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, is a fascinating one, and among its many wonders is the Cyrtopus setosus (Hedw.) Hook.f. moss. This unassuming yet remarkable plant belongs to the Cyrtopoaceae family and is commonly known as Cyrtopus. Despite its small stature, this moss plays a crucial role in various ecosystems and has captured the interest of enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
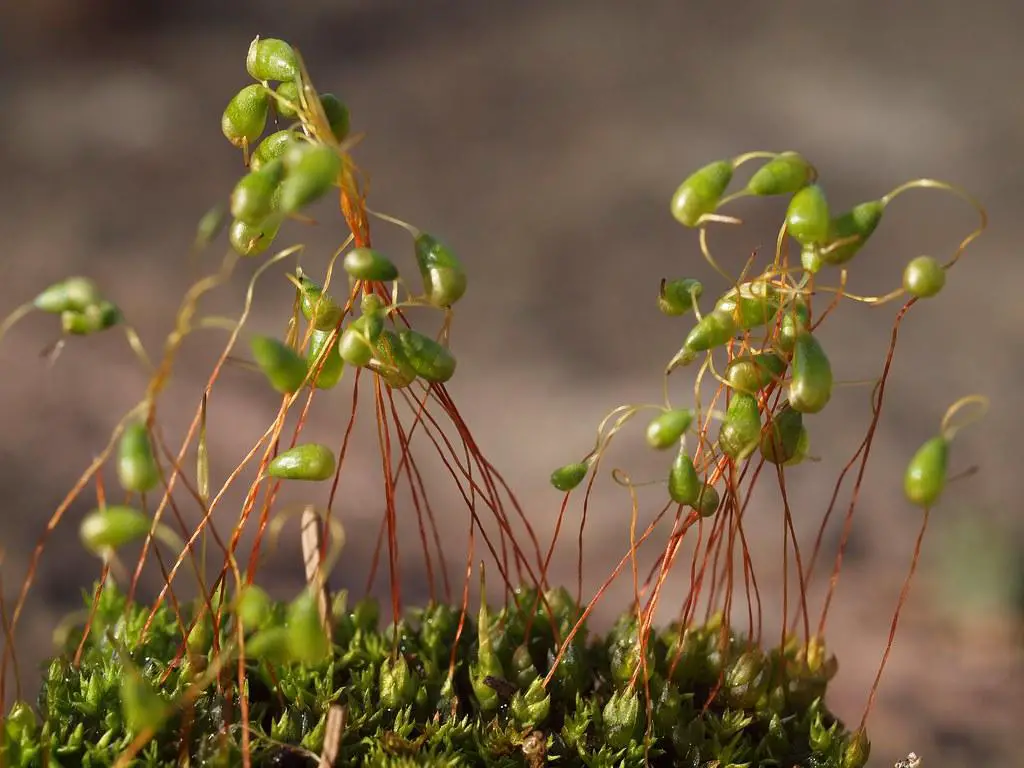

49739599727_316b649f87_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49739599727/
Before delving into the intricacies of Cyrtopus setosus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These ancient plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They have existed for over 400 million years and have played a vital role in the colonization of terrestrial environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Cyrtopus setosus is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are erect and can reach up to 2 centimeters in height. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive setose (bristly) appearance due to the presence of long, hyaline hair points. This characteristic is what gives the species its specific epithet, “setosus.”
One of the most striking features of Cyrtopus setosus is its vibrant green color, which can sometimes take on a reddish or brownish hue, depending on the environmental conditions. The capsules, or sporophytes, are erect and cylindrical, with a distinctive operculum (lid) that detaches when the spores are ready for dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
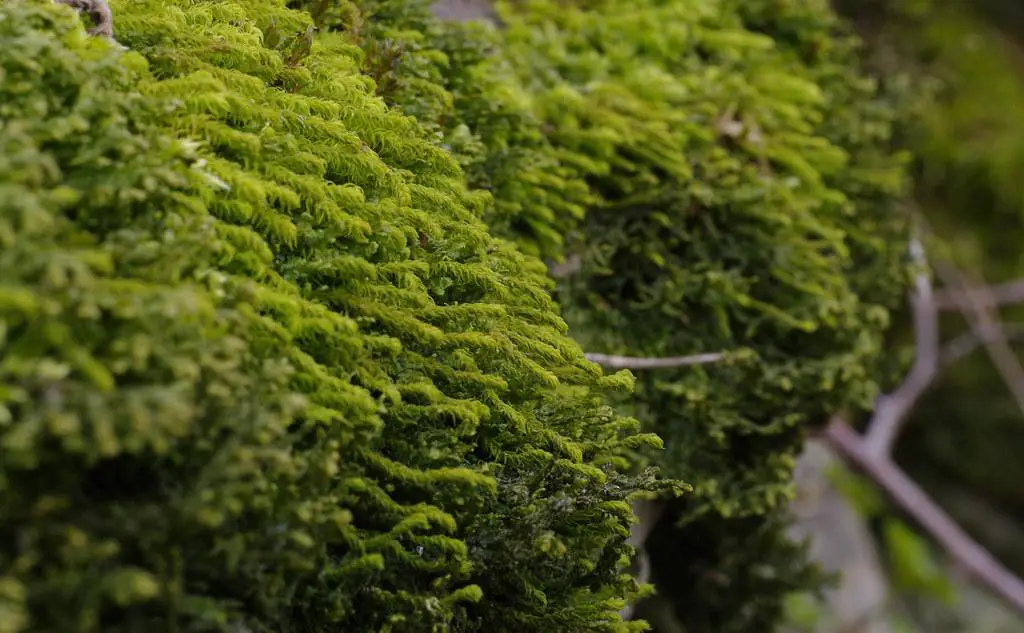

