Unraveling the Secrets of Erythrodontium longisetum: A Captivating Moss Species
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
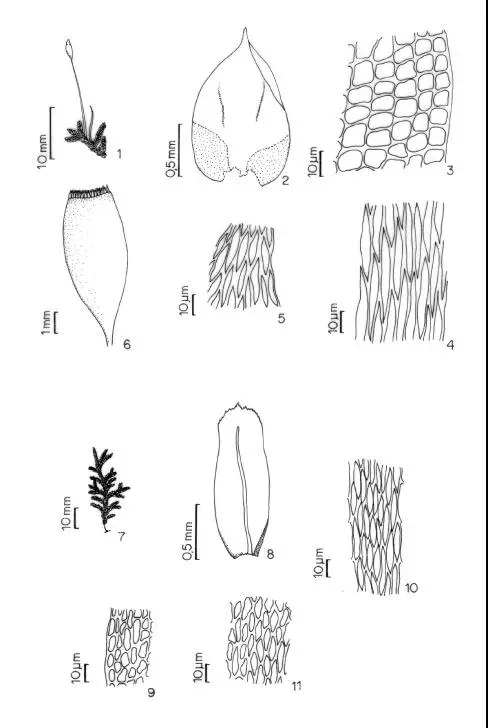
Figuras-1-6-Erythodontium-longisetum-Hook-Par-1-habito-2-filidio-3-celulas.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-1-6-Erythodontium-longisetum-Hook-Par-1-habito-2-filidio-3-celulas_fig1_26360403
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the
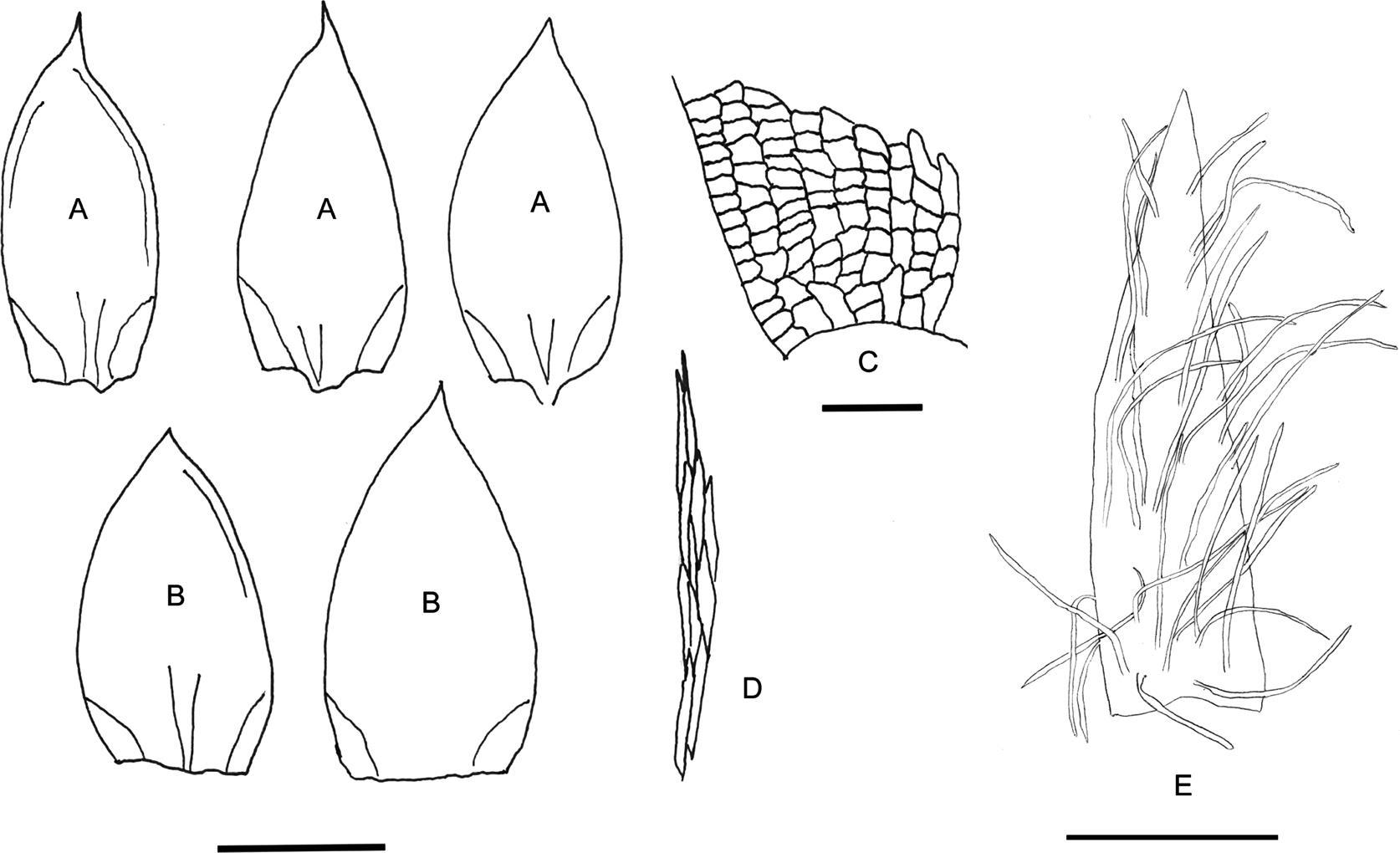
i0007-2745-112-4-804-f10.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/The-Bryologist/volume-112/issue-4/0007-2745-112.4.804/A-taxonomic-revision-of-span-classgenus-speciesErythrodontiumspan-Entodontaceae/10.1639/0007-2745-112.4.804.full
Erythrodontium longisetum (Hook.) Paris. Belonging to the Entodontaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as Erythrodontium. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Erythrodontium longisetum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/405164-Polytrichastrum-longisetum
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Erythrodontium longisetum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance make it a true delight to behold. The leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. When observed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a intricate pattern of papillae, small protrusions that aid in water retention and protection.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species can be found across various regions of the world, including

