Unveiling the Enigmatic World of Taxithelium Moss: Exploring a Tiny Ecosystem
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
Hygrobiella-laxifolia-Hook-Spruce-an-alpine-species-occurring-in-deep-gorges-of.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Hygrobiella-laxifolia-Hook-Spruce-an-alpine-species-occurring-in-deep-gorges-of_fig1_344462073
Exploring the Fascinating World of Taxithelium concavum Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play important roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Taxithelium concavum (Hook.) Spruce ex J.Florsch., commonly known as Taxithelium moss. This small but mighty plant is part of the Pylaisiadelphaceae family and has some unique characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at this fascinating moss!

spruce-branch-blue-lichen-green-moss-close-up-spruce-branch-blue-lichen-green-moss-143499451.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/spruce-branch-blue-lichen-green-moss-close-up-spruce-branch-blue-lichen-green-moss-image143499451
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the specifics of T. concavum, it’s helpful to understand some basics about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Taxithelium concavum

19450002983_8cb5927f58_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/98771984@N05/19450002983/
is a pleurocarpous moss
lichen_tree_soredi_se_astflechte_ramalina_farinacea_pflaumenflechte_evernia_prunastri_fouling_moss-877185.jpg!d from: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/877185
, meaning it has a branching, mat-forming growth habit. The stems are creeping to ascending and irregularly branched. Leaves are ovate-lanceolate and concave, with a short, double costa (midrib). Leaf margins are entire and often recurved. Sporophytes (spore-producing structures) are common, with cylindrical capsules on long setae.
Some key characteristics for identifying T. concavum include:
- Concave, ovate-lanceolate leaves
intermediate-hook-moss-final-1500×2053.jpg from: https://lizzieharper.co.uk/image/intermediate-hook-moss-scorpidium-cossonii/
- Short, double costa
20063426832_da15344d8d.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/98771984@N05/20063426832/
- Recurved leaf margins
- Cylindrical capsules on long setae
small-spruce-germ-growing-from-the-moss-on-the-old-stump-R0C2B4.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/small-spruce-germ-growing-from-the-moss-on-the-old-stump-image224000088.html
Global Distribution and Habitat
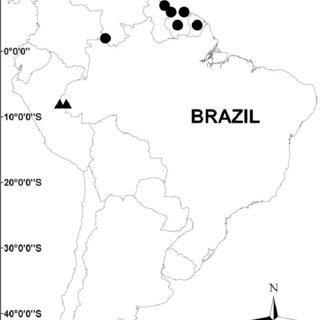
Taxithelium concavum has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including Central and South America, Africa, and Asia. It grows on a variety of substrates including tree trunks, logs, rocks, and soil, often in humid forests from lowlands to mountains.
This adaptable moss is able to thrive in a range of light conditions from deep shade to partial sun. It prefers warm, moist environments but can tolerate some drying out between rain events.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, T. concavum

a-spruce-branch-resting-on-a-bed-of-moss-polytrichastrum-formosum-DHE552.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/a-spruce-branch-resting-on-a-bed-of-moss-polytrichastrum-formosum-image62391646.html
plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and small invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling as it grows and decomposes
Taxithelium concavum has several adaptations that allow it to succeed in its native habitats:
- Concave leaves help collect and retain water
- Branching growth form maximizes surface area for photosynthesis
- Spore dispersal enables colonization of new areas
- Tolerates low-nutrient substrates by efficiently recycling nutrients
Distribution-map-for-Taxithelium-concavum-circles-and-Taxithelium-juruense-triangles_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-map-for-Taxithelium-concavum-circles-and-Taxithelium-juruense-triangles_fig5_261697502
Conclusion
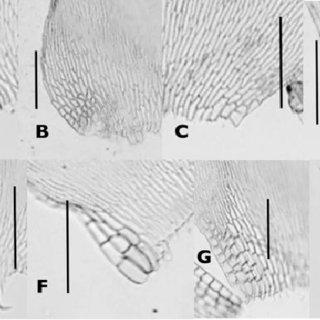
Variation-of-alar-region-among-the-eight-species-of-subgenus-Taxithelium-Scale-bars_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261697502_A_Review_of_Taxithelium_Subgenus_Taxithelium_Bryophyta_Pylaisiadelphaceae
From its unique morphology to its important ecological roles, Taxithelium concavum is a prime example of how fascinating and important mosses can be. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look and see if you can spot this small but mighty plant!
What other cool mosses have you encountered? Share in the comments below!