33358084131_a7fac16e5b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/33358084131/
Cyrtopus setosus is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents. It has been reported in Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, and South America, as well as in various oceanic islands. This widespread distribution is a testament to the moss’s adaptability and resilience.

Anomodon-viticulosus-(Hedw.)-Hook.-y-Taylor-437752.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Anomodon-viticulosus-(Hedw.)-Hook.-y-Taylor-img437752.html
In terms of habitat, Cyrtopus setosus is commonly found growing on soil, rocks, tree bark, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs. It thrives in a wide range of environments, from forests and grasslands to urban areas, and can tolerate varying degrees of moisture and light conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
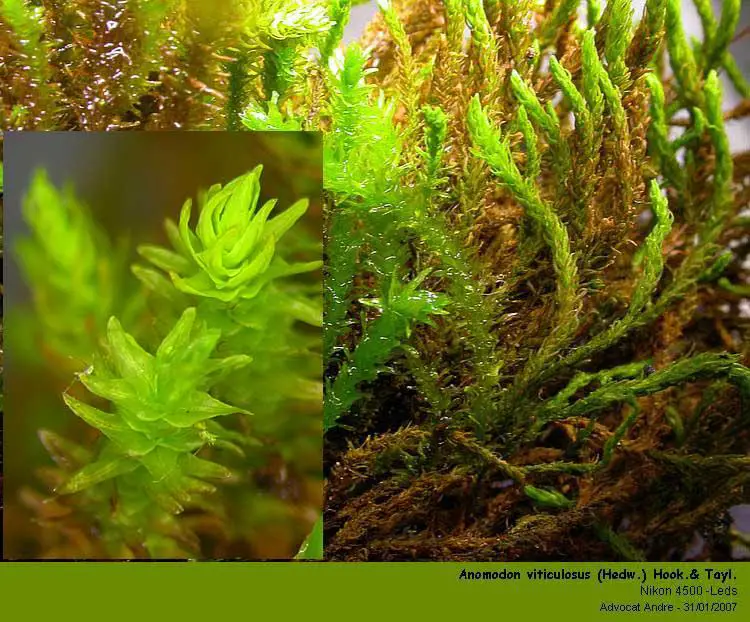