20191018_a-hook-moss-leucodon-sp.-02-kb.jpg from: https://wcbotanicalclub.org/20191018_a-hook-moss-leucodon-sp-02-kb/
North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on decaying logs, tree trunks, and rocky outcrops. Erythrodontium longisetum is particularly fond of old-growth forests, where it contributes to the intricate tapestry of biodiversity.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Erythrodontium longisetum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It acts as a

Cenchrus_longisetus_(Pennisetum_villosum)_Zottiges_Federborstengras_P1070595.jpg from: https://galasearch.de/plants/15121-cenchrus-longisetus-pennisetum-villosum
pioneer species, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide a microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Erythrodontium longisetum is its ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and rapidly resume growth when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
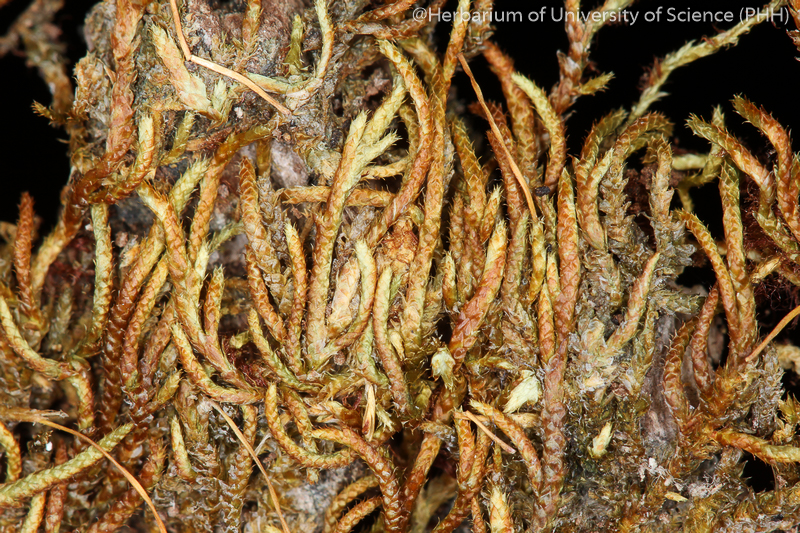

PHH0034014b.png from: https://cryptogam-phh.hcmus.edu.vn/index.php/en/bryophtes?page=30
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Erythrodontium longisetum plays a crucial role in the intricate web of life within old-growth forests. These ancient ecosystems are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, many of which rely on the moss for shelter, moisture retention, and nutrient cycling.
Technical Table

e78e46ae9429695858a4ec179d29b390.jpg from: https://homefail21.pythonanywhere.com/southern-trees-with-hanging-moss.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
 Plagiothecium-mauiense-from-the-NY-Herbarium-DD-Baldwin-221-NY01256708-A-the-plain_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-diagnosis-of-Plagiothecium-longisetum-Lindberg-1872_fig3_344804154 |
| Order | Entodontales |
| Family | Entodontaceae |
| Genus | Erythrodontium |
Species
 789749bd-5e14-4979-9e21-53bf547ebf14.jpg from: https://shflora.ibiodiversity.net/pages/Polygonum_longisetum_var_rotundatum.html |
longisetum |
| Common Name | Erythrodontium |
Conclusion
Erythrodontium longisetum (Hook.) Paris is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. From its delicate beauty to its vital ecological roles, this moss species reminds us of the intricate interconnectedness of life on our planet. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder: What other hidden gems await our discovery, and how can we better protect and preserve these invaluable treasures?

Eleocharis_palustris.jpg from: https://swbiodiversity.org/seinet/imagelib/imgdetails.php?imgid=9389