post-25-1170262160.jpg from: https://forum.mikroscopia.com/topic/5514-anomodon-viticulosus-hedw-hook-tayl/
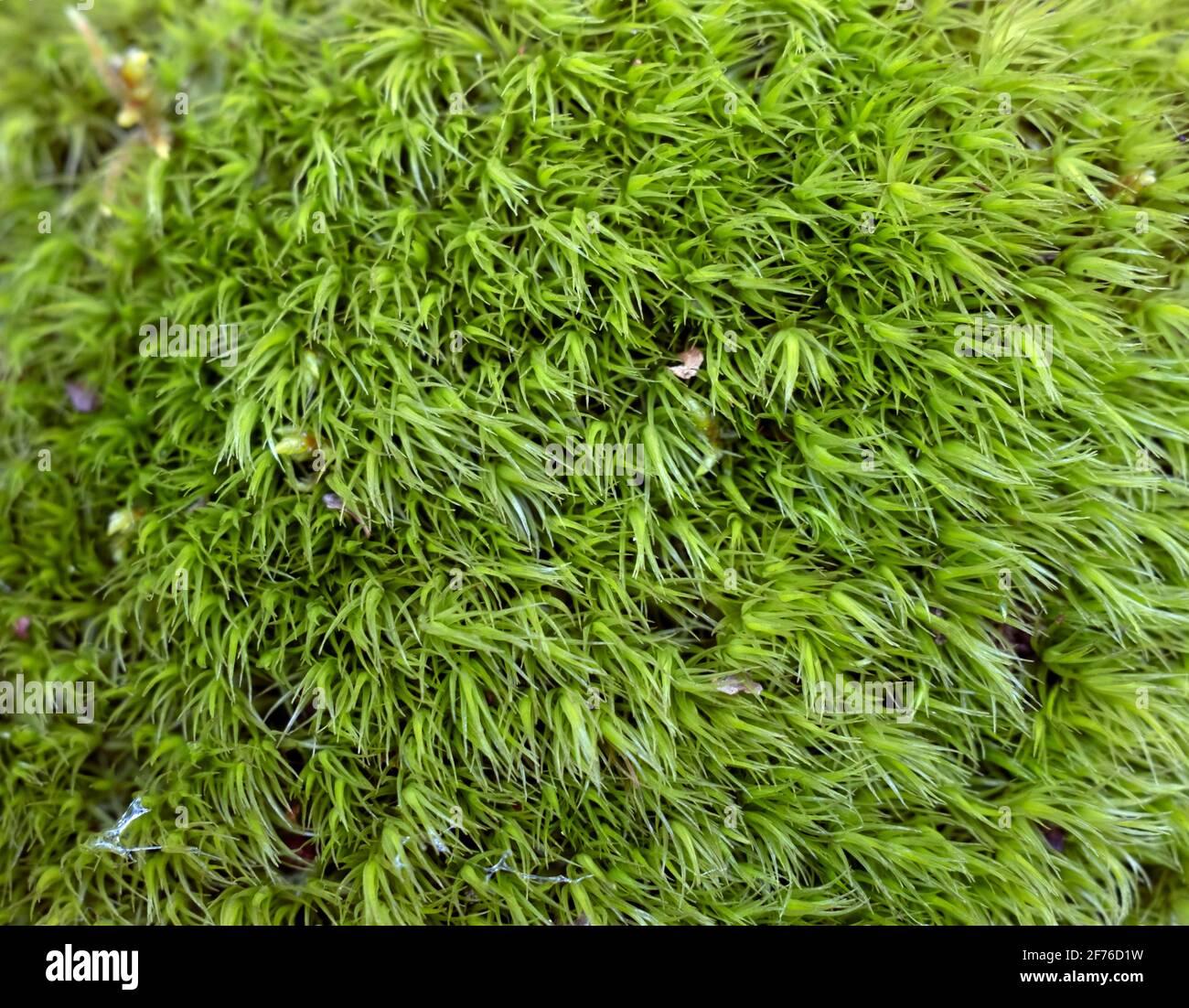

cypress-leaved-plait-moss-hypnum-cupressiforme-hedw-in-closeup-2F76D1W.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/cypress–leaved-moss.html
Despite its diminutive size, Cyrtopus setosus plays a crucial role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps in the colonization of bare or disturbed areas, stabilizing the soil and creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Cyrtopus setosus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and reducing its metabolic activity. When moisture becomes available again, it can quickly rehydrate and resume its growth and reproductive processes.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban environments, Cyrtopus setosus has been observed growing on various man-made structures, such as old buildings, walls, and even gravestones. This ability to colonize human-made habitats has earned it the nickname “urban moss” in some regions.
Technical Table

echinodiumhispid2.jpeg from: https://www.kaimaibush.co.nz/mosses/echinodiaceae.html

peter_retkovsky_304835.jpg from: https://www.nahuby.sk/obrazok_detail.php?obrazok_id=304835
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Cyrtopoaceae |
| Genus | Cyrtopus |
| Species | Cyrtopus setosus (Hedw.) Hook.f. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Setose (bristly) |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, tree bark, man-made structures |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
thrips_setosus_tergviiix.jpg from: https://keys.lucidcentral.org/keys/v3/british_thrips//the_key/key/britishthysanoptera_2017/Media/Html/thrips_setosus.htm
Conclusion
The Cyrtopus setosus (Hedw.) Hook.f. moss, or Cyrtopus, is a remarkable example of the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. Despite its small size, this moss plays vital roles in various ecosystems, from stabilizing soil to providing a suitable environment for other plants to thrive. Its ability to withstand desiccation and colonize diverse habitats, including urban areas, is truly remarkable.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these unassuming yet essential organisms that play such crucial roles in our ecosystems?

Image1ZDS.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Cyrtopus-setosus.html
